Tags
A Day: Paris In the Rain, Adelard Took, Assyrians, Bag End, Bilbo Baggins, bowler hat, ceramic chariot, China, city gent, CS Lewis, elephant, Emperor Ch'in Shihuang, Greeks, Gustave Caillebotte, Jean Marius, John Howe, Jonas Hanway, Lobelia Sackville-Baggins, Marchesa Elena Grimaldi, Mary Poppins, Monty Python, Palais Galleria, Persians, Romans, Sharkey, The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, The Ministry of Silly Walks, Tolkien, umbrella, umbrella stand, Un Jour: Paris sous la Pluie, van Dyck
Welcome, dear readers, as always and, if you’re in the US, we hope you’ve had a happy and not over-stuffed Thanksgiving.
Just when we think we’ve exhausted a topic, we return and, well, here we are.

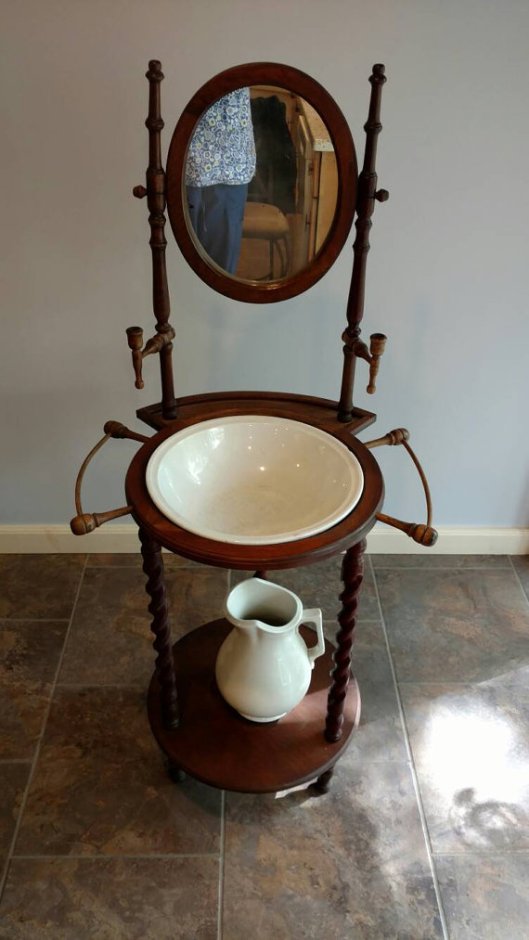
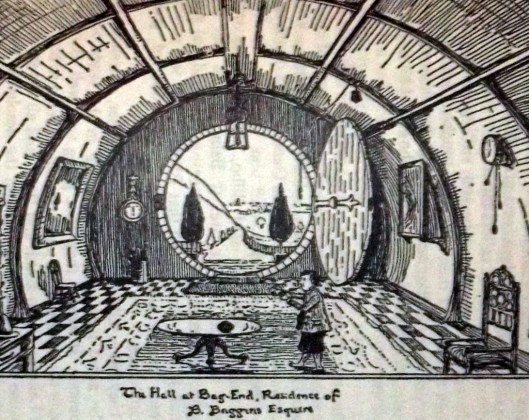
Just to the left of the door and below what we now see as a barometer, there’s a tall tube-like structure, something once common—we wouldn’t be surprised if there was one in every house in which JRRT ever lived: an umbrella stand.
As a child, one of us was fascinated by having once seen an umbrella stand made out of an elephant’s lower leg and foot—or at least the skin.

The couple we’ve seen are all identified as “Victorian”, so, as we are very fond of pachyderms, we hope that such a use is now long in the past!
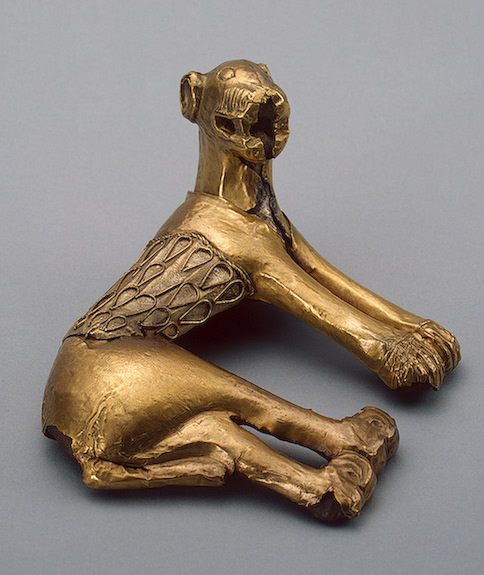
Umbrellas, at least as sunshades, appear to have been around since at least before 200BC in China, as this ceramic chariot—with large umbrella—from part of the tomb complex of the Emperor Ch’in Shihuang demonstrates.

The Assyrians had them.

The Persians had them.
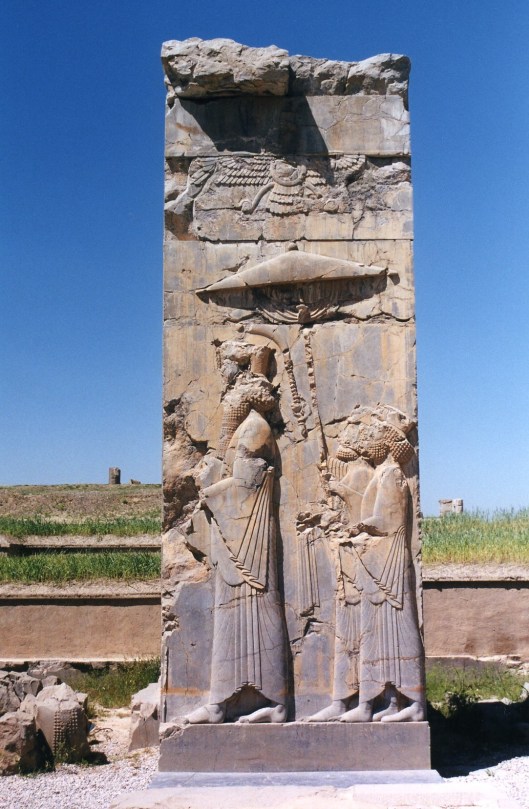

The Greeks had them.
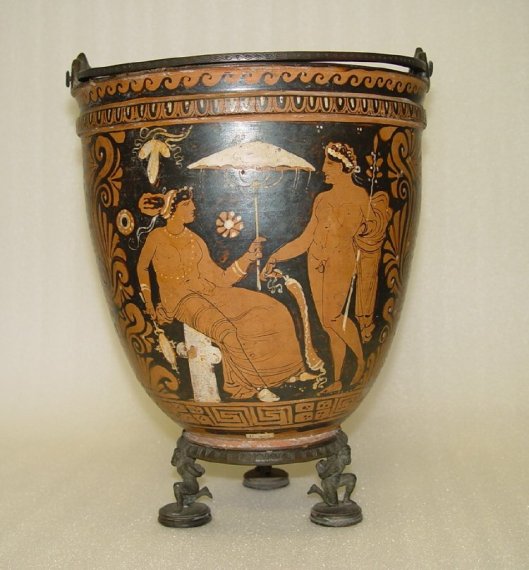

As did the Romans.

And so on for centuries, although it seems that the first modern references to them in England date from the early 17th century and appear, by the latter part of the century and into the 18th as part of “ladies’ apparel”, used as much for sun as rain as this 1623 portrait by van Dyck of the Marchesa Elena Grimaldi shows us.

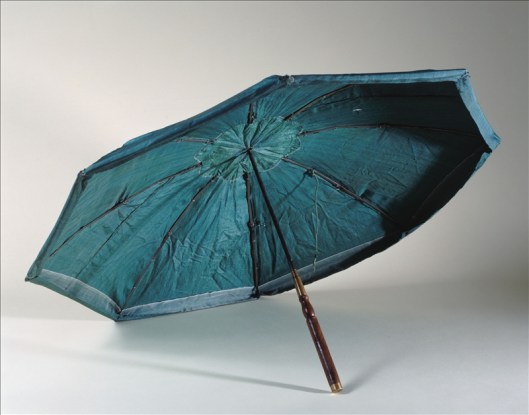
A center for the manufacture of umbrellas was Paris, and the inventor of the modern collapsible model may have been Jean Marius, who received a 5-year monopoly on his invention in 1710. Here is a later (1772) advertisement for his business

and here is a model, identified by the Palais Galleria in Paris as post-1715 because it has no Marius markings.

If there was a prejudice against men carrying them, being a combination of the association with “feminine things” and perhaps also a long-standing prejudice against the French, how did that so change that, by the 20th century, the umbrella, along with the bowler hat, became the marks of the “city gent” in London,
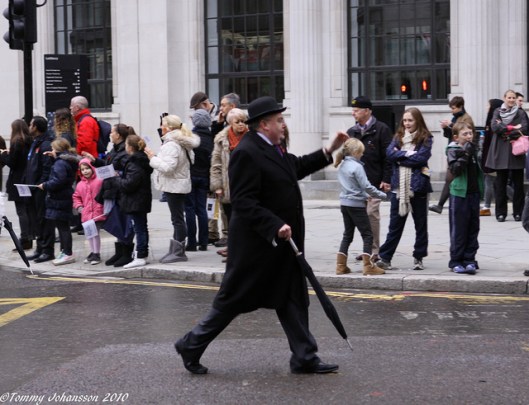

caricatured in the 20th century by Monty Python in skits like “The Ministry of Silly Walks”?

This change is said to stem from the behavior of one rather eccentric man, Jonas Hanway
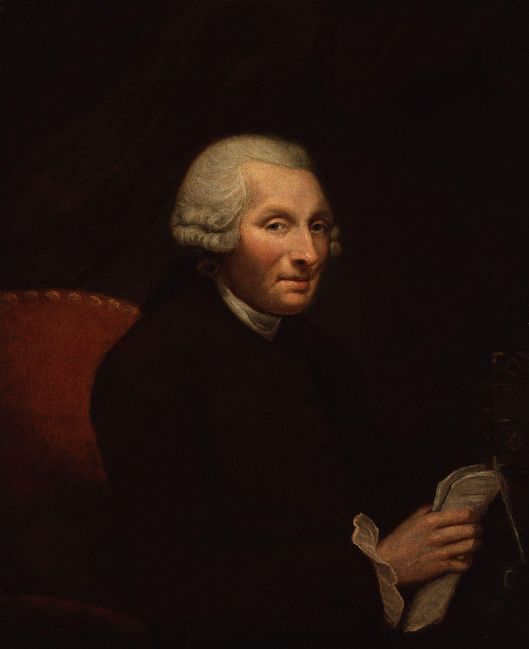

who, sometime in the 1750s, began to appear on London streets carrying an open umbrella.
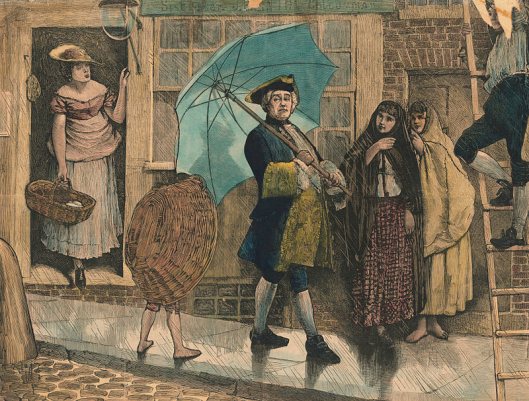

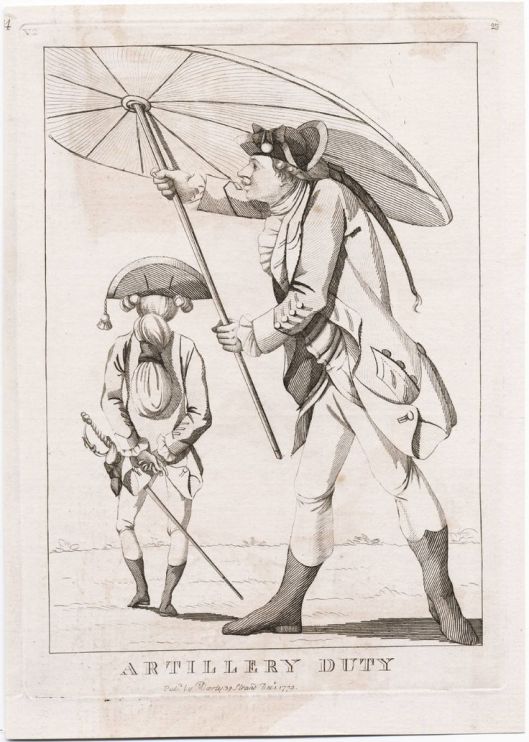
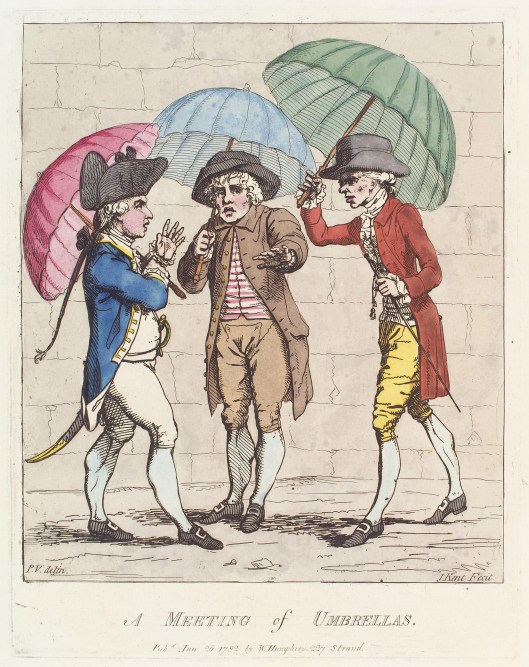
As you, sharp-eyed reader, can tell from our verbs and constructions like “seems”, “appears” and “is said to”, this, like other items of fashion and its changes, hasn’t the firmest of scholarly foundations, but, considering how many illustrations (often mocking cartoons) begin to appear by the 1770s, something happened to alter men’s behavior. Just look at these three, from 1772, 1782, and 1790.



All of this is very interesting, you may ask, but what does it have to do with Bilbo, or with JRRT? There are, in fact, a couple of references in The Lord of the Rings to umbrellas. First, there is one of Bilbo’s mocking gifts:
“For Adelard Took, for his very own, from Bilbo; on an umbrella. Adelard had carried off many unlabeled ones”. (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book One, Chapter 1, “A Long-Expected Party”)
Then there are two to Lobelia Sackville-Baggins. The first is suggestive of her suspicious behavior at the near-auction of Bilbo’s property at the end of The Hobbit (you’ll remember that some spoons never reappeared):
“He [Bilbo] escorted her [Lobelia] firmly off the premises, after he had relieved her of several small (but rather valuable) articles that had somehow fallen inside her umbrella.” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book One, Chapter 1, “A Long-Expected Party”)
The second reference is actually rather pathetic. Once “Sharkey” and his thugs take over the Shire, they evict Lobelia from Bag End and, because she resists, they drag her off to the Lockholes, as young Tom Cotton tells Merry and the others:
“She comes down the lane with her old umbrella…”
When told that “Sharkey” gave the order for her eviction (and the building of sheds at Bag End):
“ ‘I’ll give you Sharkey, you dirty thieving ruffians!’ says she, and ups with her umbrella and goes for the leader, near twice her size.” (The Return of the King, Book Six, Chapter 8, “The Scouring of the Shire”)
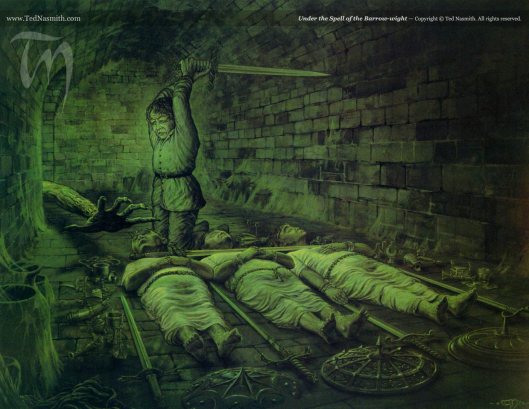
Here’s a little illustration of a defiant Lobelia by John Howe.

By the later 19th century, men with umbrellas seem quite common—even to the point of providing material for social commentary in the public press—

But, in the 20th century, we who love children’s literature see them in a completely different way, either as a mode of transportation

or as part of the origin of a favorite story, when CS Lewis, at 16, had a recurring image of “a Faun carrying an umbrella and parcels in a snowy wood” (from It All Began with/as a Picture). (We’ve seen the title cited both ways.)

But we want to end this posting not with literature, but with pure art. There are lots of paintings from the 18th and 19th centuries with umbrellas, but here is what may be our favorite, by Gustave Caillebotte (1848-1894). Although he is grouped with the Impressionists, this painting in particular shows the artist’s interest in the hard-edged world of early photography (“Un Jour: Paris sous la Pluie”—“A Day: Paris In the Rain”)

Stay dry, dear readers, and thanks, as ever for reading!
MTCIDC
CD























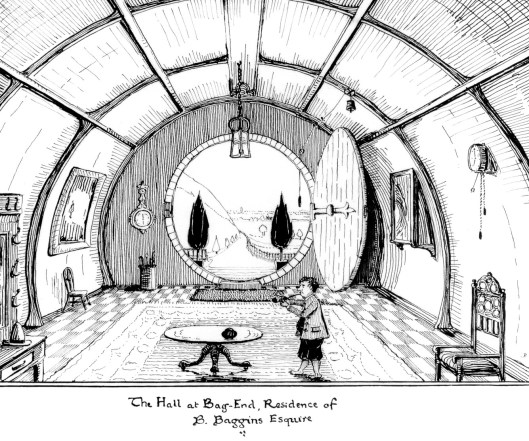



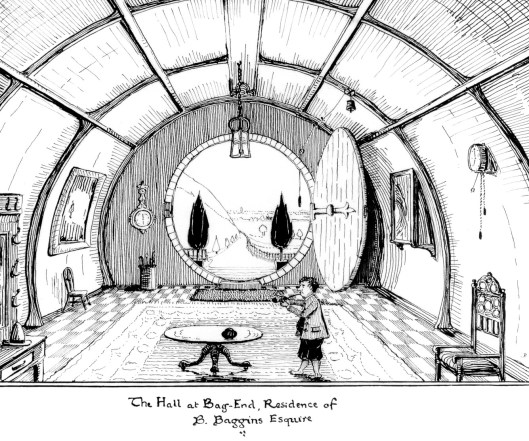





 And here’s the film version–
And here’s the film version–