Tags
Anglo-Saxon, Bayeux Tapestry, Embroidery, feudalism, Medieval, Middle-earth, Normandy, Peter Jackson, Rohirrim, tapestry, The Lord of the Rings, Tolkien
Welcome, as always, dear readers.
In this posting, we would like to continue what we began in “Behind the Rammas Echor”. In that posting, we talked about using the illustrations from medieval English psalters (the wonderful 14th-century Luttrell Psalter in particular) to try to visualize the feudal world suggested by certain aspects of Tolkien’s The Lord of the Rings.
In that posting, we said that feudalism could be broken down into two big categories, land and troops, and there we spent time looking at basic agricultural life, to imagine the look of the feudal world of Middle Earth.
Now we move on to troops. And, as much as we can, we would like to continue to use medieval images to help us.
In previous posts, we’ve praised Jackson’s depiction of the Rohirrim, both the architecture and the people. Edoras and Meduseld within it just look right—and, when you watch the material on constructing them in the extended version box set, we can only be absolutely bowled over by the care taken there, for all that we have difficulties with certain other parts of the films, both in look and in the changes to the text.



In one previous post, we suggested the kinds of models we both know and imagine Tolkien used to create the Rohirrim. These were primarily Anglo-Saxon, but combined with a horse people (which the Anglo-Saxons were not) of some sort, possibly Scythian (an Indo-European-speaking horse folk from north of the Black Sea).

As we’ve thought more about it (one, for us, of the great pleasures of solid adventure literature, new and old—is that you not only want to think more about it, but, as you do, you find more in it), we began to imagine that Tolkien might have had another visual source, based upon another famous set of medieval illustrations, the Bayeux Tapestry.
This is a roll of linen, some 230 feet (that’s about 70 metres) long and 20 inches (50 centimetres) high, into which are woven three bands of designs. The center is a long (very long!) series of adjoining panels covered in human figures, which have been stitched on with various colored woolen threads. Above and below the central band are two narrower ones which combine abstract figures (commonly on the upper panel) with human activities (on the lower one). Across the top of the central band are a series of captions in very simple Latin, describing what is happening below.

The caption here reads: “Here Harold the king has been killed.”
As it’s not through-woven, like this—

this isn’t really a tapestry, but an embroidery, in fact.

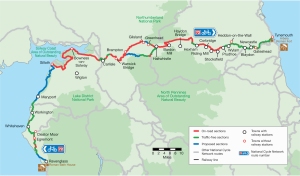
It’s linked to the cathedral at Bayeux, in Normandy, where it has been for at least 6 centuries. On the map, find Le Havre and look left and you’ll see Bayeux.

Where it really came from and who made it are two of those mysteries that it’s been fun to follow the scholarship of, but, as of 2015, there are lots of theories, some of them more convincing than others, but that’s all there are: theories. If you’d like to know more about them, go to: www.bayeux-tapestry.org.uk/whomadethetapestry.htm.
The tapestry is housed in an impressive museum in Bayeux, where its entire length is ingeniously displayed in a sort of wrap-around way.


We’ve given you lots of facts, but the one thing we haven’t mentioned is the subject of such an immense work. It is, in fact, a lengthy piece of propaganda justifying the Norman invasion and conquest of England in 1066AD. We know, then, one definite thing about it: it certainly wasn’t embroidered for the Anglo-Saxons! (Although there is at least one theory that it was made by them.)
As much as we are interested in the subject, what has caught our attention now is the look—here are soldiers from the same period as the Anglo-Saxon model for the Rohirrim, after all, but, although archers are depicted on the Norman side, and a few infantry, the Normans are mainly shown as horsemen.

Here is our first sight of the Rohirrim in The Two Towers, Chapter 2, “The Riders of Rohan”:
“Their horses were of great stature, strong and clean-limbed; their grey coats glistened, their long tails flowed in the wind, their manes were braided on their proud necks. The Men that rode them matched them well: tall and long-limbed; their hair, flaxen-pale, flowed under their light helms, and streamed in long braids behind them; their faces were stern and keen. In their hands were tall spears of ash, painted shields were slung at their backs, long swords were at their belts, their burnished shirts of mail hung down upon their knees.”

Minus the grey horses and the braids, what do you think, dear readers?
As ever, thanks for reading.
CD
MTCIDC
PS
That MTC will be Feudal Array.2, in which we consider the other forces opposing Mordor…