Welcome, as always, dear readers. In this posting, we’ll complete our survey of doors and entryways and what happens at them in The Lord of the Rings.
We began this series a little while ago when we got to thinking about Bilbo’s remark to Frodo that: “It’s a dangerous business, Frodo, going out your door.”
Bilbo had learned this the hard way when Gandalf had come to his door and he had embarked upon an adventure he, originally, had no desire to be part of.

In three postings, we’ve followed the story through doors and entryways from that moment all the way to the moment when Gandalf blocks the Lord of the Nazgul from entering Minas Tirith through its ruined main gate.

In the process, we have come to see that doors and entryways seem to come in two forms: first, there are doors which lead to safety; second, there are doors which lead to danger. We’ve added other elements, natural entryways, like fords and bridges, and the fact that many of the entryways have challenges and challengers barring the way.
In a moment of cheerful intellectual cruelty, we ended the last posting at that crucial moment in “The Siege of Gondor”, in which Grond, the battering ram of the armies of Mordor, has, with the magical aid of the Lord of the Nazgul, broken down the gate and that Lord is about to enter the city, when he meets Gandalf as the challenger:
“ ‘You cannot enter here,’ said Gandalf, and the huge shadow halted. ‘Go back to the abyss prepared for you! Go back! Fall into the nothingness that awaits you and your Master. Go!’ ”
And, just at that moment, “Great horns of the North wildly blowing. Rohan had come at last.”

[We wondered, by the way, if that “Great horns of the North wildly blowing” was an accidental or deliberate allusion to a lyric from Alfred Lord Tennyson’s

poetic criticism of the idea of women’s education, The Princess (1847),

in which we find the line “The horns of Elfland faintly blowing”—here’s the whole poem:
from The Princess: The Splendour Falls on Castle Walls
The splendour falls on castle walls
And snowy summits old in story:
The long light shakes across the lakes,
And the wild cataract leaps in glory.
Blow, bugle, blow, set the wild echoes flying,
Blow, bugle; answer, echoes, dying, dying, dying.
O hark, O hear! how thin and clear,
And thinner, clearer, farther going!
O sweet and far from cliff and scar
The horns of Elfland faintly blowing!
Blow, let us hear the purple glens replying:
Blow, bugle; answer, echoes, dying, dying, dying.
O love, they die in yon rich sky,
They faint on hill or field or river:
Our echoes roll from soul to soul,
And grow for ever and for ever.
Blow, bugle, blow, set the wild echoes flying,
And answer, echoes, answer, dying, dying, dying.
This then formed the basis of an 1870 play by W.S. Gilbert, which he converted, with his collaborator, Arthur Sullivan, into an operetta, in 1884.]


For the Aragorn and company half of the story, we see the arrival of the army of Gondor and its allies at the Morannon as the last door.

Here, there are, in fact, two challengers/challenges. First,
“When all was ordered, the Captains rode forth towards the Black Gate with a great guard of horsemen and the banner and heralds and trumpeters…They came within cry of the Morannon, and unfurled the banner, and blew upon their trumpets; and the heralds stood out and sent their voices up over the battlement of Mordor.” (The Return of the King, Book 5, Chapter 10, “The Black Gate Opens”)
In return,
“There came a long rolling of great drums like thunder in the mountains, and then a braying of horns that shook the very stones and stunned men’s ears. And thereupon the door of the Black Gate was thrown open with a great clang, and out of it there came an embassy from the Dark Tower.”
In both cases, it goes without saying that this is a door to danger, the difference being that those from Gondor want those within to come out so that, by defeating them (though they have little hope of this), those from Gondor can enter, while those within the gate want to prevent their entry (except, perhaps, as prisoners).
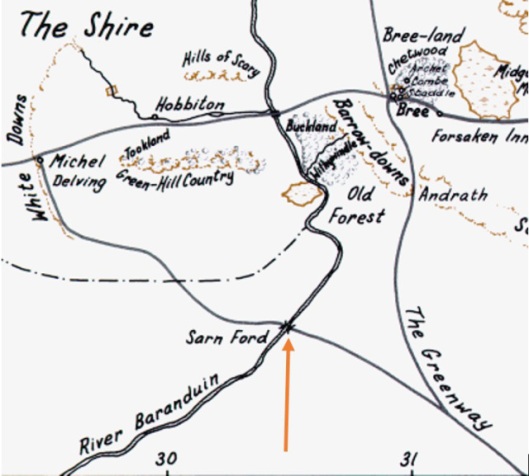
As we turn to the other half of the narrative, we begin at the same gate, where Gollum has brought Frodo and Sam.

Here, there is no easily visible challenger, just the forbidding nature of the gate, but it is still not an entryway to safety, as, on the other side is an inhospitable landscape, populated by Sauron’s vast armies, constantly on the move, as we see in later chapters. As well, from those later chapters, we gain the sense that Frodo doesn’t believe he’s going to return from Mordor anyway.
Seeing no way to enter, Frodo pushes Gollum to lead them south and, with a diversion to Faramir’s base behind a waterfall (which, to us, is reminiscent of a similar hide-out in James Fennimore Cooper’s The Last of the Mohicans (1826)

—and how can we resist mentioning that, in 1919, N.C. Wyeth illustrated an edition?)


they arrive at the southern entryway to Mordor, the pass with Minas Morgul at its western end and Cirith Ungol at its eastern.


The challengers of Minas Morgul are the Lord of the Nazgul and a vast army, on their way to attack Minas Tirith, but these are skirted, as Gollum guides the two hobbits around the site and up on a perilous climb—and into Torech Ungol, Shelob’s Lair. Safety? Gollum wants the hobbits to think so. Danger? With Shelob as a challenger, what else?

Even as Sam drives Shelob off, however, he loses Frodo, paralyzed and cocooned, and is faced with an inner door closed by the orcs as they withdraw. Climbing over it, he moves forward, cloaked by the ring, to look out towards Orodruin and the Tower of Cirith Ungol.

And, with this, we have finished our survey.
Unless, of course, we consider two more events.
First, there is what happens at Mount Doom, where Gollum is the challenger, and the door, such as it is, leads to safety for Middle-earth, but not for Sam and Frodo.

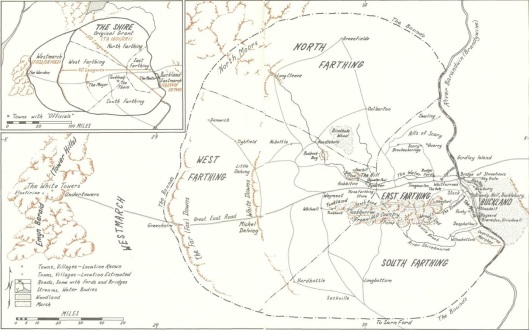
And, finally, at the edge of the Shire, in “The Scouring of the Shire”, where the returning hobbits meet with the followers of “Sharkey” at the bridge. Those followers, brain-washed by fear of “The Chief” and his “big man” followers, attempt to deny what should be a door to safety to Frodo, Merry, and Pippin, as the three had expected, but which leads, in fact, to conflict and open violence before their return home is safely accomplished.

With that, we complete the pattern and here is our chart:
| Entryway |
Source |
Challenger |
Challenged |
Outcome |
| Bilbo’s door |
The Hobbit |
Bilbo |
Dwarves |
Bilbo is tricked into hospitality |
| Beorn’s house |
The Hobbit |
Beorn |
Gandalf |
Beorn tricked into hospitality |
| Goblin cave |
The Hobbit |
Goblins |
Bilbo |
Escapes by use of the Ring |
| Mirkwood |
The Hobbit |
Elves |
Dwarves/Bilbo |
Bilbo rescues dwarves with Ring and barrels |
| Lonely Mountain (Back door) |
The Hobbit |
Smaug |
Dwarves/Bilbo |
Understanding the inscription, Dwarves open the door |
| Lonely Mountain (Front door) |
The Hobbit |
Dwarves |
Men, Elves, Goblins |
Battle of the Five Armies—eventual settlement |
| Bilbo’s door |
The Hobbit |
Hobbits |
Bilbo |
Bilbo’s things are up for auctions—Bilbo gets most things back |
| Ford of Bruinen |
The Lord of the Rings |
Wraiths |
Frodo/Elves |
After Frodo’s challenge, elf magic overwhelms wraiths |
| Moria (west gate) |
The Lord of the Rings |
Elves of Hollin |
Fellowship |
Gandalf discovers password—the group enters |
| Lothlorien (western side) |
The Lord of the Rings |
Elves |
Fellowship |
Challenged by elves, but allowed to enter |
| Edoras |
The Lord of the Rings |
Rohirrim |
Gandalf et al. |
Challenged by gate guards, but allowed to enter |
| Meduseld |
The Lord of the Rings |
Hama |
Gandalf et al. |
Challenged, but allowed to enter |
| Helms Deep |
The Lord of the Rings |
Aragorn |
Orcs/Wildings |
Aragorn warns them of their danger |
| Isengard |
The Lord of the Rings |
Merry/Pippin |
Gandalf et al. |
Greeted and offered food, drink, and smoke |
| Paths of the Dead |
The Lord of the Rings |
Oath-breakers |
Aragorn at al. |
Allowed to enter, but followed—leave safely |
| Morannon |
The Lord of the Rings |
Sauron |
King Elessar et al. |
Sauron’s army appears for battle |
| Morannon |
The Lord of the Rings |
Sauron |
Frodo/Sam/Gollum |
No way of entry—the three head south |
| Minas Morgul |
The Lord of the Rings |
Lord of Nazgul |
Frodo/Sam/Gollum |
Entry blocked by Lord’s Army |
| Torech Ungol |
The Lord of the Rings |
Shelob |
Frodo/Sam |
Gollum escapes, Frodo paralyzed by Shelob |
| Cirith Ungol |
The Lord of the Rings |
Orcs |
Sam |
With Ring as aid, Sam enters |
| Mt. Doom |
The Lord of the Rings |
Gollum |
Frodo |
Gollum gains Ring, but perishes in fire |
| Shire bridge |
The Lord of the Rings |
Hobbits |
Frodo et al. |
Hobbits climb over gate, guards run |
Because this material becomes increasingly complex, there is always the possibility that, as thorough as we try to be and as inclusive, we’ve missed something. If so, we’d be glad to hear from our readers!
Thanks, as always, for reading!
MTCIDC
CD
























































































































 )
)


































































