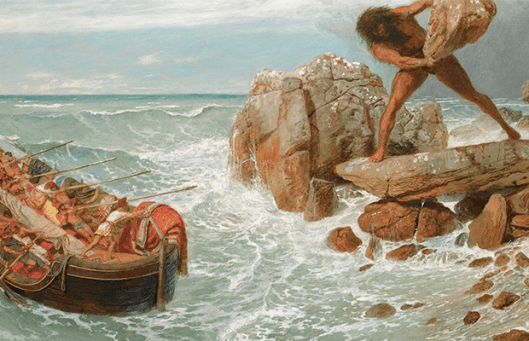Tags
Ainur, Arda, Frodo, Iluvatar, In western lands beneath the Sun, Middle-earth, Morgoth, Music, Sam Gamgee, Song, The Lord of the Rings, The Silmarillion, The Tower of Cirith Ungol, Tolkien
Dear Readers,
Welcome, as always.
For this posting, we consulted the Sortes Tolkienses, and landed upon a particular passage which had us thinking about song in Middle-earth:
“It was quiet, horribly quiet. The torch, that was already burning low when he arrived, sputtered and went out; and he felt the darkness cover him like a tide. And then softly, to his own surprise, there at the vain end of his long journey and his grief, moved by what thought in his heart he could not tell, Sam began to sing. “
At this moment, Frodo has been taken by the enemy after the two Hobbits had been led into and escaped Shelob’s lair, and Sam, though only a simple gardener from the Shire, has resolved to carry Frodo’s burden and rescue him from the tower.

Along with carrying the Ring, which would have otherwise been taken from Frodo in the tower, Sam has also brought with him Sting, Frodo’s sword, and Galadriel’s phial, which she gave to Frodo as a gift upon their leave-taking from Lothlorien.

The phial is used when the two Hobbits are pursued by Shelob, as a means both of light and of defense. Faced with a darkness he has never encountered before, however, but set on finding and rescuing Frodo, even if he’s not sure how, Sam has the option of pulling out the phial straight away when the lights in the tower of Cirith Ungol go out.
Instead, Sam sings—although he’s not quite sure why—and, in the shadow of Mordor, recalls home in the Shire:
“His voice sounded thin and quavering in the cold dark tower: the voice of a forlorn and weary hobbit that no listening orc could mistake for the clear song of an Elven-lord. He murmured old tunes out of the Shire, and snatches of Mr. Bilbo’s rhymes that came into his mind like fleeting glimpses of the country of his home. And then suddenly new strength rose in him, and his voice rang out, while words of his own came unbidden to fit the simple tune.
In western lands beneath the Sun
the flowers may rise in Spring,
the trees may bud, the waters run,
the merry finches sing.
Or there maybe ‘tis a cloudless night
and swaying beeches bear
the Elven-stars as jewels white
amid their branching hair.
Though here at journey’s end I lie
in darkness buried deep,
beyond all towers strong and high,
beyond all mountains steep,
above all shadows rides the Sun
and stars forever dwell:
I will not say the Day is done,
nor bid the Stars farewell.”
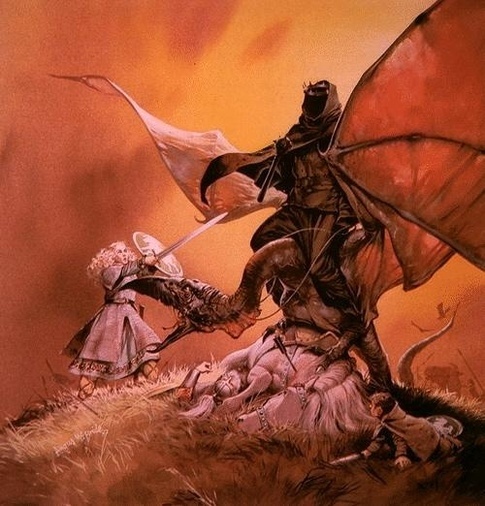
(The talented Tolkien artist, Joe Gilronan, has illustrated what Sam would have imagined singing this song– a clear contrast to the darkness surrounding him:)


Why is this, which seems like a last, desperate gesture, successful? After all, it not only revives Sam’s spirits, but it reaches Frodo who, badly injured as he has been, responds with the same song, enabling Sam to find him.
In Middle-earth, and in Arda more generally, song is both enjoyed and revered on a deeper level. The music of the creator Iluvatar is, as recounted in The Silmarillion, what brought the world into being, and it is such a strong force that Morgoth, the first dark lord, sought to challenge Iluvatar’s song and power with his own. Even here, however, music as a dark force failed.
“Then Iluvatar spoke, and he said: ‘Mighty are the Ainur, and mightiest among them is Melkor; but that he may know, and all the Ainur, that I am Iluvatar, those things that ye have sung, I will show them forth, that ye may see what ye have done. And thou, Melkor, shall see that no theme may be played that hath not its uttermost source in me, nor can any alter the music in my despite.’ ” (The Silmarillion)

Thus in The Lord of the Rings, we never hear an orc song, nor do we see singing, marching uruk-hai. They are beings created by Sauron, who has not the spiritual authority of Iluvatar, and, as Iluvatar is the ultimate creator of all life, so is he the creator of all music in Arda. In Middle-earth, besides the odd scene in The Hobbit in which the goblins sing in Goblin-town, we see only Elves singing (such as the Hymn to Elbereth), Hobbits (both snatches of Bilbo’s literary songs and drinking-songs), and Dwarves (it was their music which persuaded Bilbo to leave the Shire and join their journey).
Sam’s song, then, holds power in its own right—although it’s simply an old tune from home, its uttermost source is in Iluvatar and the first music, and it becomes clear why even a hobbit’s hum in the darkest of places can bring him comfort—it cannot be contested by darkness.
Thank you, as always, for reading.
MTCIDC,
CD