Tags
A Gest of Robyn Hode, Angus McBride, Ballads, Border Reivers, Carlisle Castle, Child Ballad, Connacht, Cuchulain, Cuchulain of Muirthemne, England, Ewan McColl, Faroe Islands, Francis James Child, Irish Iron Age, Johnnie of Breadisley, Kinmont Willie Armstrong, Loeg, Marches, Medb, Peggy Seeger, ring dance, Robin Hood, Scotland, Scott of Buccleuch, Sheriff of Nottingham, Sherwood Forest, skiparin, Tain Bo Cualnge, The Cattle Raid of Cooley, The English and Scottish Popular Ballads, The Tale of MacDatho's Pig, Ulster, West March of the Shire
Welcome, dear readers, as ever.
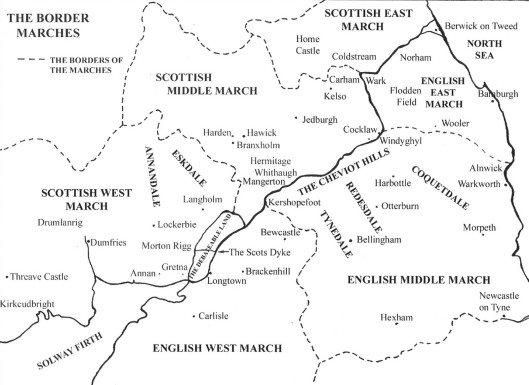
This is a continuation of our last, on borders. In that post, we began with the West March of the Shire, then talked about the idea of marches—militarized border areas—and wardens—overseers of such. Our focus was upon the border between Scotland and England and, in particular, in the very troubled 16th century.

The danger, in this world, was from reivers,

a kind of border bandit, but a more complex figure than, for example, Robin Hood.

In the Marches of Scotland and England, unlike Robin vs the Sheriff of Nottingham in Sherwood, who the heroes and villains were wasn’t always clear. England and Scotland were often at war throughout the later Middle Ages and into the Renaissance and, when not openly at war, continued to skirmish with each other. War and skirmishing brought financial problems to both sides—raids could ruin a farm or even a village on either side of the border– and there was also a certain level of vendetta—families always being bound to avenge a murdered kinsman—or rescue a living one, as we see here Scott of Buccleuch (said something like “buk-LOO”) rescuing Kinmont Willie Armstrong from imprisonment by the English in Carlisle Castle in 1596. Willie had been taken prisoner illegally during a “truce day” and Scott was the official representing Scotland on that day—so, as we said, the differences between heroes and villains aren’t always so obvious in this twilight world.

One thing reivers have in common with R. Hood, however, is that both are the subject of legends and songs. One of the first collections of those songs is A Gest of Robyn Hode, printed between 1492 and 1534.

A common form of song is the ballad. For those not familiar with the form, a ballad is a narrative poem commonly in couplets (2 rhymed lines—sometimes with a refrain—a line repeated throughout the poem—after each couplet) or in quatrains (4 lines, often rhyming on the 2nd and 4th line).
From the word, which appears to be related to the Romance language ballare/bailar/ballet, “to dance/a dance”, we might imagine that, originally, it was a song to which one danced and there are medieval illustrations of such—

This appears to be a ring dance and, in fact, resembles the ring dance and song of the Faroe Islands, where there is a central figure, a skiparin, (“captain”—just like English “skipper”) who sings a verse and all of the dancers join in on the chorus of kvaedi, or ballads.

The circle on such a dance/song can expand to the point where it looks more like a snake dance—as this link from a recent performance shows.
An easy example of the quatrain form of ballad might be the opening of “Johnnie of Breadisley” (Child 114):
Johnny rose on a May mornin’,
Called for water to wash his hands,
Saying loose to me my twa grey dogs
Wha’ lie bound in iron chains.
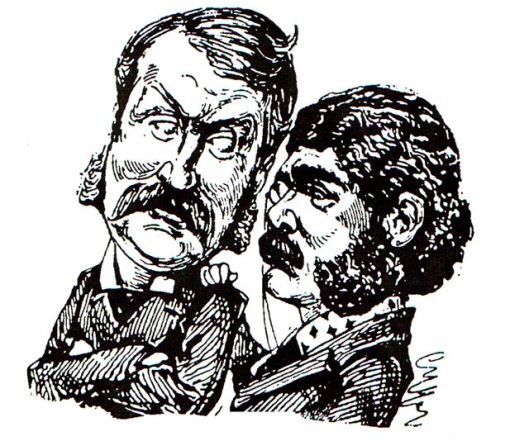
We did this from memory, it being one of the first ballads we memorized years ago. If it’s compared with the standard ballad text—that’s from Francis J. Child’s The English and Scottish Popular Ballads (1882-1898), we’re sure you’ll find that, without even knowing it, we’ve made little changes, turning it into a variant—which always happens when songs are learned by ear. (You can also see that rhyme can be very loose—sometimes only assonance, but it’s clearly less important than telling the story.) Our version came from one sung by the famous Scots folk singer/composer, Ewan McColl, shown here with Peggy Seeger, his equally-famous wife and fellow artist.

You can hear his version on YouTube here.
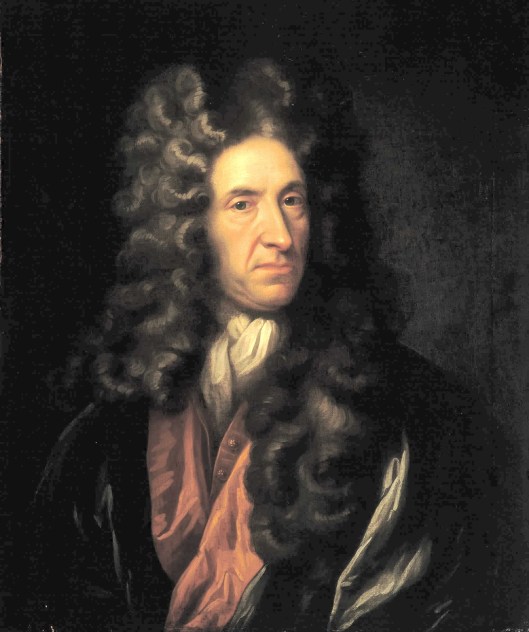
Child
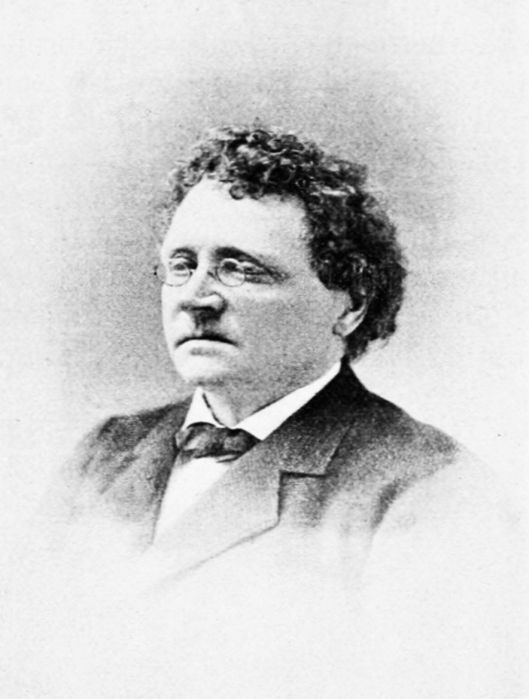

was a professor at Harvard who spent most of his adult scholarly life searching out traditional ballads and a version of his massive collection—305 ballads, with many variants—is available (based upon early editions) at the wonderful Sacred Texts. (If you are interested in adventure/fantasy/mythology and you don’t know this site, spend some time browsing it—you will be impressed.)
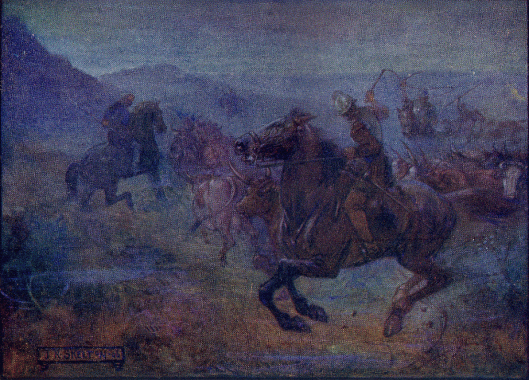
The border between Scotland and England wasn’t the only place in the UK which spawned heroic stories, however. During the Irish Iron Age, two of Ireland’s five provinces, Ulster and Connacht, were imagined to be constantly at war and raids across the border formed the basis or background of all kinds of tales, the most elaborate being the Tain Bo Cualnge (Tahn Boh KOO-al-nyeh)—“The Cattle Raid of Cooley”. In this story—a kind of prose epic, with occasional short verse inserts—Medb (Mi-YEDTH), the queen of Connacht, has decided that she must have a famous bull, owned by someone in Ulster. At the time, the warriors of Ulster are under a geis (gesh), a kind of magical prohibition, which keeps them from defending the province, which leaves only one—their best, in fact—the 17-year-old Cuchulain (Koo-HOO-lun), with his charioteer, Loeg (loig) to delay the Connachtmen. Here’s a rather over-the-top illustration by one of our favorite military artists, Angus McBride, of the pair rocketing towards the enemy.

If you would like to read a translation of the Tain, here’s a link to a really useful website, which juxtaposes the Old Irish and English (and includes, as a bonus, another great story—and the first one we read in Old Irish—the Tale of MacDatho’s Pig). If you would like to read more Old Irish Stories about Ulster and Connacht, there is Lady Gregory’s Cuchulain of Muirthemne (1902). It’s available at Sacred Texts. (And a note here: Old Irish literature has a very plain-spoken way of talking about body functions, among other things, and early translators, like Lady Gregory, quietly removed or softened such things. On the whole, however, the basic stories are there—and they’re free!)
Among those stories, we find a very different idea about otherworlds—not the fairly-strict western classical one that there is a clearly-marked border between this world and the next, but something looser and therefore spookier and we want to talk about this in our next (and mention a favorite YA author and his treatment of the subject, as well).
Thanks, as always, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD



























































































 )
)