Tags
1909 penny, Abraham Lincoln, Alexander the Great, Aragorn, Asia Minor, Augustus, bartering, Bilbo's birthday, British Royal Government, Brutus, Charlemagne, Classical Greek coins, Cleopatra VII, Coinage, daggers, Denethor, Domitian, Egypt, federal law, Frankish king, freedman, George Washington, Gondor, Greek Kings, Hanoverian kings, Hellenistic Greeks, Holy Roman Emperor, Ides of March, Julio-Claudian dynasty, Julius Caesar, libertus, Lucius Plaetorius Cestianus, Lydia, manumission, Middle-earth, Pennies, pilleum, Plebeians, portrait, Prince Charles, Ptolemy I, Queen Elizabeth II, Roman Empire, Romans, Seleucus, Senatus Consulto, The Lord of the Rings, Tolkien
Welcome, dear readers, as always.
We are veering a little to the left in this posting inspired by a comment on “Shire Portrait (2)” from our good friend, EMH. It was about currency and coins in Middle-earth and we were a little vague, but E pointed out:
- Bilbo giving “a few pennies away” before the party
- the price of Bill, the pony: “twelve silver pennies”
- Gandalf praising Barliman and saying his news was “worth a gold piece at the least.”
With E in mind, we decided to do another posting on M-e money. Long ago, we did a posting on imagined currency in Middle-earth, but, since then, we’ve thought a bit more about the subject, and, right now, dear readers, we ask you to produce a coin, any coin. As we live in the US, here’s a US coin, a fourth of a dollar, hence, a “quarter”.

This is the front, or “obverse” in coin speech, and we’re going to focus on that and not on the back (the “reverse”). We use coins all day long every day, so we probably don’t look at them more than to note value when we pay for something or receive change, but let’s look at this one a bit more closely.
It seems pretty simple:
- at the top a single word, “Liberty”
- then a low relief (that is, cut very shallowly) portrait of the first president, General George Washington
- then, to the left, a slogan, “In God We Trust”
- at the bottom, the date, 1993
Let’s start with that date—1993. In 1993, the president was Bill Clinton.
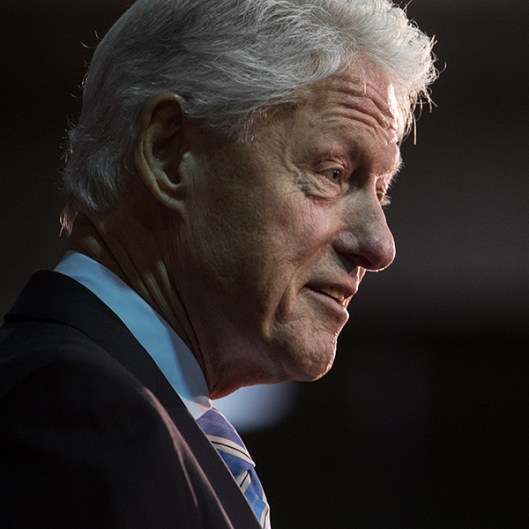

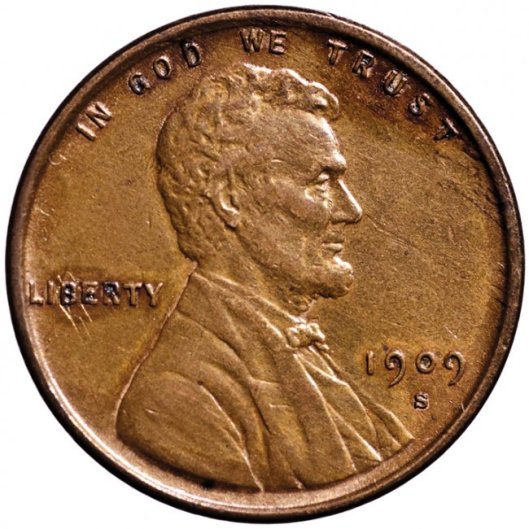
Federal law, however, prevents coins—with very special and rare exceptions—to bear the portraits of living people. The first president on a coin was Abraham Lincoln, on a penny first minted to commemorate his 100th birthday, in 1909.

The previous coin, up to 1909, had the idealized head of a Native American,
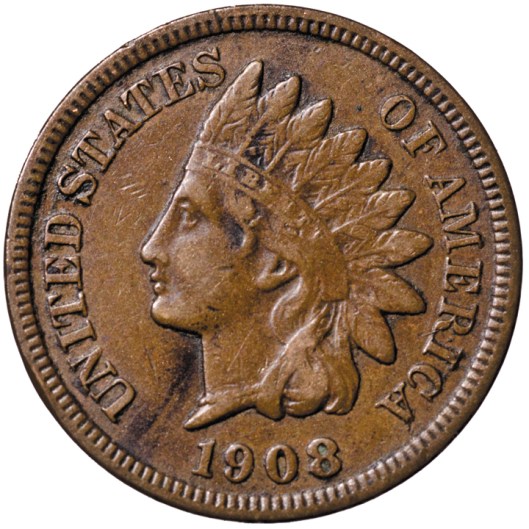

the pattern for which was first introduced in 1859.

The first coin in western European history is from the late 8th century BC, and comes from Lydia, in Asia Minor.

Classical Greek coins seem to model themselves on Lydian coins like this, having badges–city emblems and religious tokens, like the famous Athenian owl, rather than portraits of humans, like that quarter with George Washington on it.

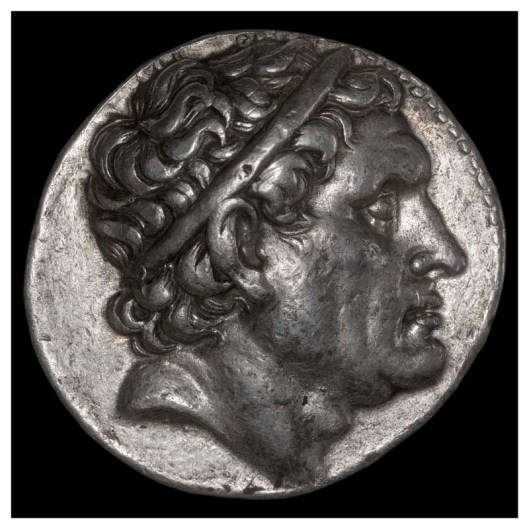
During the Hellenistic Period (post about 300bc and on), however, the Greek kings, from Greece to Asia Minor to Egypt, all began to issue coins with portraits of themselves. These were, initially, the generals of Alexander the Great, who, at Alexander’s death, had grabbed portions of his empire for themselves. We think of Seleucus, who controlled much of Asia Minor

Or of Ptolemy I,
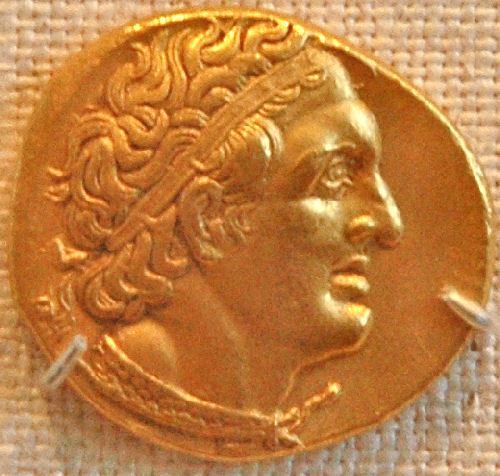

the founder of a dynasty which ruled Egypt for nearly 300 years until their final descendant, Cleopatra VII, was defeated by the Romans.

Those Romans, we imagine inspired by the Hellenistic Greeks, produced coins by the bushel .(this is an obsolete dry measurement, based upon what you can put into a basket like this:

which was, in fact, made up of four pecks

which could also be divided into two kennings of two pecks apiece.)
Considering that Rome produced coins from the late 4th century bc to late in the 5th century ad, it’s not surprising that there would be so many—and considering the size of the Roman empire, as well.

Earlier Roman coins had been unlike Hellenistic coins, however, in not depicting living people—that is, until Julius Caesar gained power.
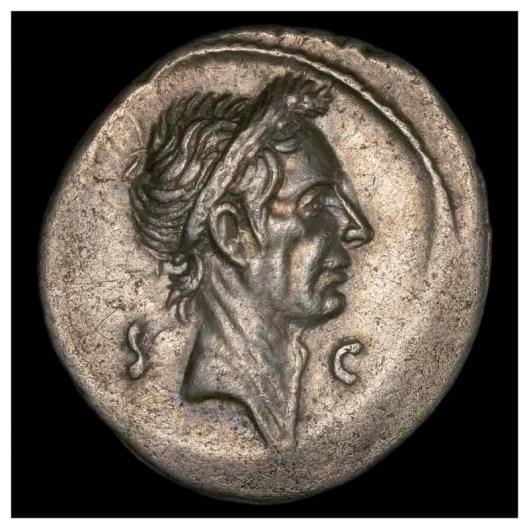

This opened the floodgates and it’s easy to see why.
Coins are short-hand wealth, originally standing in for earlier barter items, like flocks and herds.

As Romans spread out beyond farms and local markets, the wealth in animals and agricultural produce, as well as raw materials, was simply not portable enough, as this cartoon shows.

By making tokens which were accepted as a stand- in for that wealth, the agency which did so was asserting its claim to have a strong hand in, if not control of, the economy.
Julius Caesar, who had already forced the Senate to make him “Dictator for Life” (that “S…C” on both sides of his profile stands for “Senatus Consulto”—“by a decree of the Senate”), by putting his face on the currency is implying that he now is the state—and therefore possesses a power which extends to regulating the money economy by which people live and survive or prosper. (There may be a quiet joke here, as well. “SC” was stamped on bronze coins to guarantee their worth—on the back side—to have those letters surrounding Caesar on the front side, the obverse, may suggest a double meaning: he is dictator by Senatorial decree, but his worth is also being guaranteed by that decree.)
It is no surprise, then, that Brutus, one of those who murdered Caesar, would, in turn, issue his own coins—and these are even more heavily symbolic.

On the obverse, there is Brutus, his name above, to our right his title “imp[erator]”—a title given to a general by his soldiers with the implication “You rule!” To our left is an abbreviated form of the name of the moneyer, the man who directed the mint, L[ucius] Plaet[orius] Cest[ianus]. Although we said that we would only examine obverses, we can’t resist the reverse here. At the bottom is the inscription, “eid mar”, standing for “eides Martis”, the “Ides of March”, the 15th of March, the day Caesar was murdered. Above that is a “pilleum”, the kind of cap worn by a slave during the ceremony called “manumission”, in which a he was turned into a “libertus”, or “freedman”.

To both sides of the cap are daggers.

Put all of this together and we see Brutus’ claim: on the 15th of March, we murdered Caesar and, as a consequence, we freed Rome from its slavery.
Coins like Caesar’s and Brutus’ are simple in their claims. Later emperors were less so. Look at this coin of Domitian (81-96ad).

On the rim of the obverse is a pile of information:
Imp[erator] Caes[ar] Domit[ianus] Aug[ustus] Germ[anicus] P[ontifex] M[aximus] Tr[ibunicia P[otestas] VIII
“Emperor Caesar Domitianus Augustus Germanicus, Chief Priest of Rome, Holding the Power of the Representative of the People 8 Times”
In fact, Domitian was sailing under false colors—Caesar, Augustus, and Germanicus all belong to the earlier Julio-Claudian dynasty, of which his family was not a part. As for “Holding the Power of the Representative of the People”, this was an ancient elective office, which allowed a member of the lower class, the Plebeians, special powers in the legislative process. As emperor and son of an emperor most of a century after elections had been abolished, this looked like an honor, but was just an empty title. “Chief Priest” had once been an extremely important position in the state, but, from the time of the first emperor, Augustus, it had simply become another title emperors claimed.
Later European rulers, eager to suggest that they were as powerful as the ancient Romans, used Roman coins as a model. Here’s one from Charlemagne, Frankish king and first Holy Roman Emperor (768-814).
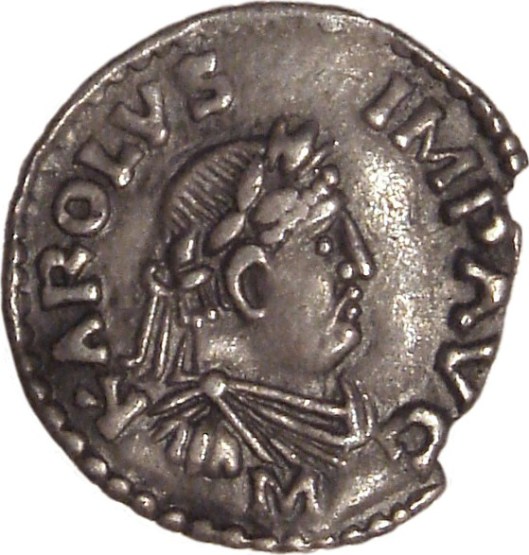

Returning to our George Washington quarter,

let’s look at the comparatively meager inscriptional material. If the coin of Domitian had so much to tell us about how important he was, the inscription on the quarter has a very different message, its focus being upon cultural values: 1.freedom; 2. religion. In our culture, probably everyone would agree with 1, but our ancestor/founders were very adamant on the subject of keeping church and state completely apart, with no influence of either upon the either, so that that 2, “In God We Trust”, shows that there is some confusion about those values. In any case, the plainness might remind us of Caesar’s coin more than Domitian’s, but, in both cases, the point of the artwork and labeling is to put the government’s stamp, whether republic or empire, upon the everyday life of everyone who buys and sells.
There is another message to be read here, as well. The George Washington quarter was first issued on Washington’s 200th birthday, in 1932, and is still on the obverse of the quarter, suggesting the continuity of what he stood for. In the case of monarchs, however, each new emperor/king/queen demands the issuing of new coinage, with the new ruler’s portrait, suggesting not only royal government continuity, but also, in some cases royal family continuity. Here are the first four Hanoverian kings of England, for example, all sons or grandsons, from 1714 to 1830.
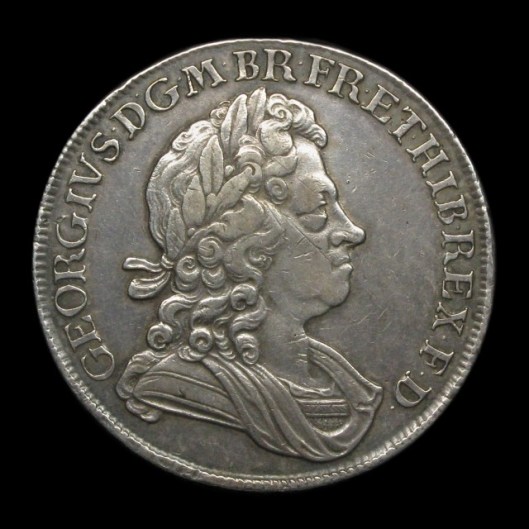
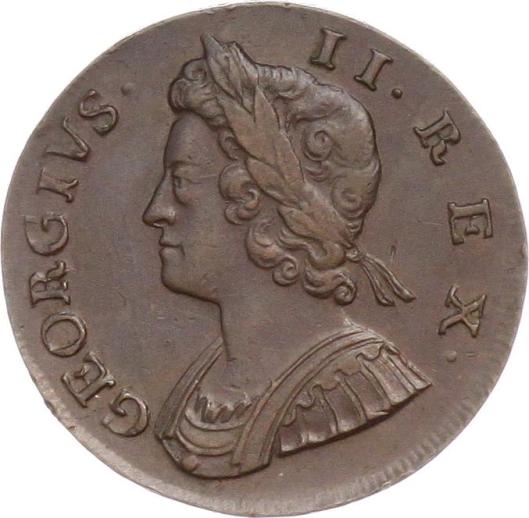
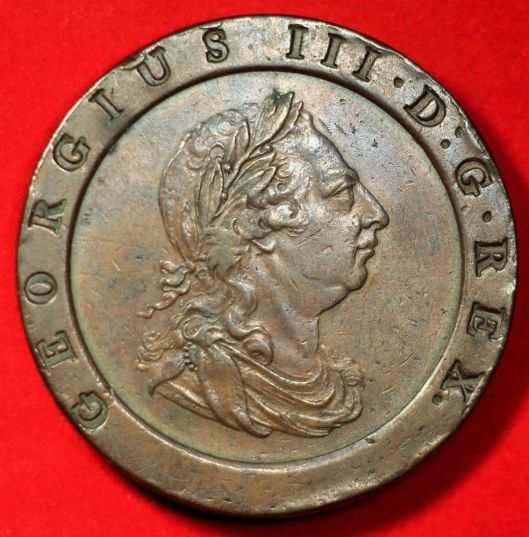
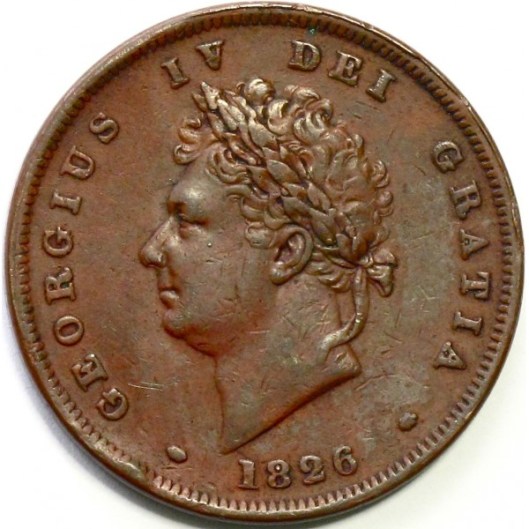


 So, When Prince Charles succeeds his mother, Elizabeth II,
So, When Prince Charles succeeds his mother, Elizabeth II,
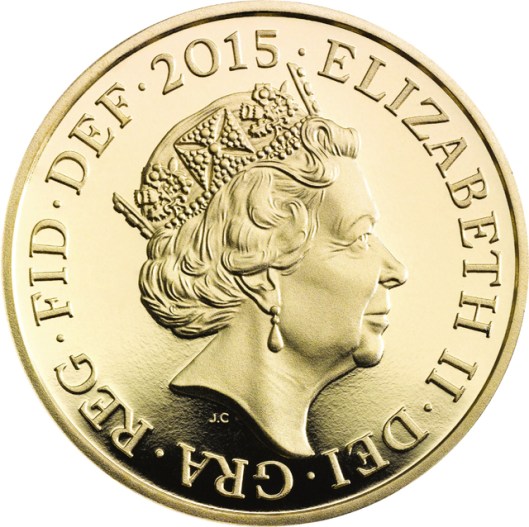

new coins will have to be minted.
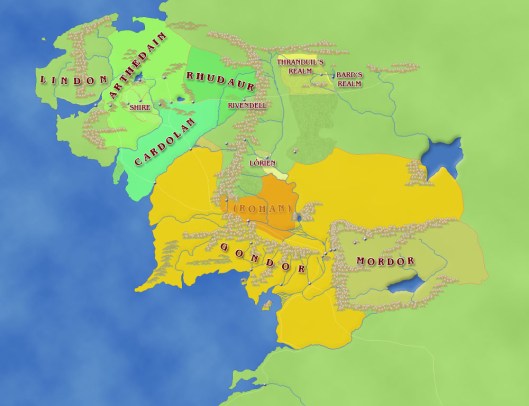
And this brings us back to Middle-earth and to a puzzle about Gondor. There are certainly coins, as our good friend has thoughtfully pointed out. There has been no king on the throne of Gondor for many centuries, however. If Denethor’s behavior is anything to go by, the Stewards have become kings in everything but title, even though Denethor avoids the royal throne. If everyone from the Hellenistic kings to Elizabeth II has his/her portrait on the coinage, are the Stewards on Gondor’s? And what happens when Aragorn becomes King Aragorn II Elessar?
MTCIDC
CD




























 Originally, this had been the site of a Gondorian strongpoint, but, as Gondor waned, it fell into disuse until taken over by Saruman with the permission of the Steward of Gondor, Beren. When
Originally, this had been the site of a Gondorian strongpoint, but, as Gondor waned, it fell into disuse until taken over by Saruman with the permission of the Steward of Gondor, Beren. When 



 Like Saruman, Macbeth is overcome, gives in, murders Duncan, seizes power, but, also like Saruman, can not retain it and, interestingly, an element in his defeat closely resembles an element in Saruman’s defeat: trees.
Like Saruman, Macbeth is overcome, gives in, murders Duncan, seizes power, but, also like Saruman, can not retain it and, interestingly, an element in his defeat closely resembles an element in Saruman’s defeat: trees.