Tags
Argeleb, Baraduin, Beleriand, Blanco, Bridge of Stonebows, Bronze Age Horse, cable ferry, coins, Dartmoor, Doriath, Dwarves, English South Downs, Fallowhide, Far Downs, Farthings, Fornost Erain, Frodo, Gloucestershire, Government, Great East Road, Green Hill Country, Greenway, Jeremy Brett, Little Delving, Longbottom Leaf, Maps, Marcho, Michel Delving, Middle-earth, Minas Tirith, Misty Mountains, Old Dee Bridge, Oxfordshire, River Baranduin, Roads, Roman Roads, Sherlock Holmes, Sidney Paget, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, Steven Spielberg, Tharbad, The Hobbit, The Hound of the Baskervilles, The Lord of the Rings, The Shire, Three Farthing Stone, Tobacco, Tolkien, Warwickshire, White Downs, Worcestershire
Welcome, dear readers, to the third installment of our rough portrait of the Shire. We call it a “rough portrait” because, so far, we’ve relied upon only three sources: The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, and The Letters of J.R.R. Tolkien. We’ll continue to do so in this installment, but we will add two works of geography, K. W. Fonstad’s The Atlas of Middle-earth and Barbara Strachey’s Journeys of Frodo (although we may take a hint of two from other works).
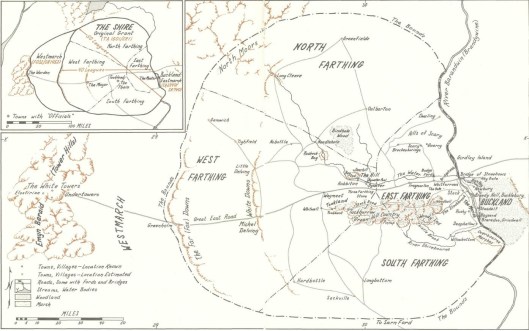
So far, we’ve discussed the government of the Shire (Shire Portrait 1) and the economy (Shire Portrait 2). In this, we want to move on to the geography of the Shire. We begin with Fonstad’s map.

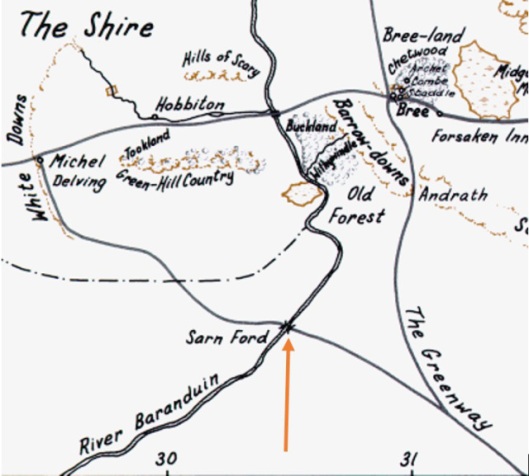
Except for Buckland, all of the Shire lies west of the River Baranduin (the “Brandywine”). This river can be broad enough to require a cable ferry

and it is navigable, at least by small boats—after all, it was in such a boat that Frodo’s parents were drowned.
As well, there is the Bridge of Stonebows on the Great East Road. Since it’s wide enough for gates and is reported to have had houses on the far side of it, we might imagine it to look like the Old Dee Bridge, at Chester, in England.

This bridge dates from Norman times (although there was a bridge there from the days of the Roman occupation—“Chester”, after all, is only a corruption of castra, Latin for “military camp”—founded as Deva Victrix in 79AD), with the present version being more-or-less 14th-century. In the Prologue to The Lord of the Rings, the Bridge of Stonebows is said to have been “built in the days of the power of the North Kingdom”, making us wonder whether the Dwarves, who had cut the Great East Road long before, had only had a ford at that place.
To the west of the river stretches the Shire, most of it to the north and south of the Great East Road, which acts as a kind of spine, there being subsidiary roads leading off it towards the various villages. Originally built by the Dwarves in the First Age, it led from Doriath in Beleriand eastward beyond the Baraduin towards the Misty Mountains. After the destruction of Beleriand, the remaining section ran only from the Grey Havens eastward. When Marcho and Blanco, the Fallowhide brothers, gained permission to colonize the area in TA1601 from Argeleb II, the only payment required was “that they should keep the Great Bridge in repair, and all other bridges and roads, speed the king’s messengers, and acknowledge his lordship”, which would have included the Great East Road.
In a previous posting, we talked about the North-South Road (later, the “Greenway”, which once ran from Fornost Erain, in the north, to Minas Tirith, in the south. Because of its ancient importance and places like the causeway and bridge at Tharbad, we imagined it to be like a Roman road—carefully laid out by engineers and paved but, no longer maintained, gone to seed.



Because of its great age and one-time importance, we’ve always pictured the Great East Road to be similar, especially when it is clear that the kings of Arnor considered its maintenance to be the equivalent of tribute or taxes from the new Shire. Subsidiary roads which split off from the East Road, however, we might see as the usual rutted country roads.

The Shire, besides being bisected by the Great East Road, is also divided into four parts—hence the name “Farthings”—like the pre-decimal English coin, which was a fourth part of a penny (when a penny obviously was worth a lot more!).
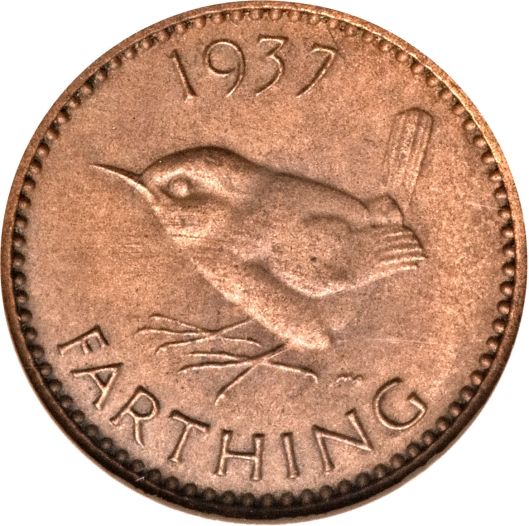

We wonder what these divisions were intended to be used for—perhaps for the election of the Mayor? In our previous posting on the government of the Shire, we quoted JRRT as saying in the Prologue to The Lord of the Rings, “The Shire at this time had hardly any ‘government’”, so, for the moment, that’s our best guess.
(We should note here the “Three Farthing Stone”, which marks more or less where the North, East, and South Farthings meet. It has been suggested that it has been based upon the actual English “Four Shires Stone”—
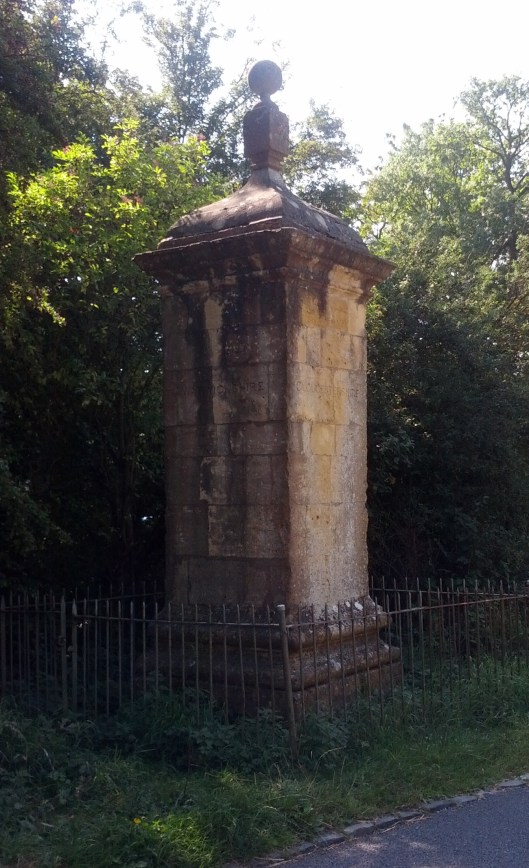

which sits at the place where, pre-1931, four shires—Worcestershire, Warwickshire, Oxfordshire, and Gloucestershire — touched. Not only is there a similarity in the names and what the stone may function as, but the Three Farthing Stone is just to the west of Frogmorton, whereas the Four Shire Stone is just east of Moreton-in-Marsh. And is JRRT having a quiet joke in that, after a boundary adjustment in 1931, the Four Shire Stone should really be called the Three Shire Stone?)
Just south of the Great East Road is the Green Hill Country, which appears to be heavily forested.

This is mirrored by a smaller wood north of the road, Bindbole.
Other than these (and, of course, the Old Forest in Buckland), the land seems to be open. To the north are the North Moors. These are windy uplands, mostly grass, with little in the way of trees.

Dartmoor (which is the image above), in southwest England, seems so bare (although it has the fallen remains of earlier cultures on it), that it can seem a little spooky—the perfect setting for Sir Arthur Conan Doyle’s Sherlock Holmes novel The Hound of the Baskervilles (first published in book form in 1902).

(We love the original Sidney Paget illustrations in The Strand Magazine, but our favorite film version is the one starring Jeremy Brett as Holmes. For pure fun, by the way, we recommend Steven Spielberg’s Young Sherlock Holmes—not for the purist, we hasten to add.)




To the west are two lines of downs, the White and the Far (or Fox) Downs. When we think of downs, we think of the chalky rolling hills southeast of the Thames in England. Here’s what the English South Downs look like

and it’s easy to imagine that the Shire version would look very similar and the chalk would easily be cut into to make Michel Delving (“Big Dig”) and Little Delving (“Little Dig”). The chalk just below the surface is exposed on the south English coast

making that name “the White Downs” clear. And we can’t resist adding another chalk artifact. In Oxfordshire (but once Berkshire), on the edge of the Berkshire Downs, is a Late Bronze Age horse, cut into the chalk. We wonder why there isn’t one in Rohan…

Last of all, there’s the South Farthing, stretching south of The Green Hill Country. As it is a tobacco-growing area, but in a temperate climate (at least, we understand that the Shire is in a temperate zone—they appear to have—or to have had—snowy winters), we visualize it as looking like the Connecticut Valley, which runs south down from Vermont, through western Massachusetts and through central Connecticut, in the US.
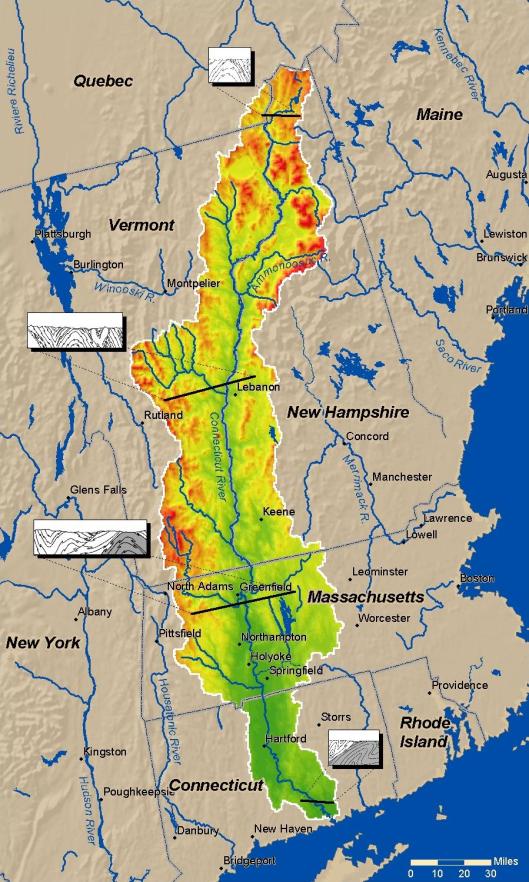
In the central part of the valley are tobacco plantations.

These always include drying barns for the tobacco—which would become the Longbottom Leaf Merry and Pippin discover two casks of in Saruman’s pantry.

The one farthing we haven’t studied directly is the East Farthing, but, as it contains a continuation of the Green Hill Country, abuts the Brandywine, and has the already-mentioned bridge of Stone Bows, and thus has no main features we haven’t mentioned, we’ll conclude here for the moment. In our next, we want to examine Shire architecture, from hobbit holes to mills.
Thanks, as ever, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD































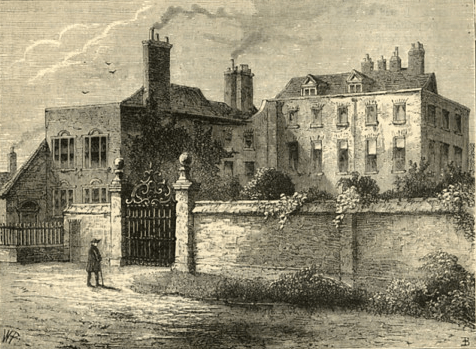


























































 )
)