Tags
Alfred Tennyson, Dreamflower, Fangorn Forest, Galadriel, Gondor, Helm's Deep, Isengard, Laurelindorenan, Lothlorien, Lotus-eaters, mallorn, Minas Tirith, Mirkwood, Old Forest, Old Man Willow, Palantir, Rath Dinen, Samwise Gamgee, Saruman, The Lord of the Rings, The Odyssey, Tolkien, Treebeard, trees, White Tree of Gondor
Welcome, as always, dear readers.

The inspirations for our postings come from many places: from something we’re reading or have just watched/seen, from a connection between two texts, or between Tolkien’s world—the real or Middle-earth—and something from the history of this world. Sometimes ideas come from the Sortes Tolkienses—our take on an ancient fortune-telling method, in which one posed a question, then opened a copy of an important text like The Bible or Vergil’s Aeneid, closed one’s eyes, and pointed and the text where the finger landed was believed, through interpretation, to contain an answer to that question. In our case, should we require inspiration, we sometimes use our 50th Anniversary hardbound of The Lord of the Rings to do this and, surprisingly often, what we find gives us an idea about what to write.
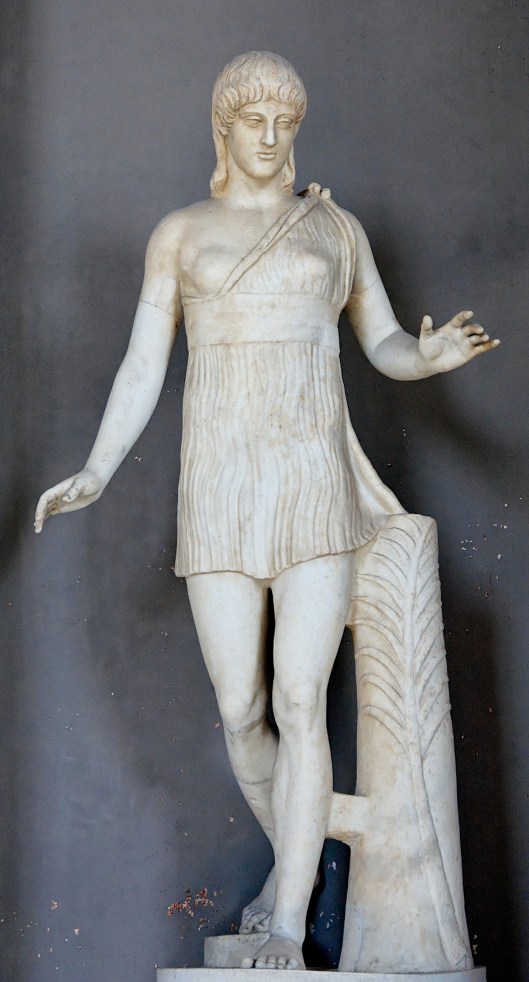
In the case of this posting, however, it was more of a “we were working on something else entirely and then there it was.” The “it” here is the White Tree of Gondor.

(We confess, by the way, that we have iphone cases with the image—and we are often complimented on them.)

We had, in fact, been thinking about another post, this one about corruption through technology, as represented by the palantiri, and had been reading references to Denethor. This had led us to his fiery death in Rath Dinen, “Silent Street”, which led to the tombs of the kings and stewards of Gondor. Besides the rulers of Gondor, however, the street had another occupant, the old White Tree, long dead,

but which, when a new sapling

was found in the mountains by Gandalf and Aragorn, was still treated with ceremony:
“Then the withered tree was uprooted, but with reverence; and they did not burn it, but laid it to rest in the silence of Rath Dinen.” (The Return of the King, Book Six, Chapter 5, “The Steward and the King”)
This seemed a rather odd thing to do to a tree and this led us, finally, to consider one function of trees in The Lord of the Rings: just as the White Tree is buried, as human rulers were, could trees act as a mirror for the condition of the human world at what would be the end of the Third Age? And can they also act as a mirror of change for the better?
Consider, for example, the dead White Tree as a symbol for the withering of Gondor itself, as Minas Tirith is described:
Pippin gazed in growing wonder “at the great stone city, vaster and more splendid than anything that he had dreamed of; greater and stronger than Isengard, and far more beautiful. Yet it was in truth falling year by year into decay; and already it lacked half the men that could have dwelt at ease there…(The Return of the King, Book Five, Chapter 1, “Minas Tirith”)
And this decay of city and tree appears to be echoed in the natural world of Middle-earth in general, as Treebeard says of Lothlorien:

“Do not risk getting entangled in the woods of Laurelindorenan! That is what the Elves used to call it, but now they make the name shorter: Lothlorien they call it. Perhaps they are right: maybe it is fading, not growing. Land of the Valley of Singing Gold, that was it, once upon a time. Now it is the Dreamflower.”
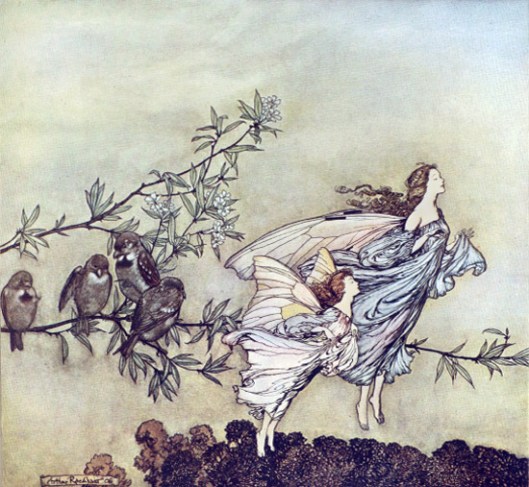
[Just a quick footnote here. “Dreamflower” immediately takes us to Odyssey, Book 9, 82-105, where a small party of Odysseus’ men, set ashore to explore, meet up with the Lotus-eaters, who give them the mysterious lotus to eat and that “whoever might eat of the sweet fruit of the lotus, no longer wished to bring word back or to return home/but wanted, feeding on lotus, to remain in the very same place with the lotus-eating men and to forget about home-going.” (94-97, our translation). This certainly could describe at least some of the Fellowship’s reaction to Lothlorien. Here’s an illustration from a cartoon-version:

Alfred Tennyson wrote a poem on the same subject—here’s a LINK, in case you would like to read his 1832 (revised 1842) interpretation.]
Beyond Lothlorien, other parts of the tree-covered natural world seem more menacing–there’s the Old Forest,

and Mirkwood,

described by Haldir:
“ ‘There lies the fastness of Southern Mirkwood…It is clad in a forest of dark fir, where the trees strive against one another and their branches rot and wither.’ “ (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book Two, Chapter 6, “Lothlorien”)
It wouldn’t take much imagination to replace “where the trees strive” with “where the humans strive against one another and their kind rots and withers”!
There is the sentient, malevolent Old Man Willow,

and even Treebeard and his forest do not at first offer the kind of invitation one hears in the first verse of this song, from Shakespeare’s As You Like It:
Under the greenwood tree
Who loves to lie with me
And tune his merry note,
Unto the sweet bird’s throat,
Come hither, come hither, come hither:
Here shall he see
No enemy
Than winter and rough weather.
Instead, when Treebeard

overhears Pippin say:
“This shaggy old forest looked so different in the sunlight. I almost felt I liked the place.” (The Two Towers, Book Three, Chapter 4, “Treebeard”)
he says, “ ‘Almost felt you liked the Forest!’ That’s good! That’s uncommonly kind of you…Turn round and let me have a look at your faces. I almost feel that I dislike you both…”
Treebeard’s hostility towards Pippin and Merry actually springs from another source—Saruman:
“He and his foul folk are making havoc now. Down on the borders they are felling trees—good trees. Some of the trees they just cut down and leave to rot—orc-mischief that; but most are hewn up and carried off to feed the fires of Orthanc.”
Treebeard’s growing anger, however, then marks a turn in the behavior of the natural world: somehow the appearance of Pippin and Merry acts as a catalyst:
“Curse him, root and branch! Many of those trees were my friends, creatures I had known from nut and acorn; many had voices of their own that are lost for ever now. And there are wastes of stump and bramble where once there were singing groves. I have been idle. I have let things slip. It must stop!”
And it’s not simply the Revenge of the Ents. Treebeard has a larger strategy, saying to the two hobbits:
“You may be able to help me. You will be helping your own friends that way, too; for if Saruman is not checked Rohan and Gondor will have an enemy behind as well as in front.”
As we know, Treebeard convinces the other Ents to help and, in a short time, they not only destroy Isengard

but also the orcs at Helm’s Deep,

effectively removing Saruman from the story except as an empty threat—and a final, petty Sauron, ruining the Shire, which included cutting down numbers of trees—among them the famous Party Tree. And here we see one more symbol, perhaps. Long before, Galadriel had given Sam a gift which, in her wisdom (and perhaps in her foresight?) seemed almost perfect for a gardener:
“She put into his hand a little box of plain grey wood, unadorned save for a single silver rune on the lid….’In this box there is earth from my orchard, and such blessing as Galadriel has still to bestow is upon it…Though you should find all barren and laid waste, there will be few gardens in Middle-earth that will bloom like your garden, if you sprinkle this earth there.’ “ (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book Two, Chapter 8, “Farewell to Lorien”)
Once the Shire has been scoured of Saruman’s final evil, Sam remembers this present and uses it, spreading the earth across the Shire:
“So Sam planted saplings in all the places where specially beautiful or beloved trees had been destroyed, and he put a grain of the precious dust in the soil at the root of each.” (The Return of the King, Book Six, Chapter 9, “The Grey Havens”)
And his plan succeeds:
“His trees began to sprout and grow, as if time was in a hurry and wished to make one year do for twenty.”
In midst of such fertility, there is an extra favor. Sam had found within Galadriel’s box “a seed, like a small nut with a silver shale [shell or husk].”
Sam planted this in the Party Field, where the tree had once stood, and, in the spring:
“In the Party Field a beautiful young sapling leaped up: it had silver bark and long leaves and burst into golden flowers in April. It was indeed a mallorn [the golden tree specific only to Lothlorien], and it was the wonder of the neighborhood.”
Just as the human world of Middle-earth, stunted by Sauron and his minions, is now free, so is the natural world free once more—no more orcs to abuse its forests, no malevolent will to taint its woods, and the reflowering of the Shire and, at its center, the mallorn, may stand as a symbol for that rebirth—and even be twinned with the new White Tree of Gondor, far to the south.

[With thanks to Britta Siemen’s blog, where we found this image—LINK here]
Thanks, as ever, for reading!
MTCIDC
CD