Tags
Agincourt, Bayeux Tapestry, Dol Amroth, Forlong, Great Gate, Harold Godwinson, hauberk, Hirluin the Fair, Howard Pyle, huscarls, Imrahil, Langstrand, Lincoln Cathedral, livery, Lossarnach, Medieval, Minas Tirith, Morthond, N.C. Wyeth, Palermo, parade, Ringlo Vale, Robin Hood, spangenhelm, The Lord of the Rings, Tolkien, Tower of Gondor
“I love a parade, the tramping of feet,
I love every beat I hear of a drum.”
–Koehler/Arlen Rhythmania (1931)
Welcome, dear readers, as always. In the past, we’ve spent a posting or two discussing military aspects of The Lord of the Rings, from the look of the Rohirrim to the attack on Minas Tirith. In this posting, we would like to go back one step from that attack to consider what is a rather melancholy moment in the lead up to that assault.
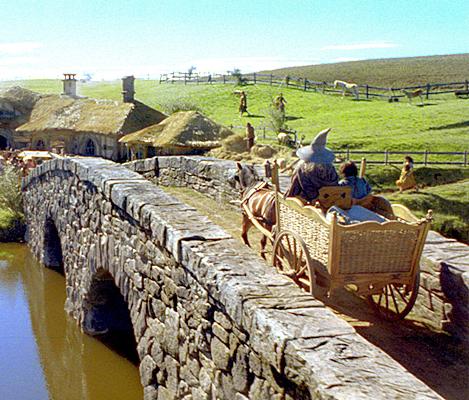
Pippin and his newfound friend, Bergil, have come down to the Great Gate of Minas Tirith.
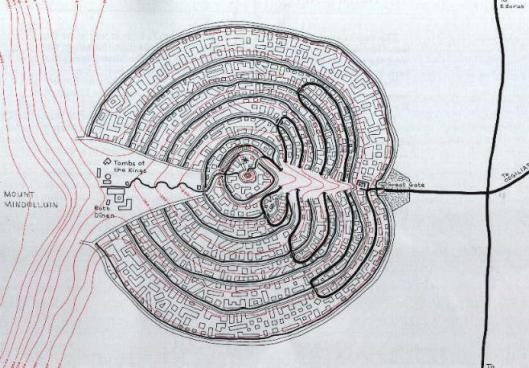
Here’s the gate from the films.
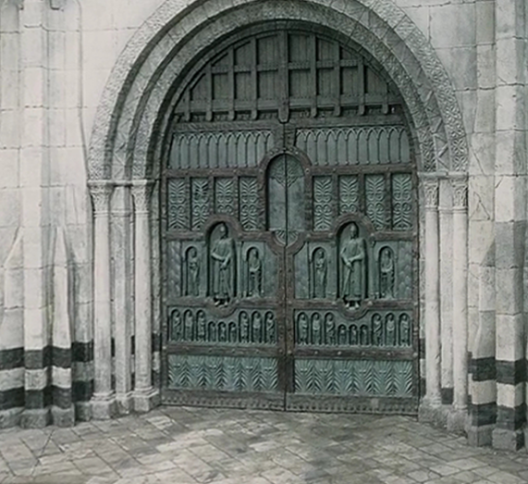

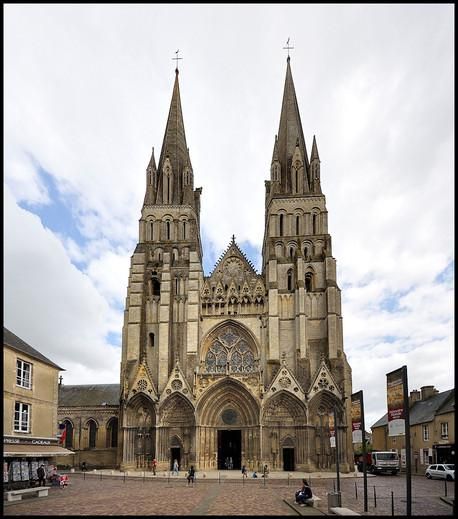
This immediately reminded us of places like the west door of Lincoln Cathedral.
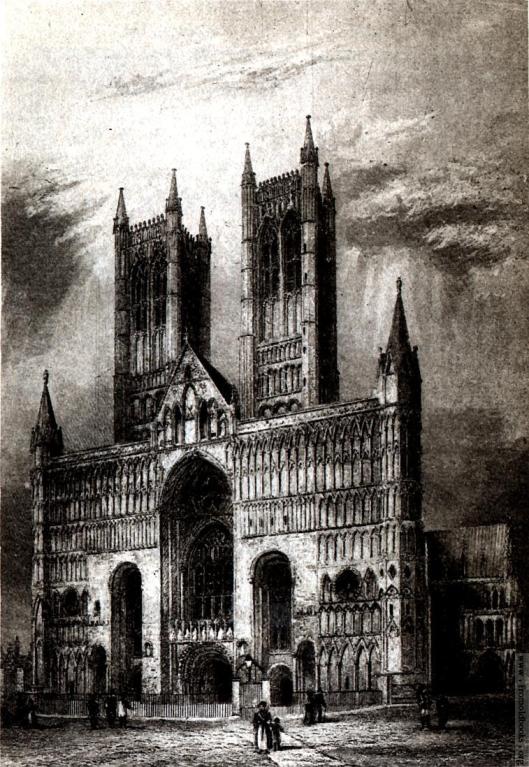


Or the main door of the cathedral of Palermo.


Because he is now a member of the Guard of the Tower of Gondor, Pippin is allowed to pass through the Gate—and to take Bergil with him out to see and hear the following:
“Beyond the Gate there was a crowd of men along the verge of the road and of the great paved space into which all the ways to Minas Tirith ran. All eyes were turned southwards, and soon a murmur rose: ‘There is dust away there! They are coming!’
Pippin and Bergil edged their way forward to the front of the crowd and waited. Horns sounded at some distance, and the noise of cheering rolled towards them like a gathering wind. There was a loud trumpet-blast, and all about them people were shouting.” (The Return of the King, Book Five, Chapter 1, “Minas Tirith”)
What happens then is a kind of parade.
When we see the defenders of Minas Tirith in the films, they are all uniformly clad.

In our medieval world, this was highly unlikely, the best being that soldiers and servants might wear the colors/crest of the lord they served. This was called “livery”. Uniformity in clothing, weapons, and armor would be some time in the future.

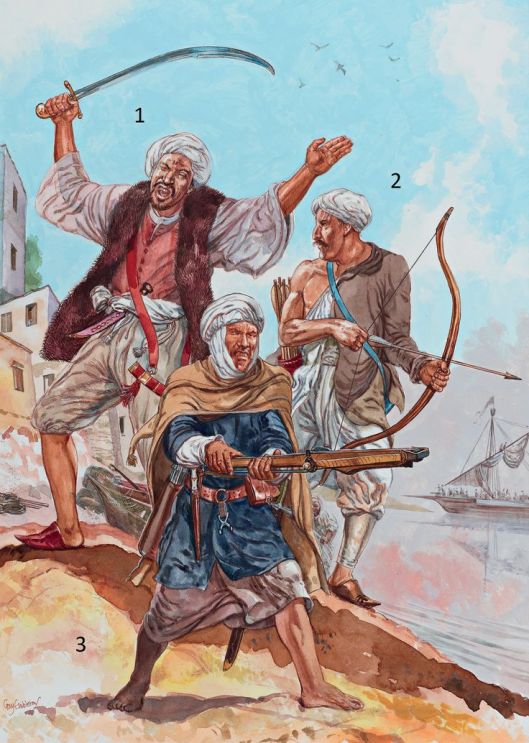
What is coming up the road from the south are reinforcements, marching in a long column of units, and those units differ greatly in look. First are the men of Lossarnach, led by their lord, Forlong:
“Leading the line there came walking a big thick-limbed horse, and on it sat a man of wide shoulders and huge girth, but old and grey-bearded, yet mail-clad and black-helmed and bearing a long heavy spear. Behind him marched proudly a dusty line of men, well-armed and bearing great battle-axes; grim-faced they were, and shorter and somewhat swarthier than any men Pippin had yet seen in Gondor.”
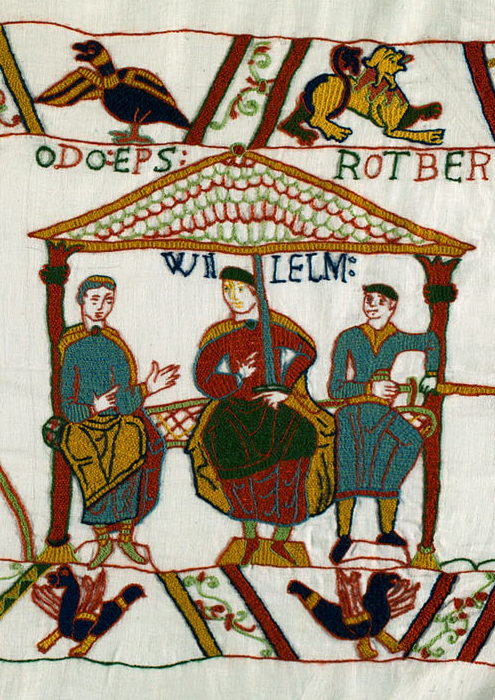
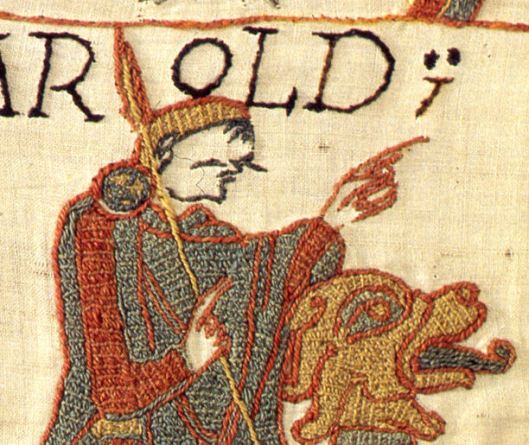
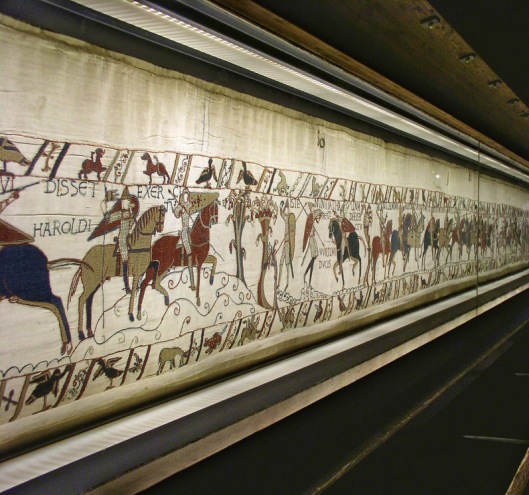
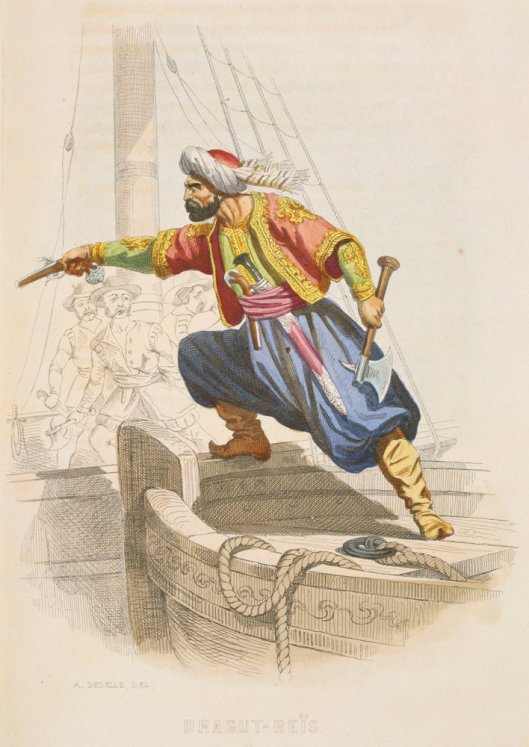
To us, those axes make the men of Lossarnach sound like the huscarls, the bodyguard of an Anglo-Saxon king, like Harold Godwinson, whom we see depicted on the “Bayeux Tapestry”.


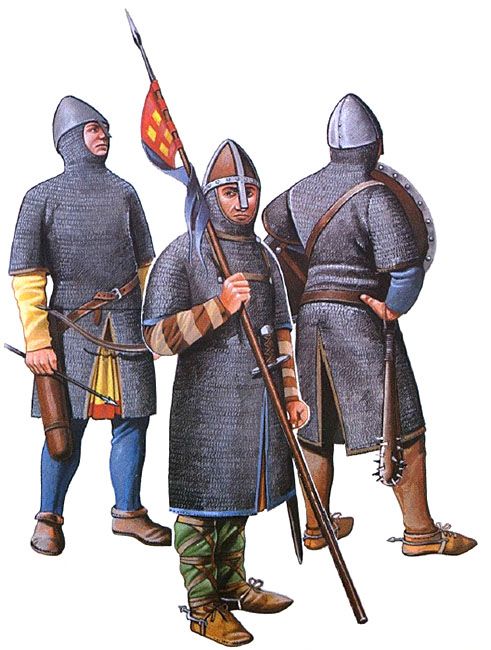
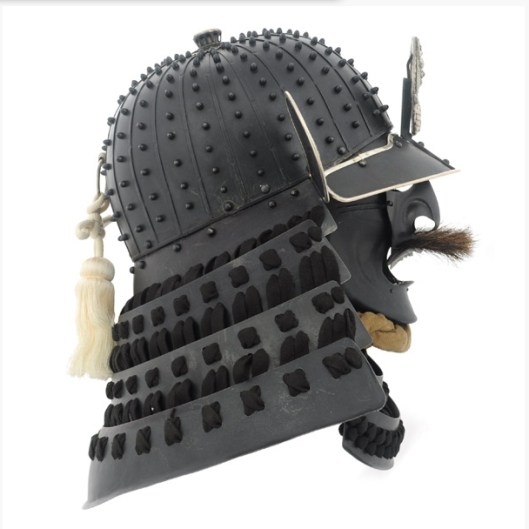
Their leader, Forlong, might be similar in appearance, wearing a type of helmet called a spangenhelm,
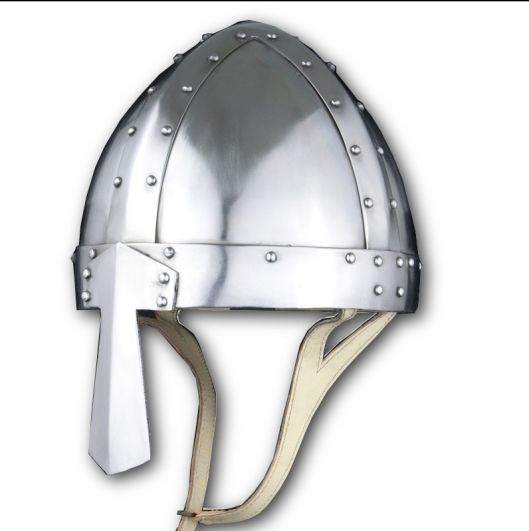

and protected by an early form of mail shirt called a hauberk.

After these, we see more units, but with little description—the men of Ringlo Vale “striding on foot”, so infantry of some sort, five hundred bowmen from Morthond, from the Langstrand, “a long line of men of many sorts, hunters and herdsmen and men of little villages, scantily equipped save for the household of Golasgil their lord”. After them, “a few grim hillmen without a captain”, and “fisher-folk of the Ethir”, all of which we imagine in their workaday clothes of hunters and shepherds and farmers and sailors, as depicted in medieval English and French manuscripts.




Next comes a unit which is perhaps wearing livery: “Hirluin the Fair of the Green Hills from Pinnath Gelin with three hundreds of gallant green-clad men.” We aren’t told how they’re armed, but that they may be in livery suggests that they may be better armed than some of the earlier contingents. (In fact, “gallant green-clad men” makes us think of Robin Hood—perhaps more archers?)

And, finally, folk we’ve discussed before:
“And last and proudest, Imrahil, Prince of Dol Amroth, kinsman of the Lord, with gilded banners bearing his token of the Ship and the Silver Swan, and a company of knights in full harness riding grey horses; and behind them seven hundreds of men at arms, tall as lords, grey-eyed, dark-haired, singing as they came.”
“knight in full harness”, as we talked about in an earlier post, probably meant, to JRRT, something from Howard Pyle or NC Wyeth, like this—
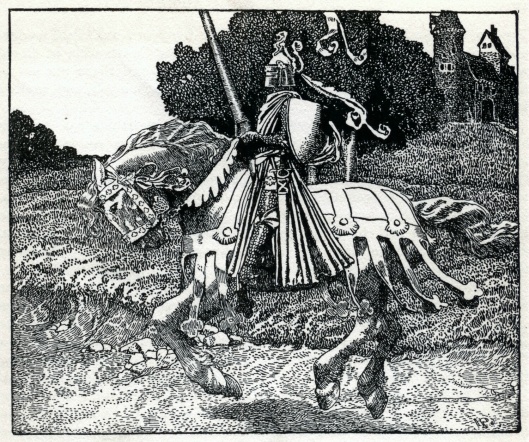
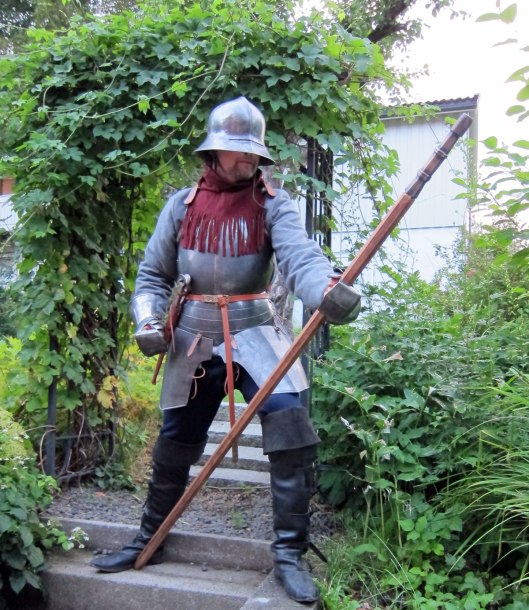
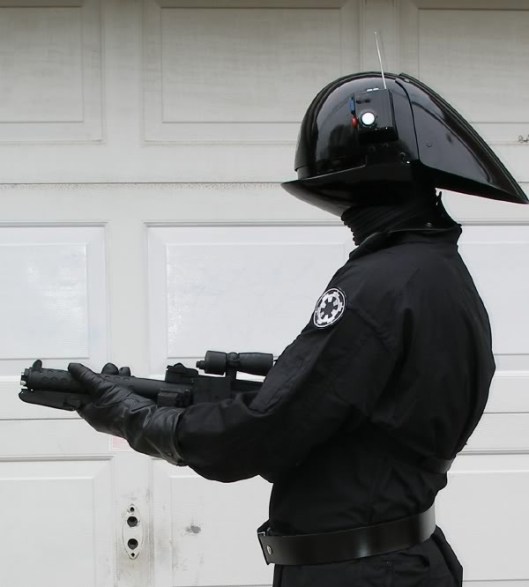
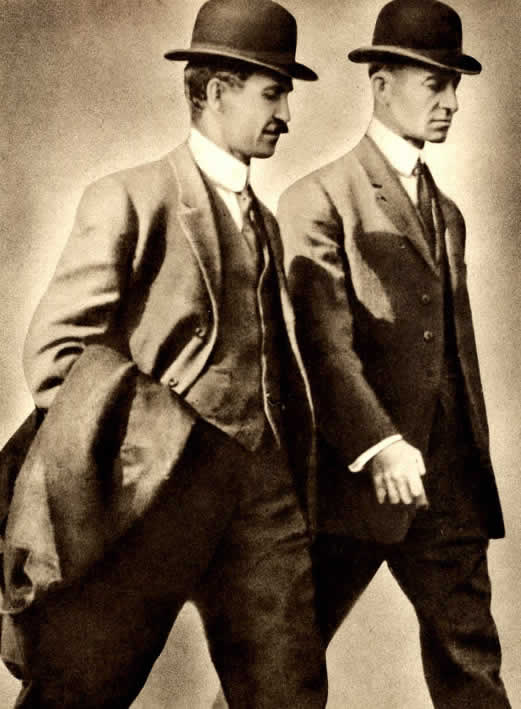
As for those “men at arms”, if they appear to be “tall as lords”, we assume that they’re on foot, which puzzles us a bit. “Men at arms” usually means “armored soldiers on horseback” in our world—perhaps with less armor than knights, but still cavalry (unless dismounted, to fight on foot, as the French did at Agincourt in 1415, for example). We see them, then, as looking like those dismounted cavalry, like these—

However they are armed and clothed, however, they are thought to be too few by those watching and, considering what Mordor eventually sends against them, they would not have been enough, if the brave Rohirrim and Aragorn’s reinforcement from the south hadn’t arrived in time. What would have happened if they hadn’t? A subject for very grim fan-fiction!
Thanks, as ever, for reading!
MTCIDC
CD