Tags
Anglo-Saxon, Battle of Hastings, Bayeux Cathedral, Bayeux Tapestry, Bishop of Bayeux, Edward the Confessor, Harold Godwinson, Lambert Leonard-Leforestier, Louvre, Musee Napoleon, Napoleon, Normans, Odo, Odo Earl of Kent, Old English Hexateuch, Rohan, Rohirrim, The Lord of the Rings, Tolkien, Tower of Babel, William Duke of Normandy, William the Conqueror
Welcome, dear readers, as ever.
In our last, we quoted JRRT on the subject of the Rohirrim:
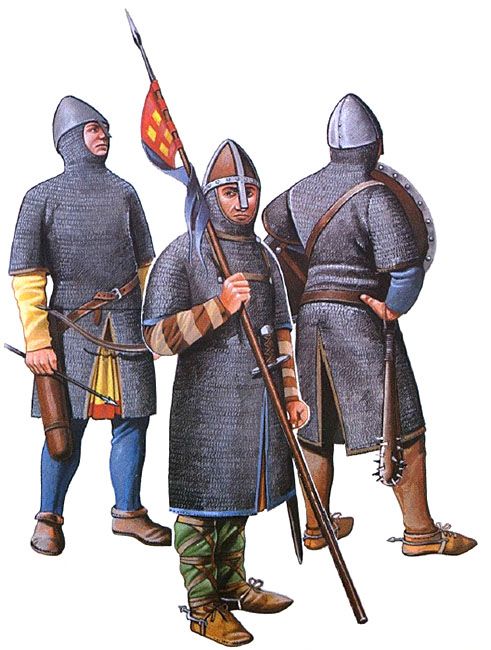
“The styles of the Bayeux Tapestry (made in England) fit them well enough, if one remembers that the kind of tennis-nets [the] soldiers seem to have on are only a clumsy conventional sign for chain-mail of small rings.” (Letters, 281)
We’ve mentioned the so-called Bayeux Tapestry before and even shown an illustration or two, but we thought that it would be fun to delve a little deeper into the subject—beginning with its name and why Tolkien added “(made in England)” to his sentence.
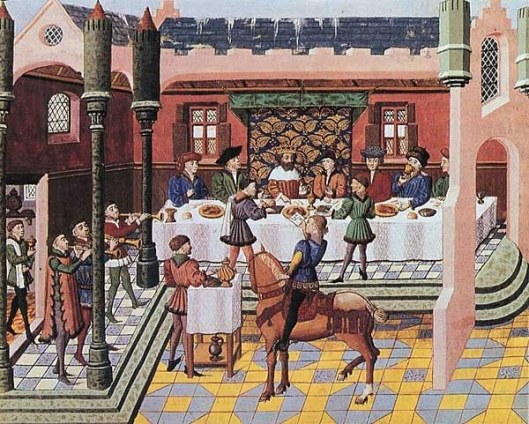
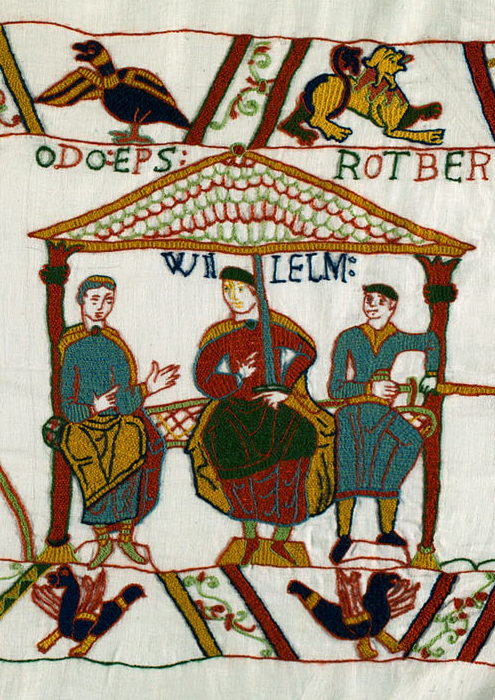
The first known reference to this approximately 230-foot-long (70.1 meters) by 20 inch high (.5m) piece of fabric dates from the latter part of the 15th century AD, from an inventory at Our Lady of Bayeux Cathedral—commonly known in English as Bayeux Cathedral—in 1476. There has been much scholarly argument over its site of manufacture, but the evidence appears to us to identify the commissioner of the work as Odo, Bishop of Bayeux, and half-brother to William, Duke of Normandy (where Bayeux is situated), aka, “William the Conqueror”. Odo is depicted and identified three times on the piece, twice in more peaceful settings—once blessing a meal,

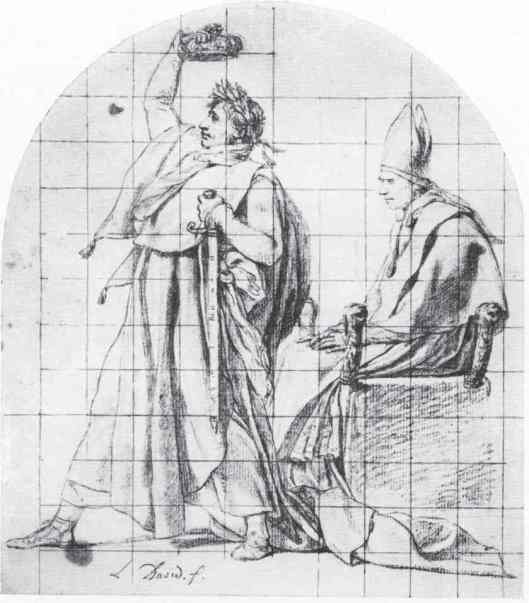
once sitting with William and his half-brother, Robert,

and once in a decidedly not peaceful setting, encouraging the troops at the Battle of Hastings, wearing a mail shirt and helmet and brandishing a club. (The Latin inscription—called a titulus—says “Here Bishop Odo, holding a club, puts strength into the lads”.)

As well, several of the figures on the piece have been identified as vassals (feudal allies) of Odo. Finally, Odo was not only the Bishop of Bayeux, but also instrumental in rebuilding the cathedral in which the artefact was first known to have been housed, Bayeux Cathedral (elements of which are buried inside this later Gothic version).
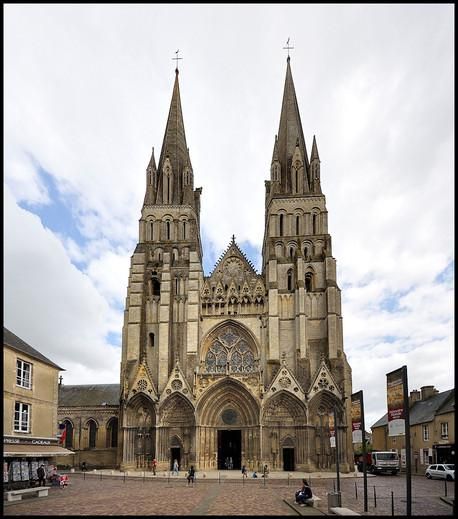

It seems natural to us, then, that he, at one time William’s right-hand man, would have been responsible for the creation of the work. (We might also add that the Norman victory made Odo Earl of Kent—one more reason for commissioning a work which shows that victory in detail.)
We said that there was argument as to where the work was made, but we, ourselves, would agree with JRRT and the idea that it was made in England for, among other reasons, the depiction of people and scenery on it remind us strongly of the Anglo-Saxon artistic tradition—especially embodied in the mid-11th-century manuscript of the “Old English Hexateuch”, with its 394 colored illustrations, which is to be found in the British Library (Cotton MS Claudius B. iv.).
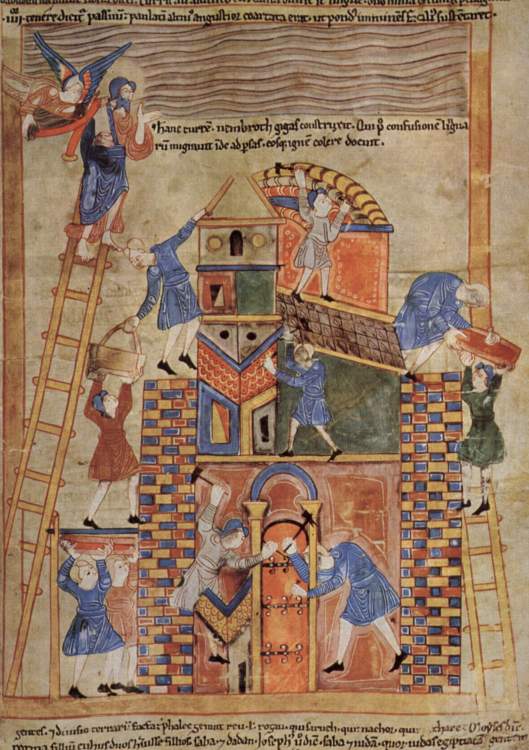

This is a depiction of the construction of the Tower of Babel. Below is a picture of Normans building ships for their invasion of England from the Bayeux work.

The Bayeux work is much sparer, but there’s that same interest in illustrating motion.
But, when we say that the Bayeux work is sparer, that is not to say that it lacks detail, as there are (at least) four visual levels throughout. If we take just one scene at random

and go from top to bottom we see:
- a narrow band of single figures—in this case, animals
- a broader band of action—in this case it’s Normans loading their equipment—and other things—for the attack on England (The titulus says: “These are carrying arms to the ships and here they are dragging a cart with wine and arms.”)
- the captions—tituli—for every scene
- a lower narrow band—again, here, animals, but there are other possibilities, as in this scene, where we see scavengers removing the arms and armor of the dead after the Battle of Hastings

The images in the “Old English Hexateuch” illustrate individual Bible stories. Those in the Bayeux work are scenes, all parts of a long historical narrative, which begins in 1064 (it is thought) with Edward the Confessor, the King of England,
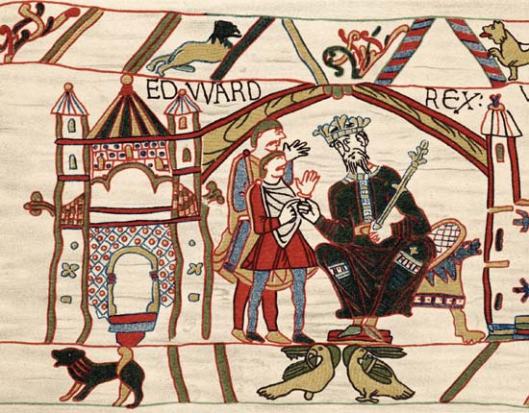

sending the powerful nobleman, Harold Godwinson, on what appears (from subsequent panels) to be a mission to France.
The last scenes, at the far end, include the death of Harold on the battlefield of Hastings

and the flight of the English from the field, with Normans in hot pursuit in October, 1066.

Throughout our discussion, we have avoided calling this work by its traditional name because, in fact, the “Bayeux Tapestry” is not a tapestry. A tapestry is a solid piece of fabric, woven on a loom.

The Bayeux Tapestry is really the Bayeux Embroidery, in which various designs are stitched onto a cloth.

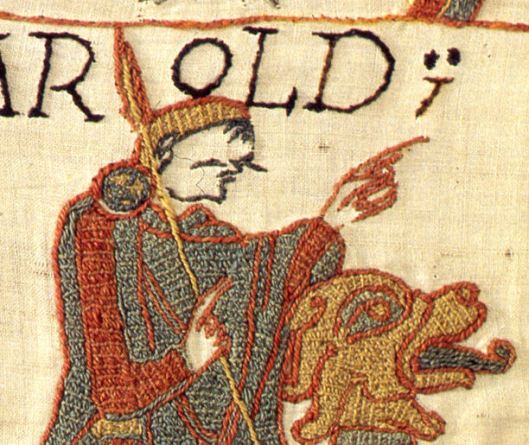
In this close-up, you can see how it’s done, with outlines giving the figures shape, as if they were drawn with a needle, then filled in. (For more on this, and on the work in general, try this LINK.)

For its size and detail and historical importance, there’s no embroidery like it from early medieval England, and perhaps from Europe, but there was one moment when it almost disappeared for good. During that period of the French Revolution when the Church (1% of the population which owned 10% of the land), was being nationalized (and plundered),

it was destined to be used for military wagon covers.

It was only saved at the last minute and shipped off to the Musee Napoleon (formerly—and subsequently—the Louvre).

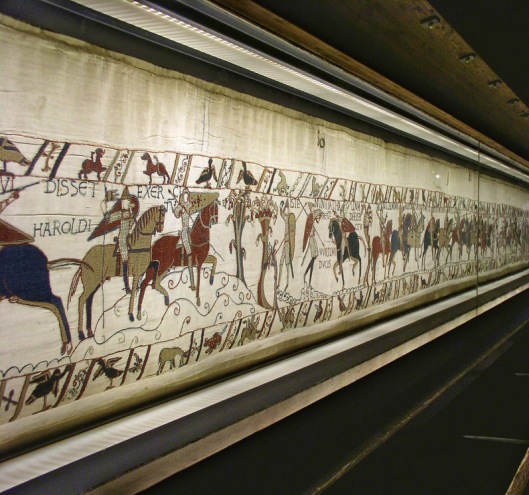
Eventually, it was returned to Bayeux where, today, it can be seen in a museum there, cleverly displayed in a way which allows the entire length to be viewed.


Without a member of Bayeux’ city council, Lambert Leonard-Leforestier, and his quick thinking, however, the last anyone might have seen of it would have been more like this—
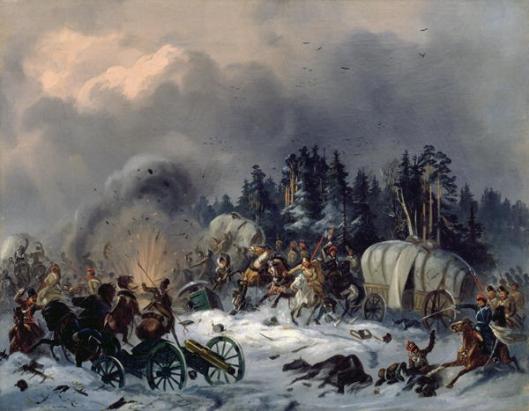

destroyed on wagons lost in Napoleon’s disastrous retreat from Russia.
Thanks, as ever, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD
PS
There is one more detail from the Bayeux Embroidery we’d like to mention. If you’re a fan of Game of Thrones, you might remember a passing comet. In fact, a passing comet—Halley’s Comet—appears on the Embroidery and, for people of the time, portended something big to come…

For more on Halley’s comet, here’s a LINK.