Dear Readers,
Welcome, as always.
This is the second of two postings which, as we said in our last, was originally just one. That earlier draft linked the Palantiri with Galadriel’s mirror, but, on reconsideration, we believed—at least at first–that, in fact, they weren’t so close as we thought and so we separated them.
In our last, we discussed the Palantiri and what might have been a possible inspiration for them. In this posting, we propose to look a little more closely at Galadriel’s mirror (but we promise not to touch the water).
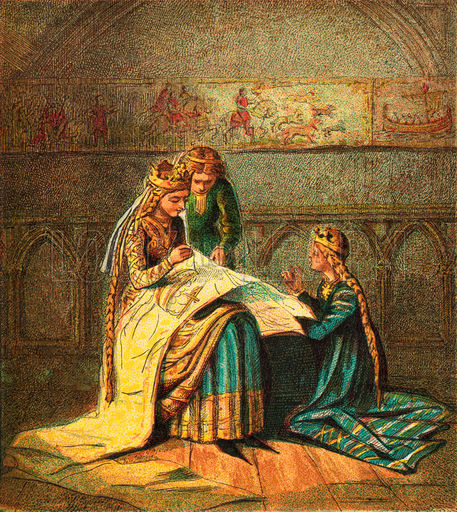
When we speak of mirrors—and, in this case, magic ones—the first one which pops into our mind is from childhood—the mirror in Snow White and the particularly creepy mirror in the 1937 Disney animated film.

In the original Schneewittchen, first published in the Grimm brothers’ Kinder und Hausmaerchen in the original edition of 1812,


the mirror belongs to Snow White’s stepmother, of whom the story says (in our translation):
“She was a very beautiful woman, but she was proud and arrogant and couldn’t allow that anyone would surpass her in beauty.”
She monitored her position by means of that mirror:
“She had a wonderful mirror. When she stepped before it and looked at herself within it, she said:
Little mirror, little mirror, on the wall,
Who is the most beautiful in the whole land?
The mirror answered thus:
Madame Queen, you are the most beautiful in the land.”

This makes us wonder about the stepmother. Was she like so many of the people we see around us every day (and not “everyday”, which is a compound adjective, meaning “commonly” as in “everyday usage does not necessarily equal correct usage in language”), compulsively fiddling with their electronic devices? How often did she go to that mirror and ask that question? As it was attached to the wall, she wasn’t carrying it in her back pocket, so, can we picture her making excuses to the king, to the prime minister, to her ladies in waiting, just so that she could go back to visit it? The text only says that she did—it’s a folktale, after all, and therefore old and so before current addictions were available, but she seems so obsessed—and familiar.
But then comes the day when the answer is:
“Madame Queen, you’re the most beautiful here,
But Snow White is a thousand times more beautiful than you.”
And the story goes on from there to places we don’t intend to follow. It is interesting, however, that the mirror itself appears to do the talking, not a visible spirit within it, as in the Disney movie, and there is a certain logic to this. After all, normally, a mirror is only a reflecting device: it shows the person who is looking into it, as we see the stepmother doing. Then again, having someone—or something—looking out when you look in raises all sorts of interesting questions: who is it? Where is it? How does it know what it knows and how to speak? Does it have limits?
We might imagine, from her single, repeated question that the woman does. She never, for example, asks “Was there anyone as beautiful before me?” or “Will I always be the most beautiful?” She seems trapped in the moment and, without a greater context, the mirror’s last reply will be that much more shocking.
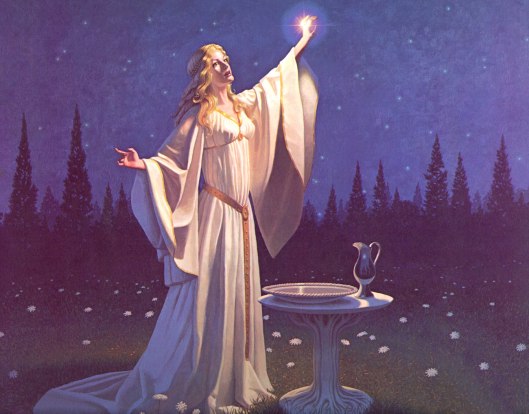
In contrast, Galadriel’s mirror, is neither on a wall, nor portable. In fact, it’s not really a mirror in the conventional sense at all.
“With water from the stream Galadriel filled the basin to the brim, and breathed on it, and when the water was still again she spoke. ‘Here is the Mirror of Galadriel,’ she said. ‘I have brought you here so that you may look in it, if you will.’ “ (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book 2, “The Mirror of Galadriel”)

When Frodo asks what might be seen therein, Galadriel replies:
‘Many things I can command the Mirror to reveal,’ she answered, ‘and to some I can show what they desire to see. But the Mirror will also show things unbidden, and those are often stranger and more profitable than things which we wish to behold. What you will see if you leave the Mirror free to work, I cannot tell. For it shows things that were, and things that are, and things that yet may be. But which is it that he sees, even the wisest cannot always tell.’ (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book 2, “The Mirror of Galadriel”)
There appear to be several possible influences here. In the ancient Greek poem, The Theogony, the Muses are described as knowing past, present, and future (Theogony 380), as they choose the shepherd, Hesiod, to become a poet.

Others have suggested that an influence upon the author here was the Urtharbrunnr, the well of fate, as it may be translated, from Norse mythology, which lies at the foot of the tree called Yggdrasil. Here the Norns, or Fates in Norse tradition, sit to do their work.

Another possibility yet might be the three Christmases who visit Ebenezer Scrooge in Charles Dickens’ A Christmas Carol and an advantage to pointing to them is that Christmas Yet to Come, although mute, shows Scrooge what turn out to be only “things that yet may be”, as Scrooge, by his change in behavior, diverts fate.

That sense of potentiality about the future is clearly a very important feature of Galadriel’s Mirror. Lorien is not only a haven from Orcish pursuit,

but also a testing ground, where the surviving members of the Fellowship are probed by the Lady of the Wood, even as she herself is inadvertently tested when Frodo offers her the Ring. Sam may suffer the most from this, being shown what appears to be the destruction of the Shire and the destitution of his own grandfather.

And yet, as Galadriel says,
‘But the Mirror will also show things unbidden, and those are often stranger and more profitable than things which we wish to behold.’ (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book 2, “The Mirror of Galadriel”)
What Sam sees shakes him for a moment to the point of stepping back from the basin, saying (almost shouting, as the sentence ends with an exclamation point), “I must go home!” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book 2, “The Mirror of Galadriel”) He recovers immediately, however, resolving, “ ‘No, I’ll go home by the long road with Mr. Frodo, or not at all.’” And thus he, like Galadriel, passes the test and perhaps that’s what the odd word “profitable” means in her explanation. Sam is confronted with what must have been that which he subconsciously dreaded most, but his new resolution ultimately proves the salvation of Middle Earth, on the one hand, and the healing of the Shire by means of Galadriel’s gift of a little Lorien, on the other. And, considering that Sam first appears in the story as an eaves-dropping gardener and hardly a giant elf-warrior, that other adjective, “stranger” may be appropriate, too.
So far, the Mirror has nothing in common with a Palantir, which was clearly designed not as a “scrying stone”, but as a communication device. And yet there is Galadriel’s remark,
“ ‘Many things I can command the Mirror to reveal,’ she answered, ‘and to some I can show what they desire to see.’ “
This strikes us as an ambiguous statement—and probably meant to be. Does Galadriel mean:
- people come to ask her, for example, to see their future—implication being that she shows them that, and nothing more
- people come, ask, and she shows them what they want to see—implication being that what they see is not necessarily what is real?
When Frodo looks into Mirror, he sees the very last thing he would want to see, however:
“But suddenly the Mirror went altogether dark, as dark as if a hole had opened in the world of sight, and Frodo looked into emptiness. In the black abyss there appeared a single Eye that slowly grew, until it filled nearly all the mirror. So terrible was it that Frodo stood rooted, unable to cry out or to withdraw his gaze. The Eye was rimmed with fire, but was itself glazed, yellow as a cat’s, watchful and intent, and the black slit of its pupil opened on a pit, a window into nothing.” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book 2, “The Mirror of Galadriel”)
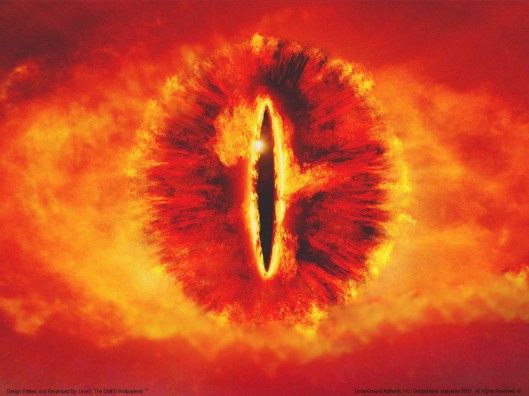
This is especially true in that:
“Then the Eye began to rove, searching this way and that; and Frodo knew with certainty and horror that among the many things that it sought he himself was one.” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book 2, “The Mirror of Galadriel”)
This is clearly not the past or the future, as Frodo sees it, but the all-too-realistic present. And this is not just a present to be viewed. Like the figure in the mirror in the old Disney Snow White, this is someone who would respond directly to what he sees, if he could. And Frodo is aware of this:
“But he also knew that it could not see him—not yet, not unless he willed it.” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book 2, “The Mirror of Galadriel”)
Does the Mirror have more potential, then? Can it be used as a communication device, like a Palantir? If it can combine the functions of “magic mirror” and Palantir, might the Palantir be able to combine functions, as well?
Certainly Sauron does something which ruins Denethor’s ability to resist Sauron’s view of the future to the point where he attempts to commit flaming suicide along with his one surviving son, having abandoned his city to its fate.

Denethor, though, is just a human, and rather a vain one, at that.
How would Sauron do the same with one of the Maiar, those beings sent by the Valar to protect Middle Earth from the danger which Sauron represents? Certainly we know that Sauron has communicated with Saruman through the Palantir.

There may be a clue in Gandalf’s reply to Saruman, just before he is held captive in Orthanc:
“I have heard speeches of this kind before, but only in the mouths of emissaries sent from Mordor to deceive the ignorant.” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book 2, “The Council of Elrond”)
What Gandalf is responding to is:
“A new Power is rising. Against it the old allies and policies will not avail us at all. There is no hope left in Elves or dying Numenor. This then is one choice before you, before us. We may join with that Power. It would be wise, Gandalf. There is hope that way. Its victory is at hand; and there will be rich reward for those that aided it. As the Power grows, its proved friends will also grow; and the Wise, such as you and I, may with patience come at last to direct its courses, to control it. We can bide our time, we can keep our thoughts in our hearts, deploring maybe evils done by the way, but approving the high and ultimate purpose: Knowledge, Rule, Order; all the things that we have so far striven in vain to accomplish,,hindered rather than helped by our weak or idle friends. There need not be, there would not be, any real change in our designs, only in our means.” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book 1, “The Council of Elrond”)
“Knowledge, Rule, Order”? It’s no wonder that Gandalf replies as he does. Such words sound more like the slogan of a totalitarian state—exactly what Mordor has become under its lidless-eyed master–than those of one of the Istari.
And how did Saruman come to have such a distorted vision of the future? Just as Denethor, bitter over his son’s death and the loss to Gandalf—he thinks—of his younger son, has been shown what must have been an increasingly-bleak picture of Gondor and its fate, so can we imagine that Sauron, sensing a latent arrogance and desire for power in Saruman, has given Saruman the second possible understanding of Galadriel’s statement. He has shown Saruman what Saruman secretly wishes for and, in doing so, he cunningly paints for Saruman, who is just wise enough to know that he will never be Sauron, a picture of an alliance which will grant him his wish. Why does Saruman, who is himself an extremely powerful figure, fall for this? Perhaps he’s like Snow White’s stepmother and limited to one question: “Little globe, little globe, who is the (second most) powerful in Middle Earth?”
What do you think, dear readers?
Thanks, as always, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD







































































































 of which there are seemingly many surviving in several media. Older yet are the Greek masks, the images of which survive in many fewer images, mostly on pots.
of which there are seemingly many surviving in several media. Older yet are the Greek masks, the images of which survive in many fewer images, mostly on pots.






 Why are they so scary? Well, for one thing, the clothing is bright and festive, but the face is dead-white and corpse-like, therefore giving a mixed signal of merriment and death at the same time. Perhaps these contradictions should have made the stepmother less trusting (it certainly made
Why are they so scary? Well, for one thing, the clothing is bright and festive, but the face is dead-white and corpse-like, therefore giving a mixed signal of merriment and death at the same time. Perhaps these contradictions should have made the stepmother less trusting (it certainly made 



































