Tags
Agincourt, Archery, arrow bag, arrows, Bard the Bowman, Battle of Poitiers, Casula Mellita, Crecy, Edinburgh, English Longbowmen, Esgaroth, Greco-Roman, gunpowder, harpoon, Hundred Years War, Laketown, longbows, Medieval-Renaissance, Napoleonic Wars, Naval Warfare, Pinkie Cleugh, Roman, sailing, Smaug, The Hobbit, The Mary Rose, Tolkien
Welcome, as always, dear readers.
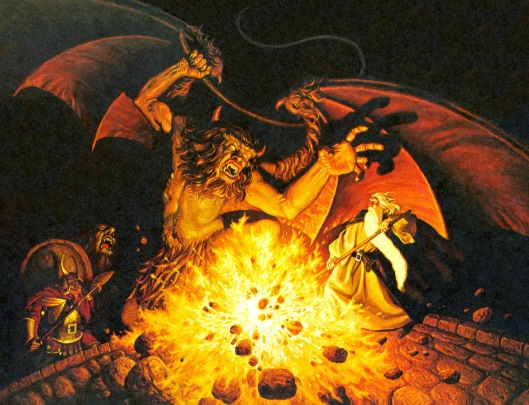
In the past, we had a posting on Bard the bowman

who rescued Esgaroth (Laketown)

from the attack by Smaug.

(We especially like this Jeff Chan Bard not only because Bard is depicted as he is in the book, as an archer, but also because it includes the thrush who tells him where he is to strike.)
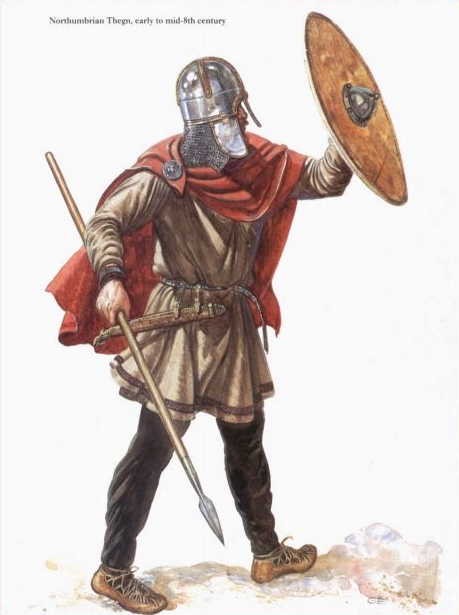
In that previous posting, we suggested that JRRT pictured Bard as looking and acting like one of the English longbowmen of the Hundred Years War

rather than as a harpooner, as in the film.


Since that posting, we did a second which included bowmen, just a few weeks ago, about Mogul-knife and arrow wound, and now we would like to add a third.
As we’ve mentioned before, one of us is preparing a new university course to be taught in the autumn on the history of warfare. As you can imagine, this is a big subject, but, in the process of shaping it, we want to include a week on developments in naval warfare over the centuries. So far, we’ve divided it into several parts:
a. Greco-Roman


b. medieval-renaissance


c. the age of sail

d. ironclads

e. dreadnoughts

While working on the Medieval/Renaissance section, we were reminded of what might be the most famous Renaissance shipwreck: the sinking of The Mary Rose, 19 July, 1545.

Medieval naval battles had been primarily infantry battles transferred to the sea, as had been Roman practice. That practice was a story in itself—the traditional Roman explanation was that they were land-fighters and so had invented a device, called a “corvus”–that’s “crow” in English—probably because the point at the enemy’s end was a bit like a pecking beak. This was a kind of gangplank which, dropped onto the enemy’s ship, stuck in place and allowed Roman marines to rush across and deal with their opposite numbers.
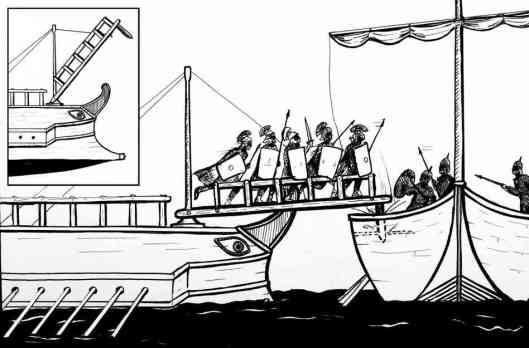

Things began to change with the invention of cannon in western Europe. (The history of gunpowder in the Far East is its own subject—and one we urge those interested to have a look at. Here’s a LINK to get you started.) Used first on land perhaps by the 13th century, the first recorded use of cannon on a ship dates from 1338 (and here’s a LINK to naval artillery, in case you want to know more).
With cannon, you could stand off from an enemy ship and—your choice—cripple it by destroying its sails and rigging—or sink it with holes below the waterline.

Boarding, as the Romans had, was still a possibility, of course, and provided the extra benefit, if the boarding was successful, of allowing for the acquisition of an extra ship. This could be added to your fleet or sold and the profits shared among the sailors—or, actually, if we go by Napoleonic British standards, the profits went to everybody at the top, including admirals who weren’t even present at the capture, with a teeny amount remaining for the seamen who’d actually taken the prize.

To do that boarding, Romans—and medievals—had loaded their ships with soldiers, and the Mary Rose was no exception, its surviving records suggesting that there were about 200 soldiers in a crew of approximately 400-450.
As a number of longbows have been recovered from the wreck,

this would suggest that many of those soldiers were archers.
These, along with the artillery (and perhaps a small number of arquebuses? To our current knowledge, none has been recovered from the ship, but, certainly, by 1545, they were in common use—at the battle of Pinkie Cleugh, east of Edinburgh, in 1547, the English army had several hundred German mercenary arquebusiers),
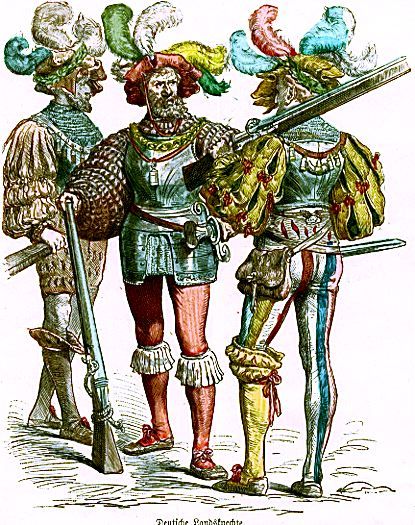

would have supplied the missile weapons of the ship.
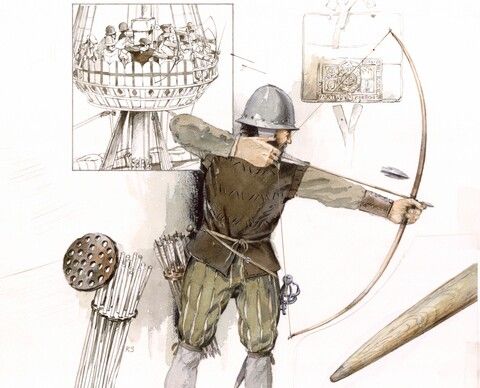
Not only were large numbers of artifacts discovered in the Mary Rose, but the skeletons of perhaps half its crew and about 90 of those were intact enough to warrant further study. For our purpose, one, in particular is very interesting.
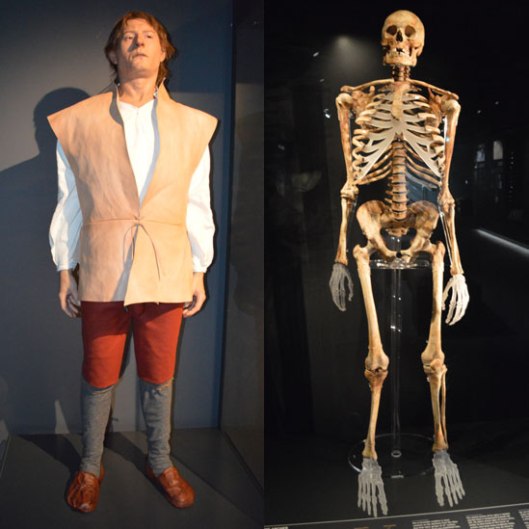

Discovered in the hold, he was a large man for his time, about 6 feet (about 183cm). As well as revealing that he would have had a powerful build, his skeleton displayed repetitive stress injuries to his upper body. There is discussion as to the pull-weight (how much muscle power it takes) of the longbow of the medieval/Renaissance period, estimates ranging from 90 to about 150 pounds (we’re sorry that we can’t readily convert this, as it isn’t pounds of weight, but pounds of force—the general idea is that it would have taken huge muscle power in either case), but, for a bow as tall as a bowman, this would have demanded great muscular strength—which would then have, over time, put huge stress upon an archer’s body. This has then led archaeologists to suggest that he was a bowman.
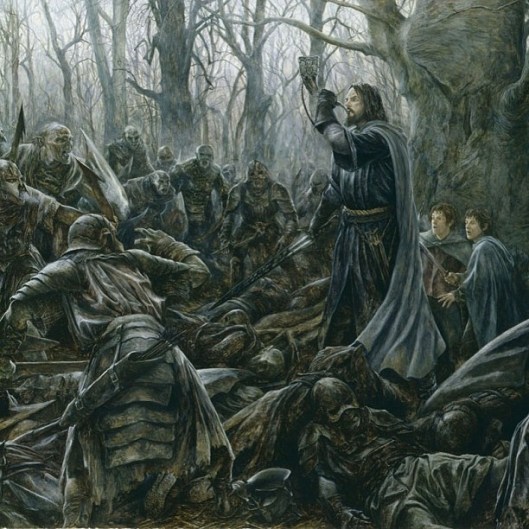
And this brings us back to Bard, the actual archer, and a suggestion as to what he might have looked like.
JRRT only says:
“But there was still a company of archers that held their ground among the burning houses. Their captain was Bard, grim-voiced and grim-faced…Now he shot with a great yew bow, till all his arrows but one were spent.” (The Hobbit, Chapter 14, “Fire and Water”)
“a great yew bow” makes us think of the English bowmen we’ve mentioned before, and those we believe were in Tolkien’s mind, the victors at the battles of Crecy (1346), Poitiers (1356), and Agincourt (1415).

To produce archers who could pull such powerful bows (and fire up to 10 arrows a minute, as we’ve mentioned in a previous posting), English archers began training as boys and continued throughout the years—as athletes of the bow, they had to keep in shape. Such training and exercise would then have produced men like that discovered on the Mary Rose—big-shouldered, strong-armed—and given to the subsequent damage inflicted on the body by archery wear-and-tear.
So, might we then see Bard as not only “grim-voiced and grim-faced”, but “broad-shouldered and imposing”? To which we can add this from The Hobbit:
“In the very midst of their talk, a tall figure stepped from the shadows. He was drenched with water, his black hair hung wet over his face and shoulders, and a fierce light was in his eyes.” (Chapter 14, “Fire and Water”)
All of which gives us: “tall, black-haired, fierce, grim-voiced and grim-faced”—and, at our suggestion, “broad-shouldered and imposing”—a worthy portrait of Bard the Dragon-slayer.
Thanks, as ever, for reading!
MTCIDC
CD
PS
It’s not known what our Mary Rose archer was doing in the hold at the time the ship went down, but perhaps he was seeking to transfer extra ammunition to the main deck? That ammunition would probably have been in the form of coarse linen bags carrying 24 arrows each—here’s a modern reconstruction

and here’s the LINK to the site from which it comes. This belongs to an amazing woman whose website is full of her life on the edge of the Great Plains, in Kansas, USA—home of Dorothy of the OZ books, of course– as well as her photos of things like the reconstructed bag in the photo above. Below is a picture of the Kansas tall grass prairie.