Tags
Bibliotheque nationale Francaise, Charles Kemble, Charles Perrault, costuming, David Garrick, Edward Burne-Jones, Extravaganzas, Faulconbridge, Folger Library, Giambattista Basile, Gianfrancesco Straparola, Histoires ou Contes du Temps Passe, Histories or Tales of Past Times, James Robinson Planche, King John, La Belle au Bois Dormant, Les Contes Des Fees, Madame d'Aulnoy, Mercure Galant, Mother Goose, Punch Magazine, Richard "Dicky" Doyle, Shakespeare, Sleeping Beauty, Sur La Lune
Welcome, as always, dear readers.
For a current writing project, we’ve gone back into our fairy tale collection (we recommend, by the way, the wonderful Sur La Lune site to help you to build yours—here’s a LINK) to reread the fairy tales of Charles Perrault (1628-1703)–

although he wasn’t the person who first called them that—that was his contemporary, Madame d’Aulnoy (1650/1-1705),
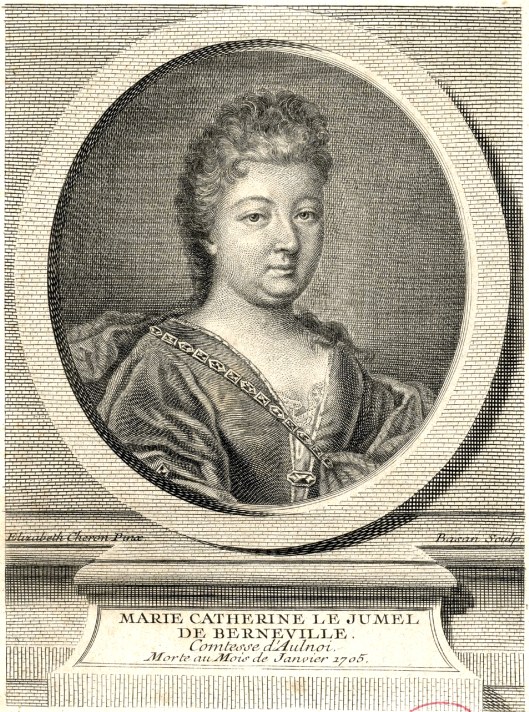

who called her stories contes des fees—“stories of fairies”.

In 1695, Perrault had circulated an illustrated manuscript of such tales, calling it Contes de ma Mere l’Oye—“Tales of My Mother Goose”.

In February, 1696, he published one of them, “La Belle au Bois Dormant”—“The Beautiful Girl in the Sleeping Wood” in an early magazine, the Mercure Galant (maybe in English something like “The Courier of Style”).

(If you’d like to read the story in French as it was first published, here’s a LINK to the BnF, the Bibliotheque nationale Francaise, where it is available on-line, which we think is just magical.)
Then, the following year, the collection was published under the title Histoires ou Contes du Temps Passe (“Stories or Tales from the Past”).

The term “contes de ma mere l’Oye” appears to have been known in literary circles from at least the 1650s and indicated rustic/countryside stories—in a sense, folktales—and Perrault had used traditional material, some of which had first appeared in print in Italian in the 16th century and could be found in the folktale collections of people like Gianfrancesco Straparola (1485?—1558) and Giambattista Basile (1566-1632).
Perrault’s stories, which include what we call “Sleeping Beauty” (you can see that that’s a mistranslation) and “Cinderella”, first appeared in English in London in 1729, translated by Robert Samber, its title being identical with the 1697 French.

In this post and (at least) two following, we thought that we would choose two of these fairy tales and see in what different forms they’ve been presented since first appearing in 1697.
Because it was the first to be published, we’ll begin with “Sleeping Beauty. (This is a Pre-Raphaelite version by Edward Burne-Jones, 1833-1898. It is one of a set of four and has a very interesting history—here’s a LINK so that you may found out more, if you wish.)

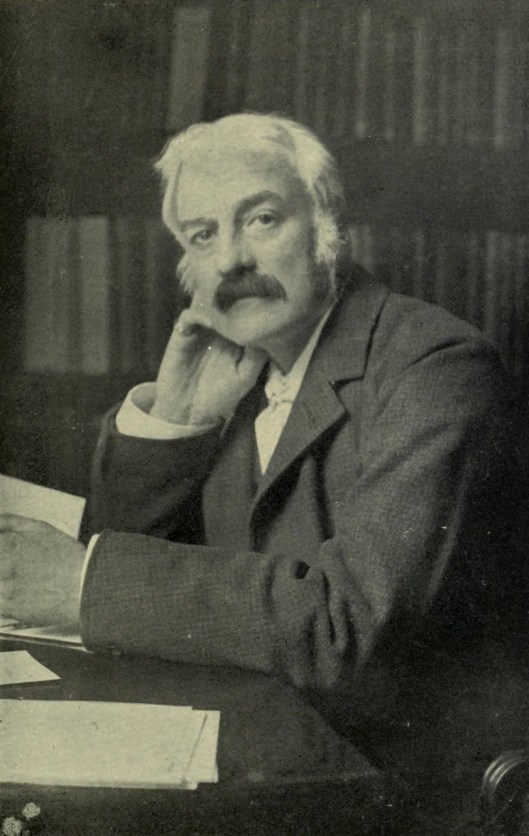
Our first work, entitled surprisingly enough, The Sleeping Beauty, is what its author, James Robinson Planche (plahn-SHAY), 1796-1880,

would call an “extravaganza”, meaning, in this case, something like a modern musical comedy. First produced in 1840, it combined dialogue in rhyming iambic (more or less) couplets with songs set to already existing tunes. Based upon Perrault, it used spectacle, everyday references which a London audience would have immediately picked up on, and gentle political/cultural satire to entertain. Unfortunately we don’t have any images of this production, but here’s a LINK to volume 2 of Planche’s “extravaganzas” so that you can form your own impression. If you know the works of the Victorian dramatist/composer team of WS Gilbert and Arthur Sullivan, you will see that Planche is their direct ancestor.
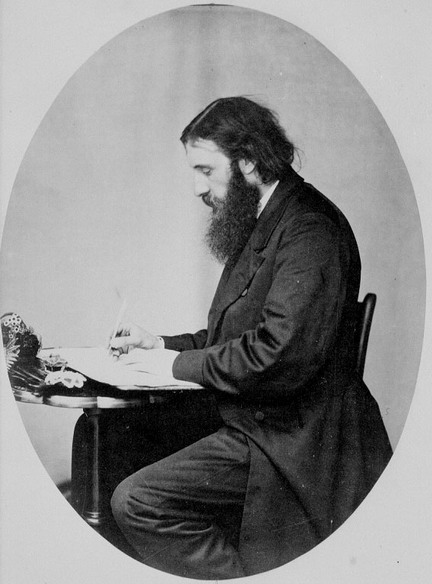
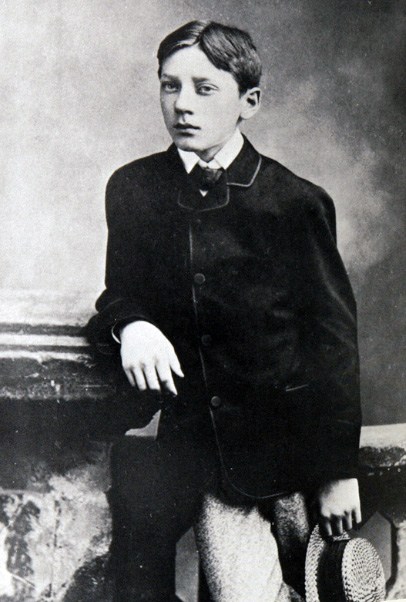
For many years, beginning in the early 1800s and continuing into the 1860s, Planche was Mr Theatre, in London, writing or co-writing at least 175 shows of various sorts. These works, like Planche himself, have faded away, but he did leave one mark. In 1823, Planche had had a conversation with a famous actor, Charles Kemble (1775-1854),

in which he suggested that, whereas money was always being spent in the theatre on spectacles, almost nothing was done for the plays of Shakespeare. In fact, Shakespeare’s plays had always been costumed in the clothing of the period of the actors, rather than the dress of the time of the events. Here’s a print of the well-known 18th-century actor, David Garrick (1717-1779) in four of the roles for which he was famous: Lear, Macbeth, Richard III, and Hamlet—by dress and props alone, perhaps we could guess that the actor with the two daggers was someone playing Macbeth (or perhaps an assassin from the 1760 version of Game of Thrones), but otherwise?

Kemble, in turn, told Planche that he would willingly put on an historically-accurate production of several Shakespeare plays, beginning with King John, if Planche would do the necessary research and design. Planche agreed and here’s a playbill of the result.

Reading the fine print, it’s even possible to see that Planche cited at least some of his sources—everything from funerary statuary to manuscript illustrations. Whereas we don’t, unfortunately, have any illustrations to show for The Sleeping Beauty, we can show you what a difference Planche made to attempting to make Shakespeare appear in period dress. Here’s Kemble playing Faulconbridge, a major character in King John, in 1819.

The historical John lived from 1166 to 1216—why would he be dressed as a sort of cosplay Roman legionnaire? And here is an engraving made from Planche’s 1823 design, with Kemble again in the role of Faulconbridge.

The Kemble/Planche look caught on—and is with us, in some form, to this day. (The Folger Shakespeare Library in Washington, DC, owns a set of the 1823 colored engravings—here’s a LINK so that you can see other costumes for the production.)
Even as his life in the dramatic world was fading, Planche continued to be a literary figure—as well as a literary recycler. In 1868, he collaborated with a prominent British illustrator, Richard “Dicky” Doyle (1824-1883),
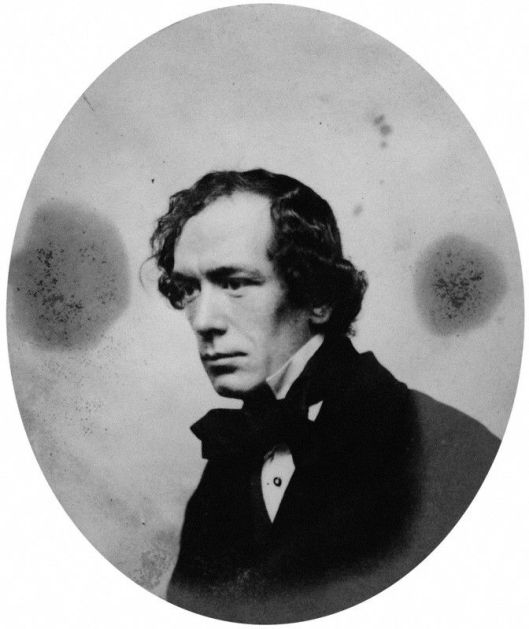

on a verse version of “Sleeping Beauty”: An Old Fairy Tale The Sleeping Beauty.

Doyle was, in fact, a very versatile artist, having, for instance, worked for the satirical magazine Punch, but his lasting fame lies in his fairy/fairy tale illustrations.

Doyle’s work was prized, but his work ethic was, apparently not: commissions came and went, sometimes filled, sometimes not, and it seems that he never quite completed the illustrations to the Planche, (perhaps why Planche’s introduction is dated 1865 and the publication date is 1868?), but here’s a sample to show what he could do, when focused. (And here’s a LINK to the book, so that you can see all of the illustrations for yourself, as well as read Planche’s text.)

So as not to overwhelm you, dear readers, we’re going to pause here, but we’ll continue in our next by looking at other forms—opera, ballet, and animated feature—which Perrault’s story has inspired, taking our story from 1890 to 1959.
In the meantime, thanks, as ever, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD































































































































 or how the grain is raised and processed to get to the mills
or how the grain is raised and processed to get to the mills