Tags
Alan Lee, Andrew Lang, Barrow-downs, Beowulf, cyclops, Dragons, George Macdonald, Goblin Feet, Goblins, Great War, Grendel, Grendel's Mother, John Howe, monsters, Polyphemus, Sir Gawain and the Green Knight, Smaug, Storia Moria Castle, Tales of Troy and Greece, The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, The Princess and the Goblin, The Red Book of Animal Stories, The Red Fairy Book, Tolkien, trenches, tumulus
As always, dear readers, welcome!
One of us is currently teaching The Hobbit and, is always seems to be the case when we are teaching an old friend, we are struck by something new. In this case, it’s the idea of “what lurks beneath” and where it might come from.
What occurred to us now was that, virtually every time there is trouble for Bilbo and the dwarves, it is strongly linked with caves and hollowed-out places: trolls who came out of a cave (“Roast Mutton”), goblins who live in caves (“Over Hill and Under Hill”), Gollum (“Riddles in the Dark”), hostile elves (“Flies and Spiders” and “Barrels Out of Bond”), and, of course, Smaug (“On the Doorstep”, “Inside Information”, and “Not At Home”). Only the wargs, the overgrown spiders, and the men of Lake-town in the Battle of the Five Armies have above-ground origins, as, after all, the other forces—goblins, elves, and even Iron Hills dwarves (we assume), have subterranean dwellings.
We knew that JRRT thought to become a classicist early in his academic career and we can imagine right away that one influence upon him for this underground menace would have been Polyphemus the Cyclops, who, after all, lives in a cave.

Before he read that part of Odysseus’ story in Greek, he might have seen it in Andrew Lang’s 1907 Tales of Troy and Greece—


Tolkien tells us that, as a child, he had read other Lang works and a story in one, The Red Fairy Book (1890), might even have influenced some Middle-earth geography, from “Storia Moria Castle”.


Another childhood favorite (although he appears to have changed his mind later in life) were the fantasy novels of George Macdonald

and his The Princess and the Goblin (1872),

as its title suggests, is full of goblins and their underground world. These goblins are powerful, but have one fatal flaw—tender feet—which JRRT said that he never believed (see Letters, 178)—although Tolkien’s first published poem was entitled “Goblin Feet” (Oxford Poetry 1915).
Beyond possible childhood reading, there is his career focus, which includes two other potential underground influences.
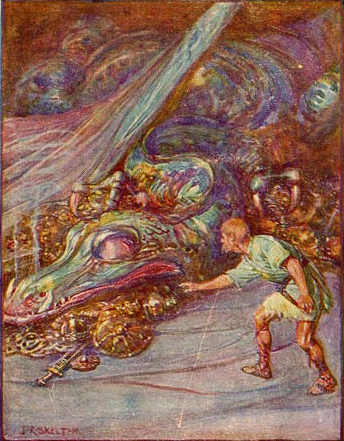
First, there is Beowulf. Grendel, the monster in this poem,

lives in a cave at the bottom of a pool with his mother and, in the second part of his monster-slaying, Beowulf has to dive into that pool to deal with her.
This illustration comes from another Andrew Lang book, The Red Book of Animal Stories (1899).

(The picture of Grendel is by Brian Froud. We found it on the website of K.T.Katzmann, I Write Monsters. Here’s a LINK.)
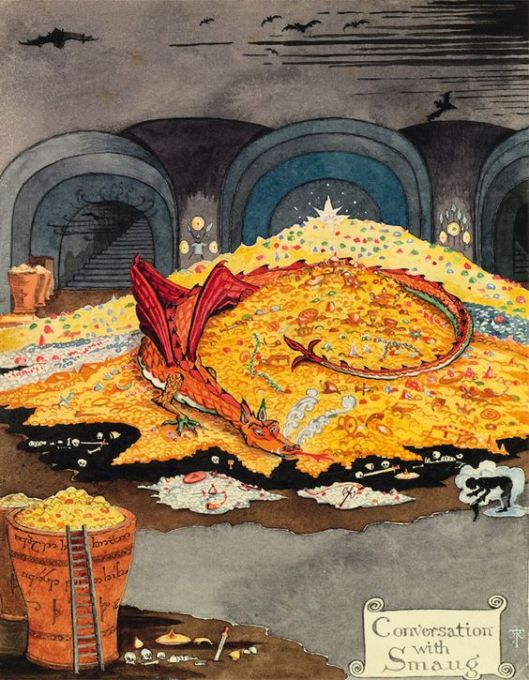
Then, of course, there’s that dragon, against whom Beowulf fights and dies—and which is the direct ancestor of another famous and familiar dragon…
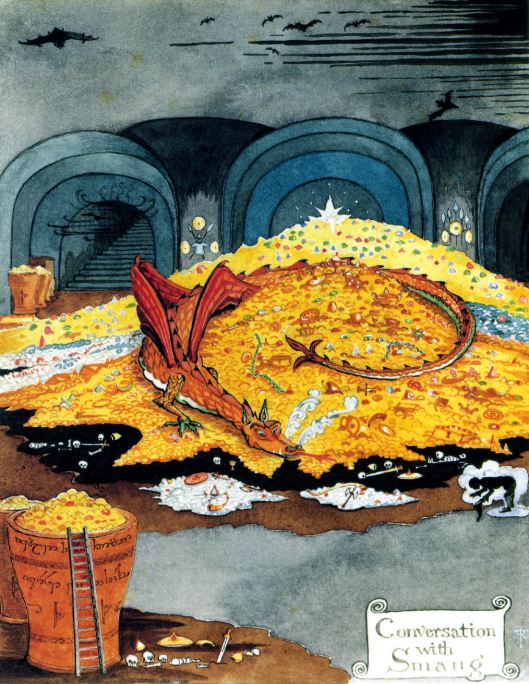

We are told that it lives in an abandoned tumulus—that is, an ancient grave mound, like this one.

(This is, in fact, a famous Neolithic burial at Gavrinis, in Brittany.)
JRRT worked in Middle English, as well as Old English, and here we find one more possible source in his own edition (with E.V. Gordon) of the 14th-century poem Sir Gawain and the Green Knight.

The Green Knight who challenges King Arthur’s court to a mutual head-chopping contest, is said, in the fourth part of the poem, to inhabit a “green chapel” and to appear out of a hole when Sir Gawain, who has accepted the challenge and cut off the Green Knight’s head, makes his appearance there to fulfill his half of the contest.
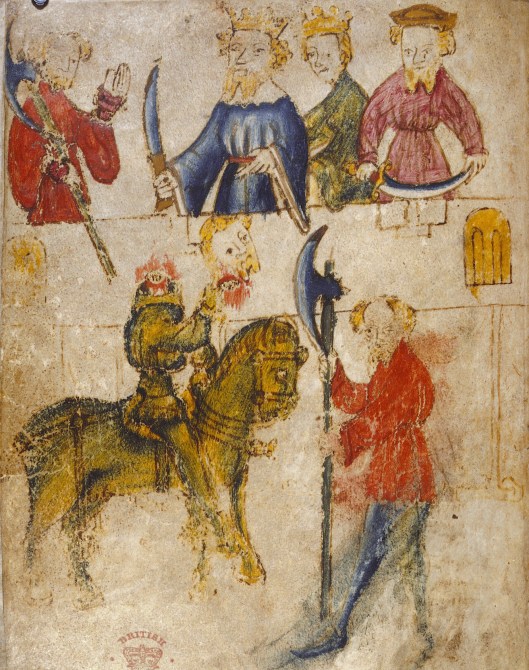

This chapel has sounded like a tumulus to generations of scholars and here’s John Howe’s 2003 illustration, complete with chapel as tumulus (not to mention a very large green man).

Tumuli also make their appearance, of course, in The Lord of the Rings, when Frodo and his party go astray on the Barrow Downs.
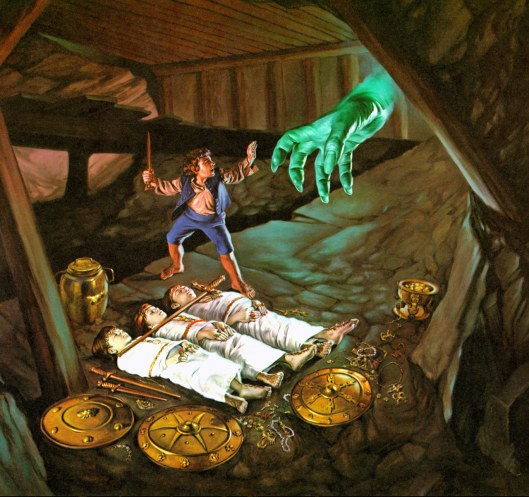

We can’t finish this posting without at least suggesting one more source, something even more personal than JRRT’s scholarly work: his experiences in the Great War.
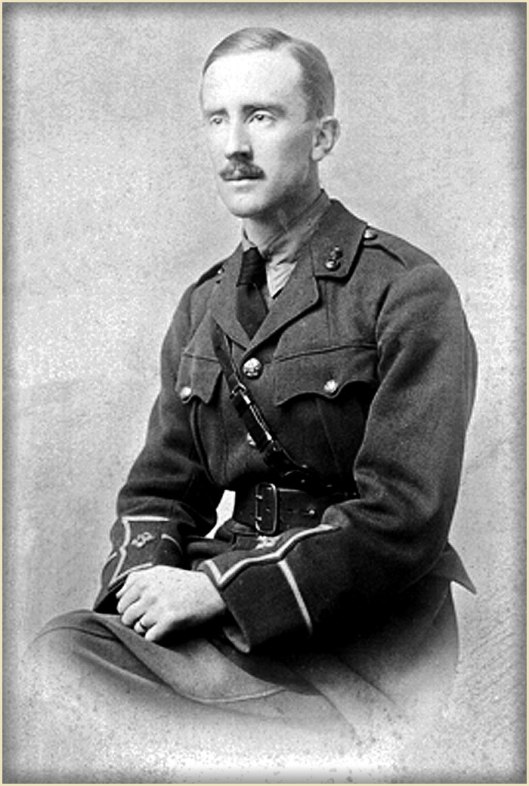

By the time Tolkien entered the service in France, the Western Front was, basically, a 500-mile trench, from Switzerland to the North Sea.
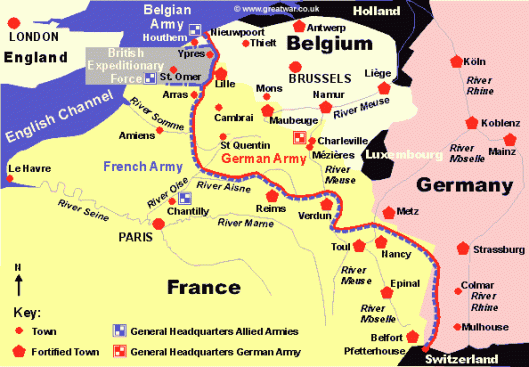
Much of the entrenching was simply deep, reinforced ditching.
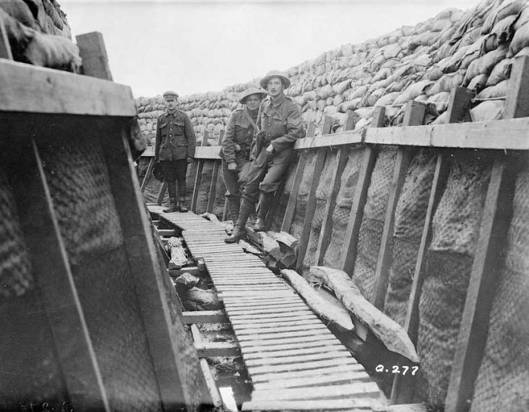

But some—particularly on the German side—could be elaborate, even built with stone or concrete, and set far enough into the ground as to be almost impervious to bombardment.

And we imagine that, with all of that earlier literary work in his mind, JRRT might have faced such defenses wondering whether what was inside them would be Germans

or something much worse.

And did this haunt his later writing as much as the Great War haunted the minds of soldiers all over the world?
Thanks, as ever, for reading!
MTCIDC
CD






















































































































 (As usual with so many old and established things, there is argument over where the word “penny” comes from. Personally, we’ve always imagined that it’s an English diminutive of a Brythonic word—as it exists today in Welsh—“pen” = “head”, the idea being that coins had portrait heads on them. Certainly some pre-Roman British coins had them
(As usual with so many old and established things, there is argument over where the word “penny” comes from. Personally, we’ve always imagined that it’s an English diminutive of a Brythonic word—as it exists today in Welsh—“pen” = “head”, the idea being that coins had portrait heads on them. Certainly some pre-Roman British coins had them