Tags
advised by elves, Aelfraed, Aethelwulf, Alaric Hall, Alfred, Alfred of Wessex, Alfred the Great, Anglo-Saxon, Aragorn, Boudicca, council, Counseling the Scippigraed, Danish invaders, Elder Days, Elves, Elves in Anglo-Saxon England, Frodo, Galadriel, Gildor Inglorion, Grey Havens, Hamo Thornycroft, Hobbits, Mirror of Galadriel, Morgul Knife, Shire, statue, T. A. Shippey, The Council of Elrond, The Lord of the Rings, Tolkien, Tolkien in the New Century, Tom Shippey, With Faerstice
Welcome, dear readers, as ever. In this posting, our attention was caught by the first paragraph of an article in Tolkien in the New Century: Essays in Honor of Tom Shippey (McFarland, 2014). The article, entitled, “Counseling the Scippigraed: How T.A. Shippey Taught Us to Read”, by John R. Holmes, begins:
“The Christening of Alfred Aetheling of Wessex in 849 may have played a role in his greatness. Alfred’s father, Aethelwulf, had wanted to establish his own name-prefix, Aethel, which means (more or less) “noble,” as the sign of the royal line: he gave it to his first four sons and a daughter. By the time his sixth child came along, however—his fifth son—there didn’t seem to be any point in giving him the Aethel- prefix, since there seemed to be no reasonable chance this infant could ever become king. But wishing the lad wisdom and happiness, Aethelwulf named him Aelfraed, “advised by elves.” While we have no historical proof that Alfred actually received counsel from elves, there is no evidence to the contrary, and the boy certainly prospered as if he had. Alfred, Elf-counsel, not only outlasted four older brothers to become king, but also would be the only English monarch known to history as “The Great”. “ (11)
Alfred, king of Wessex from 871-899, was perhaps the most distinguished ruler of pre-Norman England. Against heavy odds, he eventually stabilized Wessex against a powerful wave of Danish invaders

and even forced the second Danish leader both into a treaty and into conversion to Christianity. As well, he was active in promoting Anglo-Saxon intellectuality and the rise of a vernacular literature.

(this statue, from 1901, by the way, was done by Hamo Thornycroft, the son of the man who did the famous Boudicca plus chariot statue on the Thames embankment—erected 1902, but created much earlier–)

For us, however, what was interesting was none of this, but rather the idea that it might be possible for someone in the 9th century AD to have the kind of contact with elves we see in The Lord of the Rings.

We have always imagined Elves as belonging to the Elder Days and that, eventually, like Elrond and Galadriel, they had all traveled to the Grey Havens and taken ship for the West.

Suppose, however, we said to ourselves, that, as JRRT suggests about hobbits, Elves continued to exist, even down into actual historical times:
“Hobbits are an unobtrusive but very ancient people, more numerous formerly than they are today…They do not and did not understand or like machines more complicated that a forge-bellows, a water-mill, or a hand-loom, though they were skillful with tools. Even in ancient days they were, as a rule, shy of ‘the Big Folk’, as they call us, and now they avoid us with dismay and are becoming hard to find. (The Lord of the Rings, “Prologue”)
Of elves, the actual Anglo-Saxon people of the period don’t appear to have much good to say, in fact. The 11th-century recipe, called the With Faerstice (“Against a Stabbing Pain”), suggests that elves were dangerous and, should they attack you, it required serious medical treatment, including what looks like a magic spell, to cure you of the wound, which was made by something which reminded us of the tip of the Morgul Knife broken off in Frodo’s wound.

Even in Middle-earth, Elves aren’t considered to be the most direct of people, however, as Frodo quotes:
“ And it is also said…’Go not to the Elves for counsel, for they will say both no and yes.’ “
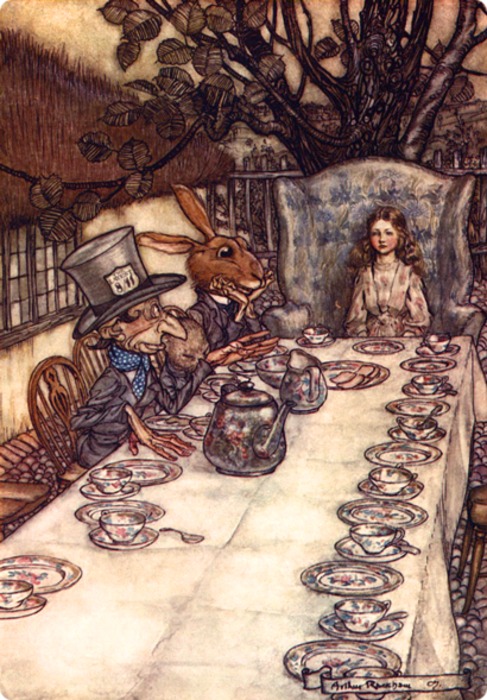
And yet, in this scene, from The Fellowship of the Ring, Book 1, Chapter 3, “Three is Company”, in which Frodo, Sam, and Pippin fall into the company of Elves,

their leader, Gildor Inglorion, does offer advice and the way he frames it might provide us with a model for how Alfred could have been counseled.
To begin, we might picture the elves as being unimaginably older than the Anglo-Saxons, and, with that age, having a longer view of things. As Gildor says to Frodo, when Frodo says, “I knew that danger lay ahead, of course; but I did not expect to meet it in our own Shire.”:
“But it is not your own Shire…Others dwelt here before hobbits were; and others will dwell here again when hobbits are no more. The wide world is all about you: you can fence yourselves in, but you cannot for ever fence it out.”
Great age, then, can lend great perspective. When you’ve lived as long as the Elves, you have seen much more of change within time, and what concerns them might be very different from what engages humans, as Gildor tells Frodo:
“The Elves have their own labours and their own sorrows, and they are little concerned with the ways of hobbits, or of any other creatures upon earth. Our paths cross theirs seldom, by chance or purpose.”
So what would be the kind of raed (“advice/counsel”) which the elves would have given Alfred? we asked ourselves. It’s easy to imagine his approach: often, particularly in the early years of his kingship, Alfred was faced with defeat. The Danes were numerous, powerful, and unscrupulous, once even killing hostages after swearing to a peace agreement. His question might then have been: how can I beat the Danes and regain my kingdom?
The elves would have been cautious, of course. Gildor says:
“Elves seldom give unguarded advice, for advice is a dangerous gift, even from the wise to the wise, and all courses may run ill.”
This is spoken by someone who has many centuries of experience behind him, as would an elf advising Alfred. Time and its changes had clearly taught the Elves both caution and patience and we imagine that those two elements would have been the basis of a reply—and, in fact, it appears to have been Alfred’s method, as we learn from the first biography, by Bishop Asser, a contemporary, who was asked by Alfred to join his court. Rather than seek victory in one climactic battle, had that been possible, Alfred attacked the problem from multiple angles, doing things which not only contributed to the Danish defeat (and to the defeat of a subsequent invasion), but also strengthened the kingdom in general, changing and improving the tax and military systems, building the first English navy, as well as producing a law code and encouraging education in Anglo-Saxon. This method brought peace and stability to Wessex (much of southern England), but did so over the period of twenty years or more, suggesting to us that the counsel of elves had surely been at work.
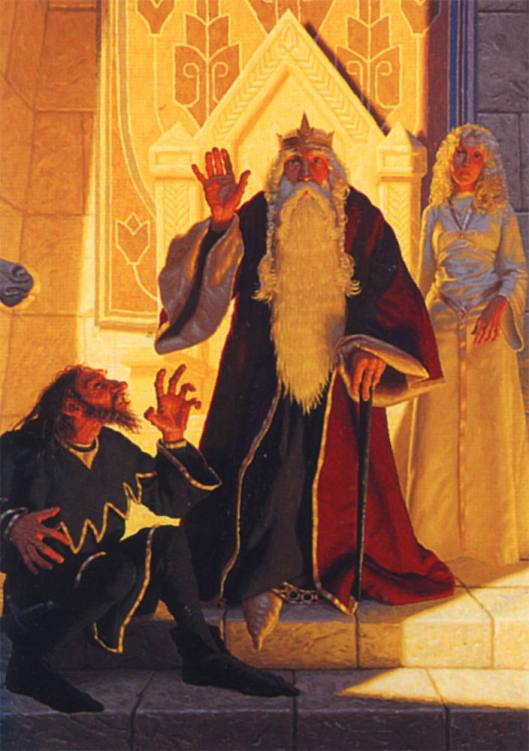
When we picture the scene of Alfred receiving the elves’ advice, we think of this Hildebrandt painting of Galadriel and Aragorn.

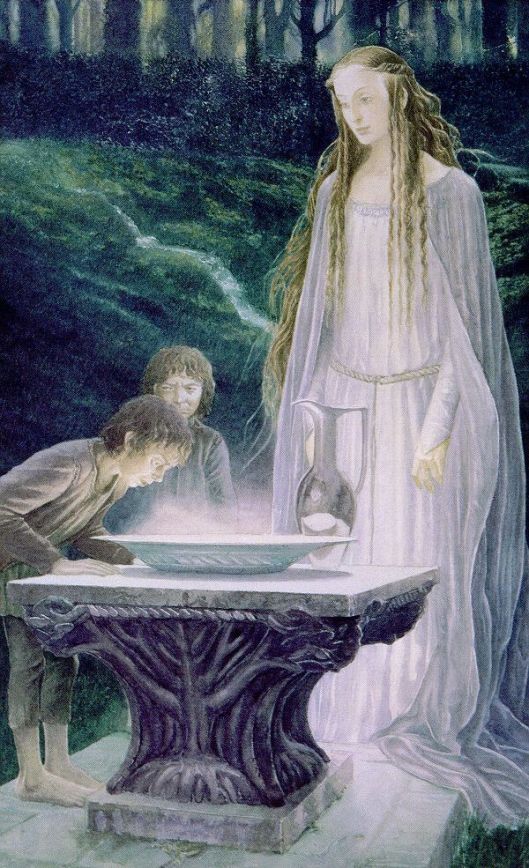
And perhaps those elves said the same thing to Alfred which Galadriel said to Frodo before her mirror:
“ ‘Do you advise me to look?’ asked Frodo.
‘No,’ she said, ‘I do not counsel you one way or the other. I am not a counsellor. You may learn something, and whether what you see be fair or evil, that may be profitable, and yet it may not. Seeing is both good and perilous. Yet I think, Frodo, that you have courage and wisdom enough for the venture, or I would not have brought you here. Do as you will!’ “ ( The Fellowship of the Ring, Book 2, Chapter 7, “The Mirror of Galadriel”)
In Alfred’s case, he would have been brave and wise enough, and therefore has come down to us both as “Alfred the Great” and as “Alfred Elf-counsel”.

Thanks, as always, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD
PS
If you are interested in knowing more about Anglo-Saxon attitudes about elves, we very much recommend Alaric Hall’s Elves in Anglo-Saxon England which is, miraculously, available for free on-line.