Tags
Adze, Alan Lee, Axe, Bayeux Tapestry, Bilbo, Dane Axe, Dwarves, francisca, Gimli, Harold Godwinson, Helm's Deep, Huscarl, mithril, Skylitzis, The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, Thorin, Tolkien, Varangian Guard
As always, dear readers, welcome.
Ever since we saw the original Lord of the Rings films, we’ve been thinking about Gimli and his major weapon.

In The Hobbit, it would appear that the dwarves had not been armed until they used what was in the Lonely Mountain after Smaug had gone:
“Now the dwarves took down mail and weapons from the walls, and armed themselves. Royal indeed did Thorin look, clad in a coat of gold-plated rings, with a silver-hafted axe in a belt crusted with scarlet stones.” (The Hobbit, Chapter 13, “Not at Home”)
This is where the mithril coat which eventually protects Frodo in Moria and turns up in the hands of the Mouth of Sauron comes from, when Thorin gives it to Bilbo.
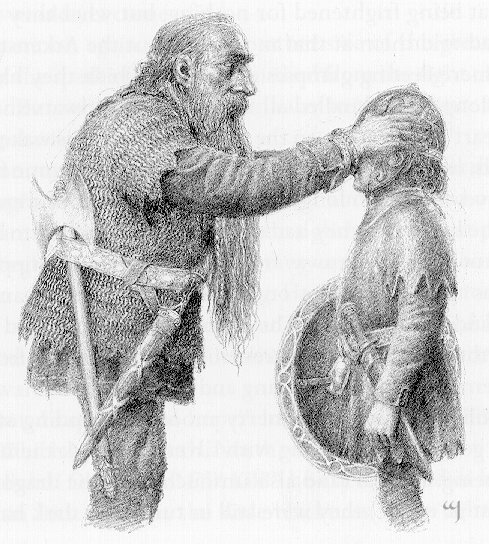

Not long after we first meet Gimli, at the Council of Elrond, however, we see Gimli already kitted out for war:
“Gimli the dwarf alone wore openly a short shirt of steel rings, for dwarves make light of burdens; and in his belt was a broad-bladed axe.” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book Two, Chapter 3, “The Ring Goes South”)
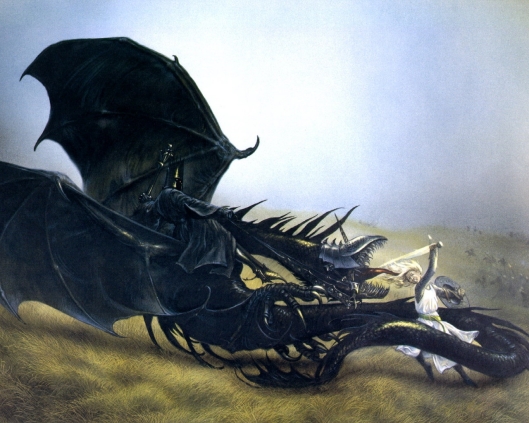
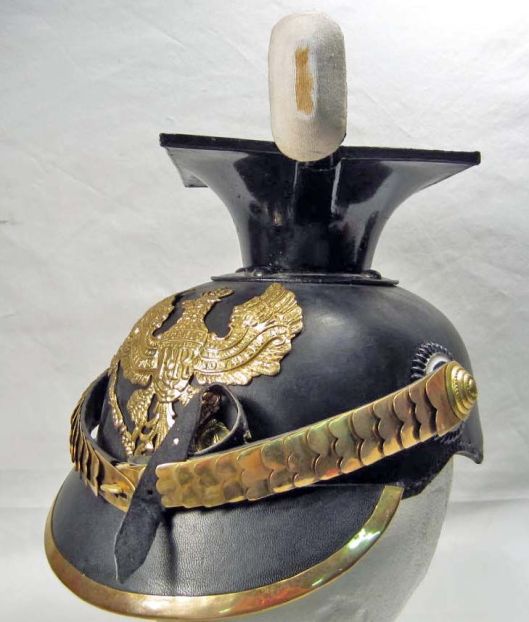
Certainly, the axe in Gimli’s right hand in the photo wouldn’t fit through a belt and allow for comfort or freedom of movement and we note that, in that same photo, Gimli appears to have another—but that looks too long for comfort, as well.

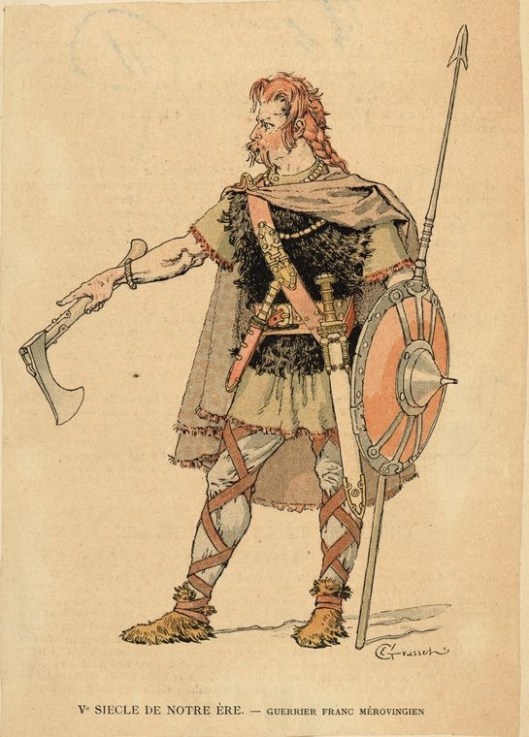
That the two axes fit in with the general persona of dwarves, however, seems to be true—after all, the translation of our title for this post is “Axes of the dwarves!” (to be followed by Khazad ai-menu! “the dwarves are upon you!”), which is the dwarves’ rallying cry. What kind (or kinds) of axes these are doesn’t seem so clear, then. Alan Lee, for example, shows us a dwarf with something which isn’t really an axe at all, but looks more like an adze, which is a tool used in woodworking to smooth and shape wood.

Because JRRT describes Gimli’s axe as being tuckable, we wondered whether he was thinking of the kind of throwing axe, a francisca, used by Frankish warriors (and which gave them their name).


When we actually see Gimli in battle, however, he isn’t throwing, but swinging his axe. At Helm’s deep he says to Legolas, “Give me a row of orc-necks and room to swing and all weariness will fall from me!” And then he swings that axe: “An axe swung and swept back. Two Orcs fell headless.” (The Two Towers, Book Three, Chapter 7, “Helm’s Deep”)
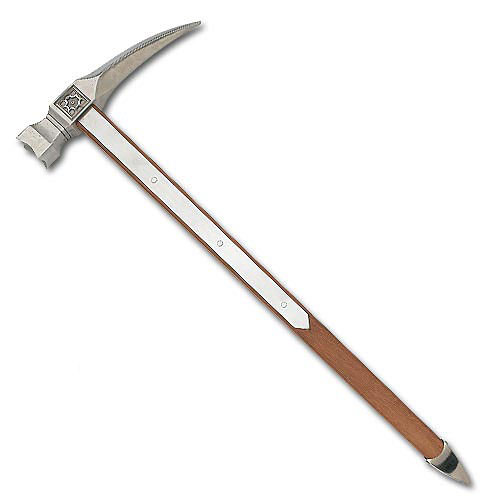
This leads us to ask if perhaps JRRT himself wasn’t clear about Gimli’s weapon. He never throws it, using it always as a chopper, and, when we thinking of axes with a haft—that is, handle–long enough to do that, we don’t think of that odd item in the image above—which doesn’t look substantial enough to cut through cervical vertebrae—

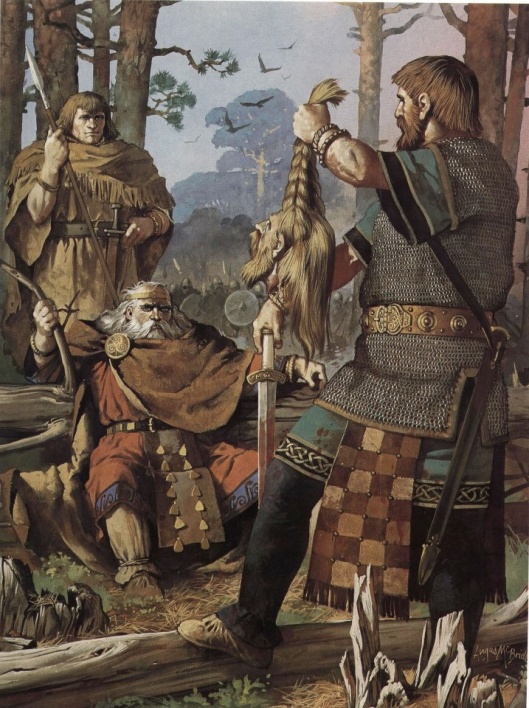
but rather of the long-hafted axe, or “Dane axe” perhaps carried by the giant Viking who defended Stamford Bridge single-handedly against the Anglo-Saxons on 25 September, 1066,


with its razor-sharp blade.

This was the kind of axe that we see carried by the huscarl, the bodyguards, of the English king, Harold Godwinson, in the depiction of the Battle of Hastings, 14 October, 1066, on the so-called Bayeux Tapestry.
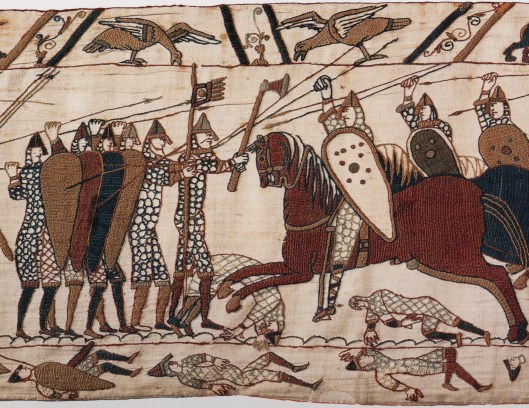


One of which Harold may himself been carrying when he was killed, if the caption on the cloth is referring to Harold being cut down by the mounted Norman in this part of the tapestry.

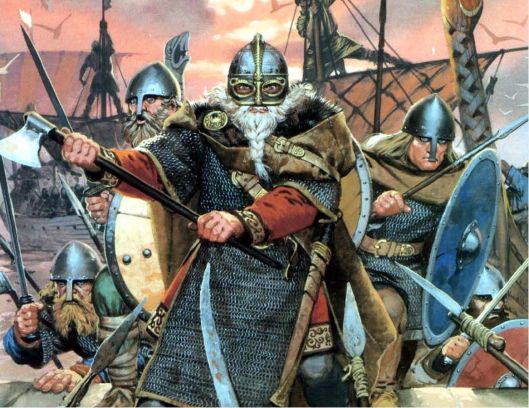
These same axes also appear to turn up as part of the armament of the Varangian Guard, the bodyguard of a number of Byzantine emperors from the 10th to 14th centuries, as depicted in the 11th-century Skylitzis Chronicle.

Much of this guard was made up of Norsemen and Anglo-Saxons, so the pattern of axe, we imagine, was something which both groups brought with them from their original homes.

This is clearly the sort of thing to whack off heads, even two at a time, and so, if we can quietly detach it from Gimli’s belt and have him stand, perhaps even leaning on it, we have the Gimli who competes with Legolas at Helm’s Deep in the number of orcs each has dispatched.

Thanks, as ever, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD