Tags
Alexander of Macedon, Athenian Empire, Babylon, Cleopatra VII, Delian League, Mongol Empire, Mordor, Persians, Plataea, Ptolemy, Sauron, Tolkien, W.H. Auden
Welcome, dear readers, as ever.
It is one of the pleasures—perhaps we should say even blessings—of JRRT that there is such a richness available within his work—and within him—that no subject can ever be discussed to a perfect conclusion. In an earlier posting, we talked about Sauron and his demands, but, as we watch our current world and certain powers who are maneuvering to gain increasing control over land and sea, we have come back once more to wondering about what it is that Sauron has planned to do and what he will have if he succeeds.
In an unpublished reply to a review by W.H. Auden, JRRT wrote:
“The theatre of my tale is this earth, the one in which we now live, but the historical period is imaginary. The essentials of that abiding place are all there (at any rate for inhabitants of N.W. Europe), so naturally it feels familiar, even if a little glorified by the enchantment of distance in time.” (Letters, 239)
Thus, we can feel justified, we think, in looking at a would-be world conqueror from an actual historical period to see if we can better understand the fictional Sauron.
If we consider Alexander of Macedon,

we see someone who began with a project which, in part, went back for a century and more before his own time: to take back the western shore of northern Asia Minor from its Persian overlords. This had been begun by the Delian League,
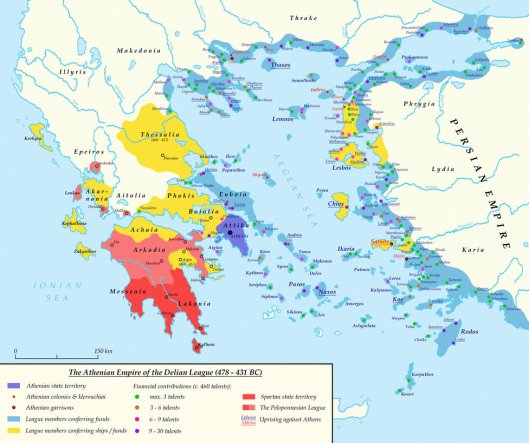
a group of Greek city-states who had been participants in the ultimate battle defeat of the invading Persians, at Plataea, in 479bc.

After he had defeated the southern Greeks at Chaeronea in 338bc with the aid of his son, Alexander, it had been Philip II of Macedon’s plan to do what the League had planned and take back Asia Minor from the Persian empire. Philip was murdered (by a “lone spearman”) in 336, but Alexander, took over the plan and, in 334, invaded the Persian empire and, within three years or so, had conquered it—
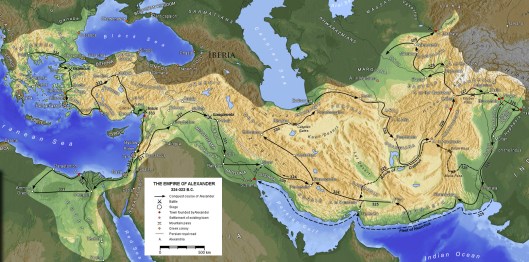
but then had kept moving eastward, besieging cities, winning battles, all the way into western India, where his army finally revolted and refused to go farther.

He returned to his new capital, Babylon, to die there in 323bc.

Because Alexander had no grown male heirs, his new empire fell apart very quickly, his chief generals seizing big chunks and defending them against other generals. We can presume, we think, that he hadn’t been planning to die young (he was born in 356), so we assume that he was out to do something permanent. His generals—the successful ones—founded dynasties, the longest-lived of them being that of Ptolemy,

who grabbed Egypt, and whose last descendant to rule was Cleopatra VII (yes, that Cleopatra), who committed suicide in 30bc.

If Alexander was planning to do something similar, only on a larger scale, how do we understand it? What was all of that conquest for and why was it never enough?
Part of the explanation may lie in the analogy of the folk-tradition about sharks: that they have to keep moving to breathe. This is apparently not true (google Discovery.com/tv-shows/shark-week).

It’s a good image, however, of how an expanding kingdom has to work: the more land you have, the more people you have, the more people you have, the more food you need, therefore you need an increased food supply, which means either buying it or taking it from outside, or making the land itself produce more or simply acquiring more land—and the cycle begins again. This may have been what caused the rapid expansion of the Mongol empire in the 13th century ad, although, in their case, it may not have been expanding population so much as expanding flocks and herds which needed more pasture land.

We might see Sauron in the same light: he needed huge armies to conquer Middle-earth, his huge armies, both humans and orcs, would need feeding (even orcs ate, after all, although as to what they ate…) and therefore would have needed a huge amount of growing land to be fed from, and so on and so on. Certainly Mordor was not the place for gardens and grain fields.
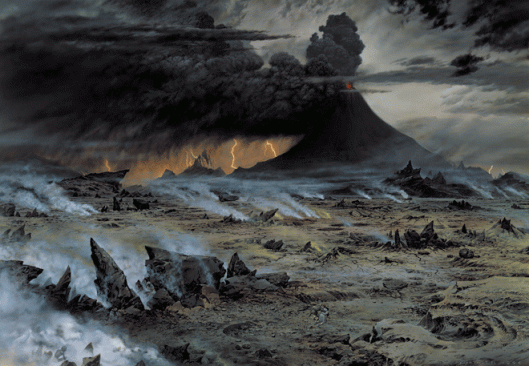
JRRT says of Sauron:
“Sauron desired to be a God-King, and was held to be this by his servants; if he had been victorious he would have demanded divine honour from all rational creatures and absolute temporal power over the whole world.” (Letters 243-244)
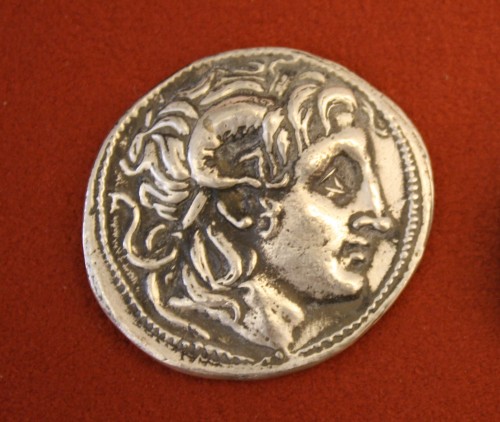
And perhaps this offers another view of Alexander, in turn. As Sauron would have needed land to feed his armies, perhaps Alexander was intent upon collecting worshippers? Certainly he allowed rumors to circulate that he was at least semi-divine—as we see in this coin portrait, where he is portrayed with the horns of Zeus/Ammon, a combination Greek and Egyptian god.

Alexander succeeded in gaining territory—although not so much as he wished—but died before founding the dynasty which might have given his kingdom stability. Sauron lost, not only his kingdom-in-the-making, but his corporeal form and the bulk of his power. JRRT has given us a hint as to one side of his plans—founding a religion with himself as the god, but perhaps Alexander has given us a clue as to another side, the need to support his means of conquest. In turn, Sauron may supply a clue to another side of Alexander’s plans: inserting himself into the religion of his Greek subjects, then expanding his cult throughout as much of the world as he could conquer.
Thanks, as ever, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD