Tags
Alan Lee, Allen and Unwin, Angus McBride, casting, forging, Home Alone, literary belief, literary theory, The Lord of the Rings, The One Ring, Tolkien
Dear Readers,
Recently, one of us came up with an interesting question about our friend JRRT and the One Ring: how would such a small thing with such power have been made? In The Silmarillion, Tolkien, as he so often does, has an answer for this:
“And much of the strength and will of Sauron passed into that One Ring… and Sauron forged it in the Mountain of Fire in the Land of Shadow” (The Silmarillion, 287-288).
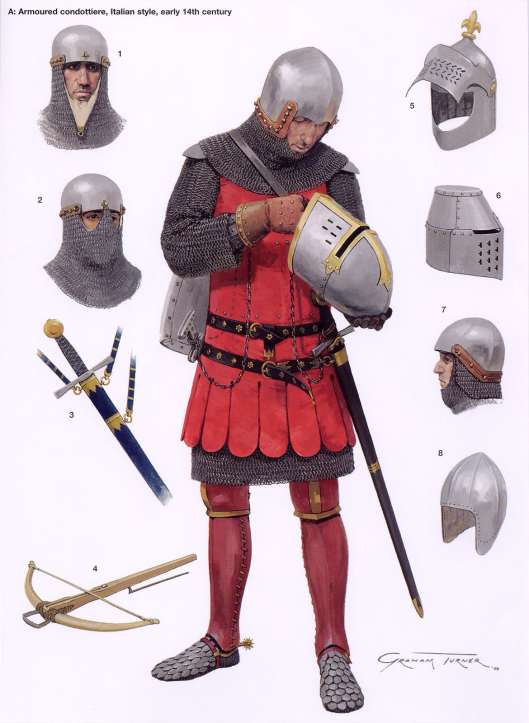
In the histories of Middle-earth, Sauron is said to have “made” and “forged” the One Ring—JRRT uses both words more than once in his letters, LOTR, and The Silmarillion, and this has led us to another question: how would the Ring have been forged? We did a little research, and found that the typical process of forging is (according to the ever-useful wiki page on the subject) a manufacturing process using compressive forces, such as a hammer, to shape metal in a particular way. If Sauron “forged” the One Ring in the fires of Mount Doom, it’s safe to assume that he used the process of “hot forging”, where the metal is heated in a forge (or in this case, very hot fires of a volcano). The last two items of wiki’s “commonly forged” list are weapons and jewelry—both on the list of Middle-earth’s most wanted Christmas gifts of 3018—and we’ve seen weapon-forging before:

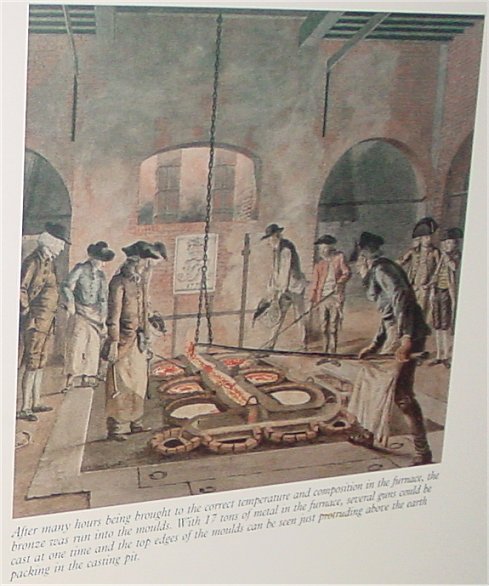
But rings are usually cast, using a mold and molten metal. Peter Jackson’s prologue to The Fellowship of the Ring acknowledges this, although the Ring is still said to have been “forged”:

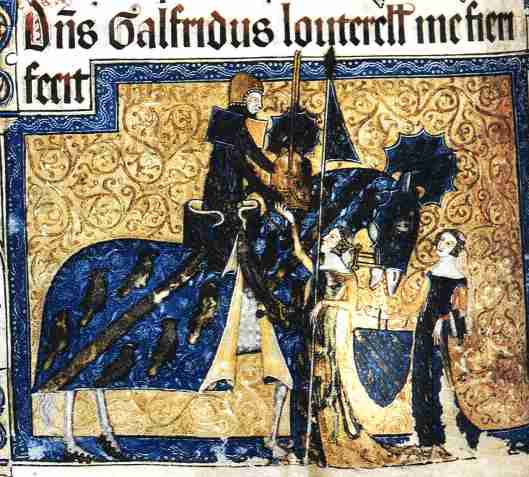
But, in the illustrations of Tolkien illustrators Alan Lee

And Angus McBride

This detail—perhaps even an error on Tolkien’s part—has been overlooked. Is it that the artists have made the same error, or are they simply letting it go in favor of the story?
From here, we can ask several questions: what material was the Ring made of? Where did he get the material? How did Sauron make it a magic ring? How did he get the Black Speech/Elvish inscription onto the Ring?
While there may be one or several answers to these questions, we wonder just how far into detail we’re meant to go—and how far JRRT means for us to go. He created a world so intricate that his work has been named a “legendarium”, and in several previous postings, we’ve discussed details of Middle-earth, such as trade and coinage. Could the man who took such care to design Middle-earth’s moon phases have answers to these questions—or should he?
(And here, for those who know the movie Home Alone, we hope not to sound like the little boy from across the street who asks the van driver endless, empty questions!)
The concept of the One Ring begins in Gollum’s cave in The Hobbit. At that point, it was only a magic ring, serving the purpose of a plot device: JRRT had not yet planned a sequel to The Hobbit. In fact, the magic ring was not yet the One Ring in Tolkien’s stories until after JRRT published the book.
Tolkien said himself of the matter in his Letters:
“The Hobbit… was quite independently conceived: I did not know as I began it that it belonged.”(Letters, 145)
And, of the Ring:
“Rayner has, of course, spotted a weakness (inevitable): the linking. … But I don’t feel worried by the discovery that the ring was more serious than appeared… the weakness is Gollum, and his action in offering the ring as a present.” (Letters, 121)
This was a response to publishers Allen and Unwin; Rayner (Unwin’s son) had read the story and commented to the author:
“…. Converting the original Ring into this new and powerful instrument takes some explaining away and Gandalf is hard put to it to find reasons for many of the original Hobbit’s actions…” (letters, 120)
Nowhere in his criticism does Rayner ask what the Ring was made of, how Sauron had made the Elvish script, or how it would have been either forged or cast, and neither does JRRT in his answer; their focus is placed upon converting the magic ring into the One Ring, and using the Ring as a crucial plot element in both The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings. Tolkien writes in another letter:
“The magic ring was the one obvious thing in The Hobbit that could be connected with my mythology. To be the burden of a large story it had to be of supreme importance. I then linked it with the (originally) quite casual reference to the Necromancer…” (Letters, 346)
Although Tolkien’s work provides a great richness of material to discuss, question, and write about, we suppose that we can forgive JRRT for this small detail. Then again, when JRRT gives us so much, when should we stop asking questions or expecting answers? As we’ve found in writing these postings, JRRT seems to have an inexhaustible amount of material, although even he sets limits to the interpretation of his work; in fact, these “hidden meanings” annoyed him:
“I am honoured by the interest that many readers have taken in the nomenclature of The Lord of the Rings… But I remain puzzled, and indeed sometimes irritated, by many of the guesses at the ‘sources’ of the nomenclature, and theories or fancies concerning hidden meanings… many of them seem to show ignorance or disregard of the clues and information which are provided in notes, renderings, and in the Appendices” (Letters, 379-380).
We don’t believe that this was meant to be a discouragement. Instead, it is a pointing by the author towards the extra material meant to help his readers to understand and study what Tolkien says he wishes he’s achieved: “the ‘literary belief’ in the story as historical” (Letters, 279).
But this leaves us at another crossroads.
If the answers aren’t to be found there, however, should we stop? We’ve said that we’re haunted by the image from Home Alone: if we persist, should we be cast in Home Alone 4 as two kids, pestering the English academic with “So how was this Ring really made, mister? Is it really made of gold? Is it really powerful? How powerful? For how long?”
Or should we leave those details about the Ring as they are, accepting that it’s a magic ring forged in the fires of Mount Doom by Sauron—without interrupting JRRT to ask too many questions about details which aren’t essential to the story, believing that it is more important that he masterfully took a simple plot element—a magic ring—and focused on converting it into the crucial element of Frodo’s quest in The Lord of the Rings.
As always, we ask: what do you think, Dear Readers?
Thanks for reading,
MTCIDC,
CD