Tags
A Game of Thrones, Bag End, basins, Bree, British monarchs, Buckland, canopy, cart, Cirith Ungol, Coronation Chair, Coronation Throne, Crick Hollow, Edoras, Edward I, Edward VII, Edward VIII, Edwardian, Elizabeth II, Elrond's house, Furniture, George V, George VI, Gondor, high table, Iron Throne of Westros, Lia Fail, Lothlorien, Medieval, Middle-earth, Minas Tirith, monopodium, Moot Hill, parlor, pubs, Rivendell, Rohan, Shire, Stone of Scone, Tara Ireland, The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, The Prancing Pony, the Stone of Destiny, throne, Tolkien, Tom Bombadil, UK pubs, Victorian Bedroom, Victorians, washstand
Welcome, dear readers, as always.
In our last, we were talking about furniture in Middle-earth—in that post our subject was The Hobbit. We continue with The Lord of the Rings and conclude with one specialized piece of furniture.
We begin where we began last time, with Bag End.
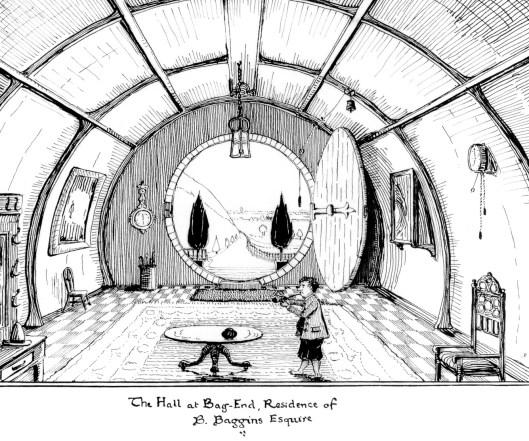
With all of its rooms and the stuff in them, we suggested then that what JRRT was really doing was depicting the kind of overcrowded place later Victorians and Edwardians—the people with whom he, born 1893, would have grown up around—would have preferred.

[Note, by the way, the table in the middle of the entryway in Tolkien’s picture of Bag end, and compare it with this “monopodium” table with claw feet, which could be seen in such a parlor.]

Once the three Hobbits leave Bag End for their journey to Crick Hollow,
having sent “two covered carts…to Buckland, conveying the goods and furniture…” (and the next day sending off another) (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book One, Chapter 3, “Three is Company), they will spend a great deal of time walking (and paddling and riding), but will enter few buildings. Here, by the way, is a cart—we imagine “covered” simply means that a blanket of some tough coarse fabric, like canvas, (called a “tilt”) would have been pulled over the load.

Our chances of getting much furniture detail are not high, then, but let’s see what we find.
Beyond Buckland, the first indoors for the hobbits is Tom Bombadil’s house. As the hobbits enter, they are in:
“…a long low room, filled with the light of lamps swinging from the beams in the roof; and on the table of dark polished wood stood many candles, tall and yellow, burning brightly.
In a chair, at the far side of the room facing the outer door, sat a woman…” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book One, Chapter 7, “In the House of Tom Bombadil”)

The hobbits are given “low rush-seated chairs”.
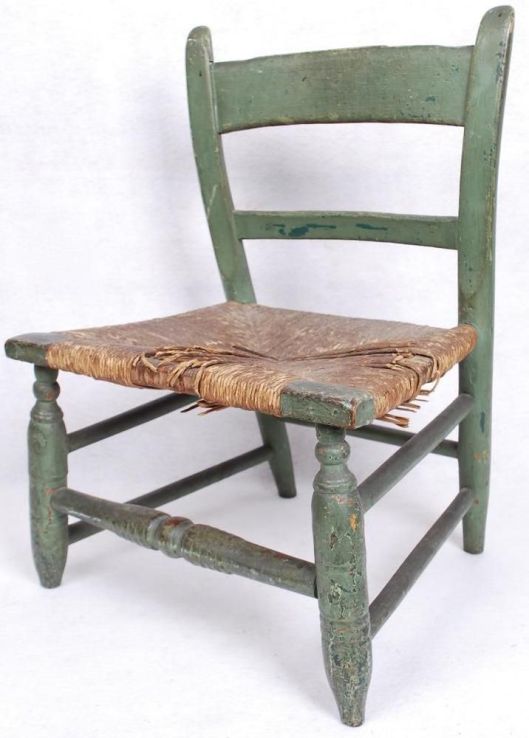

And, shortly, are shown their bedroom:
“They came to a low room with a sloping roof…There were four deep mattresses…laid on the floor along one side. Against the opposite wall was a long bench laden with wide earthenware basins, and beside it stood brown ewers filled with water…”
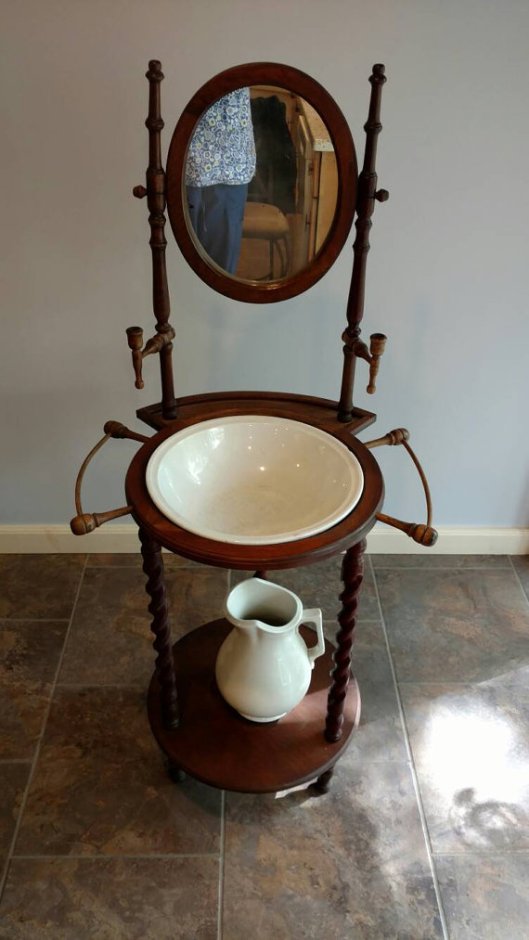
Not much to go on here. We’ll presume that the bench is wooden and plain, and the basins and ewers (a big pitcher—ultimately from Latin aquarius, “having to do with water”) are of the kind one would have seen in a Victorian bedroom, when indoor bathrooms were still only a wish—or were only in the homes of the extremely wealthy.

[Victorians, by the way, could have specialized places for such pitcher/basin combinations. They’re called “washstands” and here’s a simple but functional one.]

Next on their journey (we won’t count the barrow—although the Wight does mention a “stony bed”) is the Prancing Pony.
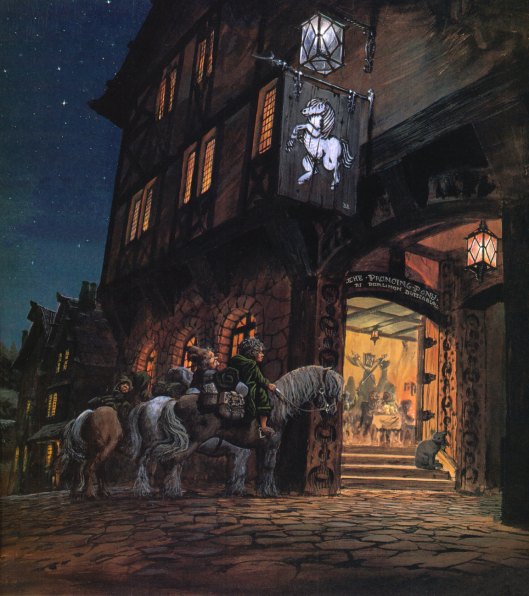

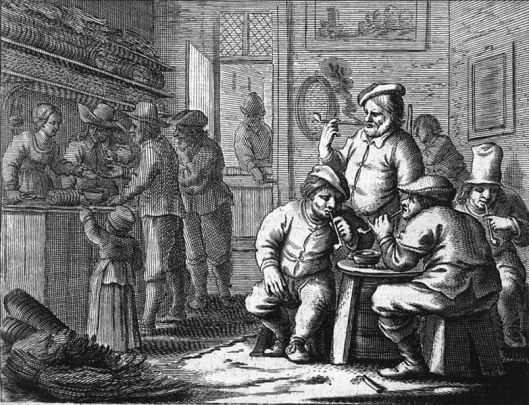
Again—what we have is functional. The hobbits are initially led to what the landlord, Barliman Butterbur, calls “a nice little parlour” where “There was a bit of bright fire burning on the hearth, and in front of it were some low and comfortable chairs” and “a round table, already spread with a white cloth”. (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book One, Chapter 9, “At the Sign of the Prancing Pony”)
This sounds like a small, private room, found in some UK pubs, and called a “snug” (etymology unclear—but used to mean “comfy” as early as the 1620s). Here’s one, in fact, from an Irish pub. (We don’t advertise—this was simply the image which fit best with both our impression and the book. And “fit best” does a double duty here, as “snug” can also mean “fitting tightly”.)

The same will be true of the bedroom the hobbits don’t use—and just as well!—plain and nondescript.
So when, if ever, are we given something with more detail? If not in Bree, perhaps in Rivendell?

Frodo comes to in a generic bed, but the “hall of Elrond’s house” is a bit more promising:
“Elrond, as was his custom, sat in a great chair at the end of a long table upon a dais…In the middle of the table there was a chair under a canopy…” The Fellowship of the Ring, Book Two, Chapter 1, “Many Meetings”)
A “dais” is a raised platform. If you’re a Harry Potter fan, you’ll remember it at “High Table” (as it’s called in English schools), where the students of the four different colleges meet to dine and the faculty sit on such a platform.

This is a left-over medieval custom, when royalty/nobles sat on a kind of stage, above the lesser folk, for formal meals.
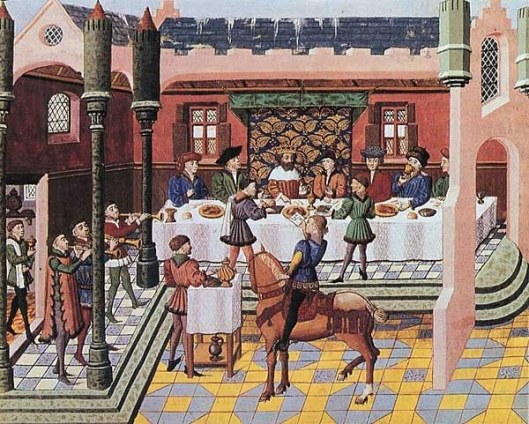

(Oh—and don’t ask about the horse—but it wasn’t required. Horse and rider do appear at a banquet, of course, in the 14th-century poem “Sir Gawain and the Green Knight”—which JRRT once edited.)

And that “chair under a canopy” reminds us of thrones with canopies, like this at the Palace of St. James, in London.
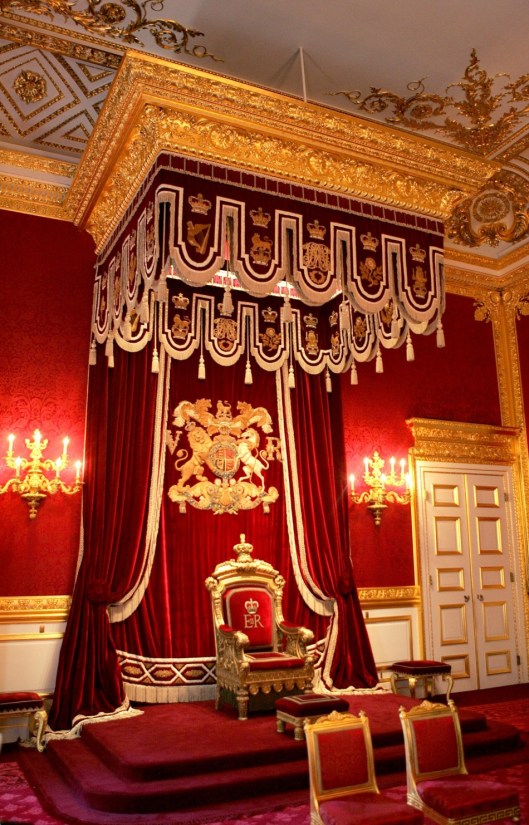

Which brings us to the subject of thrones, in general. After Rivendell, indoors will consist of Lothlorien

for the fellowship, then nothing for Sam and Frodo till Faramir’s cave hide-out and, beyond, the Tower of Cirith Ungol

Hardly places to find any furniture beyond the functional!
For the others, we have Edoras

and Minas Tirith.

And here we want to conclude by discussing a similar piece of furnishing in each—those thrones.
These days, when we say or write “thrones”, well, what comes immediately? A Game of Thrones and the Iron Throne of Westeros.
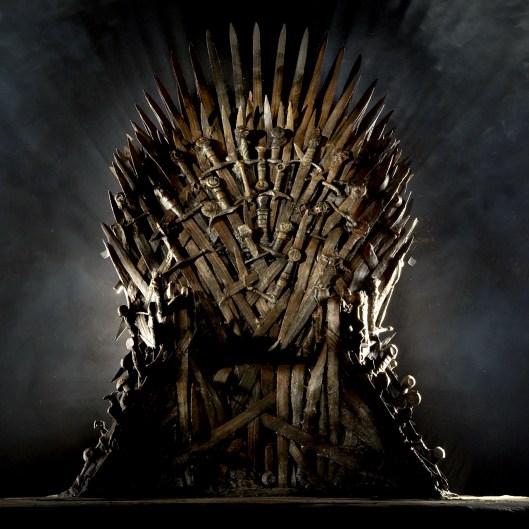

The thrones of Rohan and Gondor are a bit less complicated.
Theoden’s is described simply as “a great gilded chair” on a “dais with three steps”. (The Two Towers, Book Three, Chapter 6, “The King of the Golden Hall”).
Here’s Allen Lee’s interpretation

and here is the Hildebrandts’.

The throne of Gondor is just a tiny bit more elaborate:
“At the far end upon a dais of many steps was set a high throne under a canopy of marble shaped like a crowned helm…” (The Return of the King, Book Five, Chapter 1, “Minas Tirith”)
Here’s an image from the film.

But wait—there’s no one on it. Let’s look lower:
“At the foot of the dais, upon the lowest step which was broad and deep, there was a stone chair, black and unadorned, and on it sat an old man gazing at his lap.”
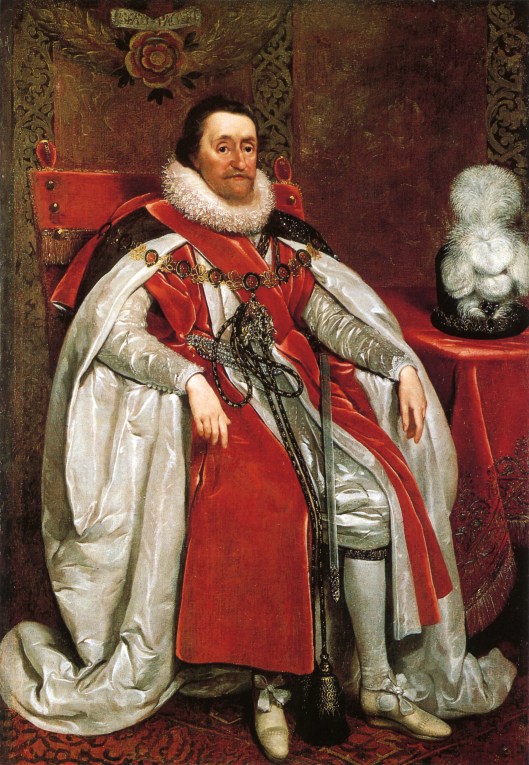
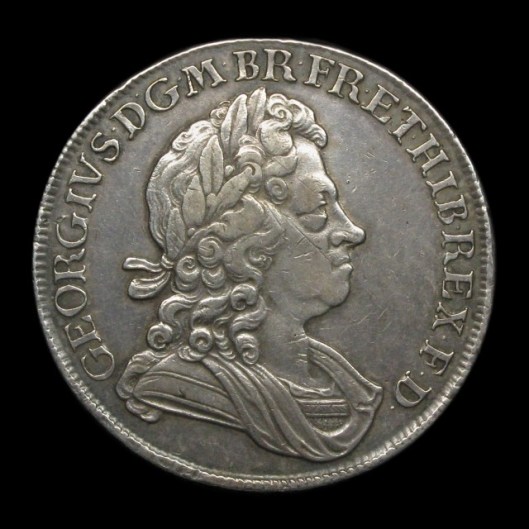
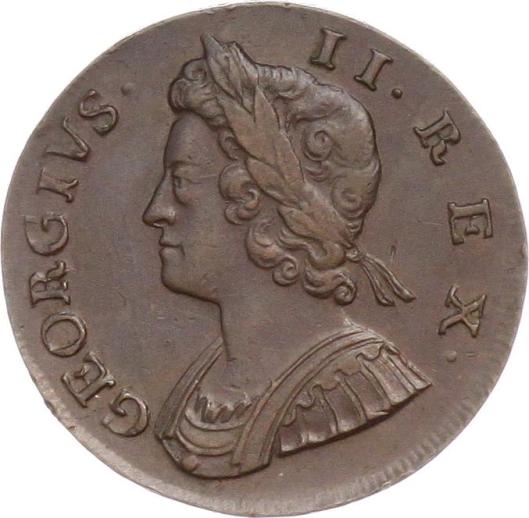
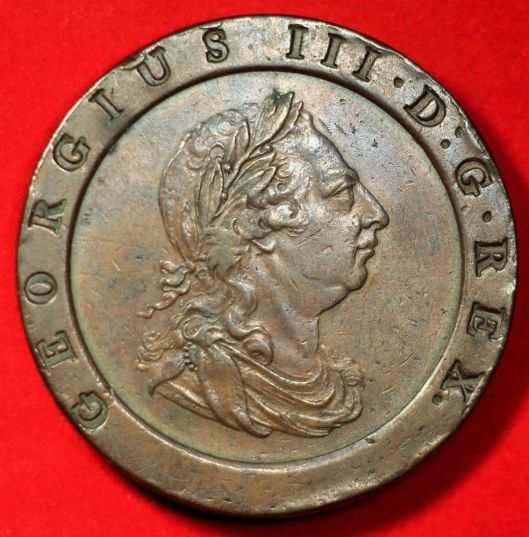
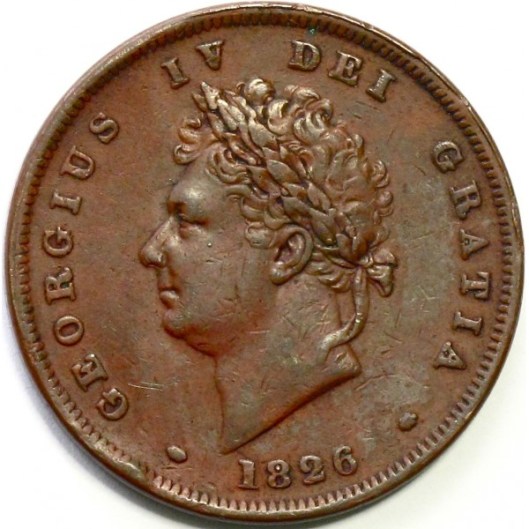
During his lifetime, JRRT would have seen the coronation of five British monarchs:
Edward VII
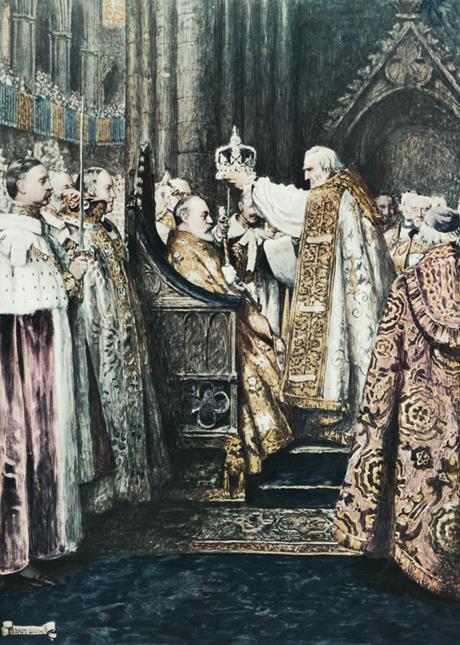

George V

Edward VIII

George VI

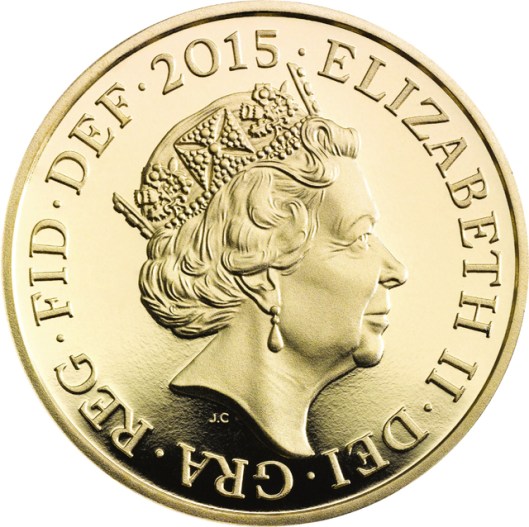
and the current monarch, Elizabeth II.
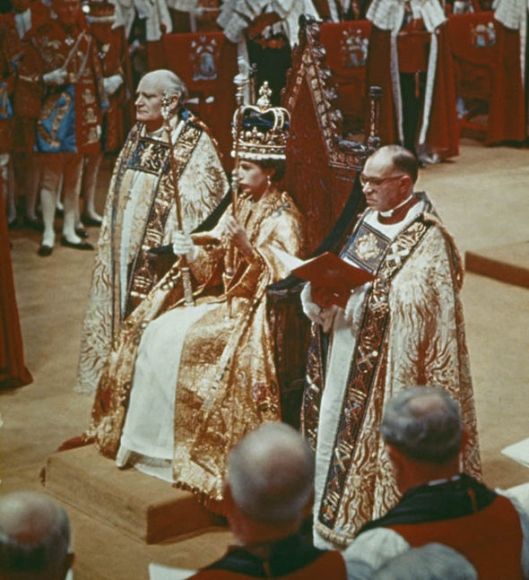

You’ll notice that, in every case, the throne is the same.

This is the so-called “Coronation Chair”, built between 1297 and 1300 and used since for crowning English monarchs. It was especially commissioned so that it could hold the “Stone of Scone” (pronounced “skoon”—not like the pastry). This was an ancient piece of Scottish royal history which Edward I,

in an effort to control Scotland, had stolen from its place on Moot Hill, near the Abbey of Scone.

Supposedly, it was a stone used in the crowning of Scottish kings back to the time of the first one, or that it was even older, having been lugged from Tara, in Ireland, where, under the name “Lia Fail”, “the Stone of Destiny” it was used in coronation ceremonies there. Its purpose was confirmation: tradition had it that, when the true king bestrode it (a great old verb form), it gave a great shout.

As far as we know, no shouting has been reported, over the centuries—perhaps because it’s being used for English kings and therefore the stone is holding its tongue till it’s taken back to wear it belongs?
What do you think, dear readers?
Thanks, as ever, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD
PS
And did you notice something(s) out of place in JRRT’s drawing of Bag End? We’ll talk about it in our next…

























 So, When Prince Charles succeeds his mother, Elizabeth II,
So, When Prince Charles succeeds his mother, Elizabeth II,