Tags
Adventure, Byzantine Empire, Byzantium, Constantinople, Gondor, Justinian, Megara, Mehmet II, Milton Waldman, Minas Arnor, Minas Tirith, Mont Saint Michel, Ottoman Empire, Ted Nasmith, The Lord of the Rings, The Tower of Guard, Theodosian walls, Theodosius, Tolkien
Welcome, as always, dear readers.
The title of this posting is taken from a very long letter (10,000 words), written to Milton Waldman probably in 1951 (Letters No.131, 157). Waldman represented the English publisher, Collins, which had expressed an interest in The Lord of the Rings and The Silmarillion when Allen & Unwin had been hesitant. Determined to justify the simultaneous publication of both, Tolkien wrote in great detail about the general narrative, with an emphasis upon the religious aspects.
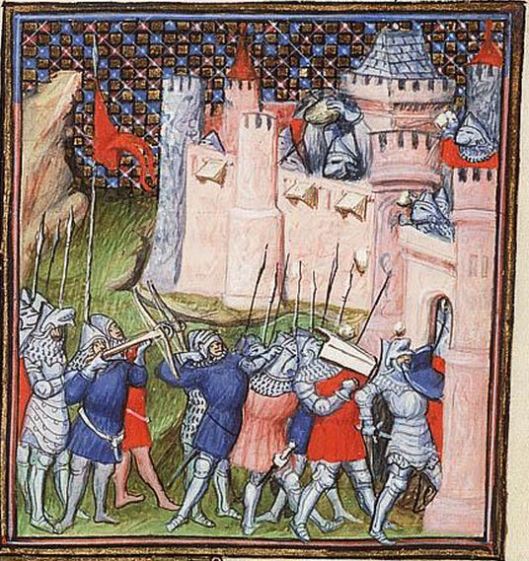
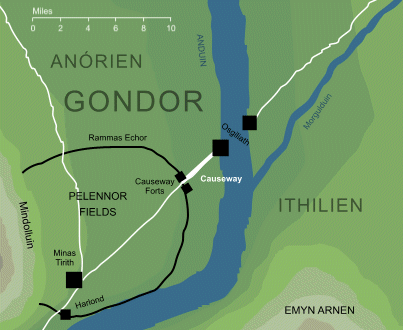
In the process, he likened Gondor to the Byzantine empire, a comparison which immediately attracted our attention. We ourselves had suggested in an earlier posting that the attack on its capital, Minas Tirith, had been like the siege of the Byzantine capital, Constantinople.


What was JRRT thinking of when he likened the two?
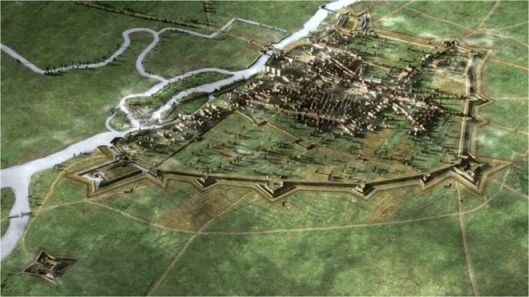
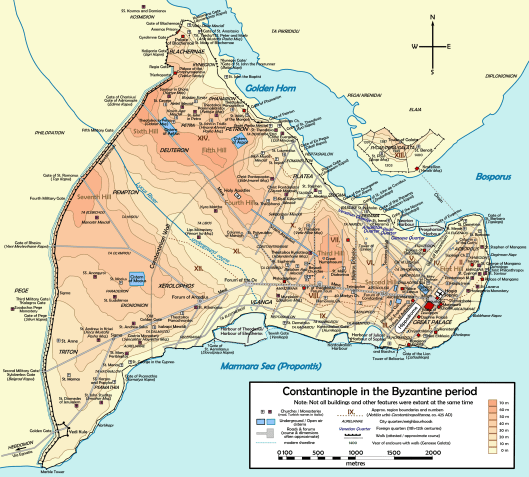
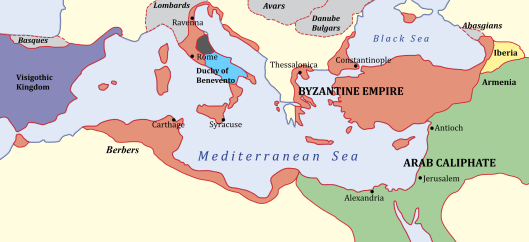
First, they both were—or had been—large kingdoms—in the case of Byzantium, an empire, really, as these maps demonstrate.
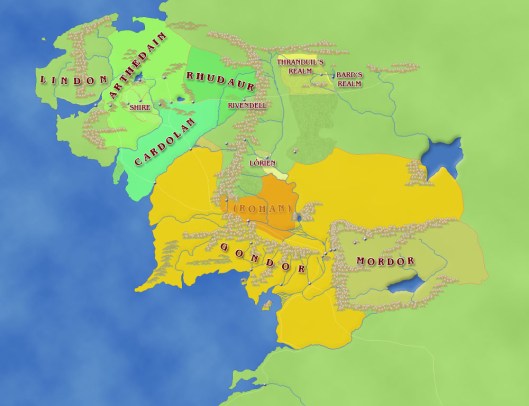
Their capitals were both of great age. Minas Tirith, “The Tower of Guard”, had been built originally as Minas Anor, “Tower of the Sun” in SA 3320 by Anarion, the younger son of Elendil, but only became the capital of Gondor in TA1640, after Osgiliath had been devastated by a plague. If we add its time in the Second Age (121 years) to the whole of the Third Age (3021 years), we reach a total of 3142 years at the defeat of Sauron. (For comparison, we might look at Athens, whose continuous habitation began before 3000BC, giving it a more-than-5000-year history.)
Constantinople, is old, by anyone’s standards, having been founded in 667BC as a Greek colony (there’s a bit of argument over the dating of this, which is typical of such things), and is still inhabited (and an absolutely amazing place!), but a bit younger than Minas Tirith at the time of The Lord of the Rings by some 500 years or so.
Third, there is the matter of the elaborate construction of these capitals.
“For the fashion of Minas Tirith was such that it was built on seven levels, each delved into the hill, and about each was set a wall, and in each wall was a gate. But the gates were not set in a line: the Great Gate in the City Wall was at the east point of the circuit, but the next faced half south, and the third half north, and so to and fro upwards; so that the paved way that climbed towards the Citadel turned first this way and then that across the face of the hill. And each time that it passed the line of the Great Gate it went through an arched tunnel, piercing a vast pier of rock whose huge out-thrust bulk divided in two all of the circles of the City save the first. For partly in the primeval shaping of the hill, partly by the mighty craft and labour of old, there stood up from the rear of the wide court behind the Gate a towering bastion of stone, its edge sharp as a ship-keel facing east. Up it rose, even to the level of the topmost circle, and there was crowned with a battlement; so that those in the Citadel might, like mariners in a monstrous ship, look from its peak sheer down upon the Gate seven hundred feet below.”
The Lord of the Rings, Book 5, Chapter 1, “Minas Tirith”
Here’s one of our favorite paintings (by Ted Nasmith—one of our favorite Tolkien artists).

And here’s the film.

The designers have said that they were influenced by the look of Mont Saint Michel, a medieval monastery just off the coast of Normandy in France.
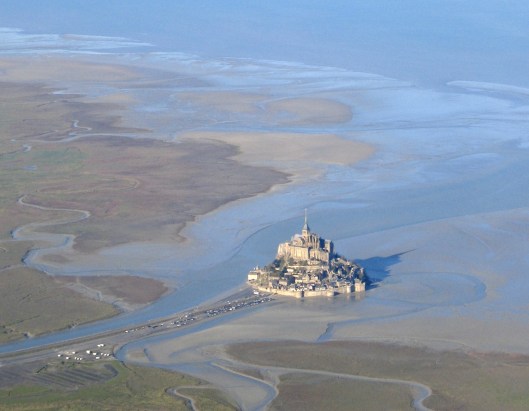


The complex nature of the place is captured in this diagram.

Byzantium (or, Constantinople, its later name) began its life, as we said, as a colony of the Greek mainland city of Megara. In the 4th century AD, the Roman emperor Constantine I, the last survivor in a long civil war, chose the site for his new capital. As much of the weight, both of commerce and defense, lay in the eastern part of the Roman world by this time, he chose very wisely: his new city was placed to control trade with the rich Black Sea region and to provide a strategic jumping-off point for dealing with invaders and emerging kingdoms in Asia Minor.
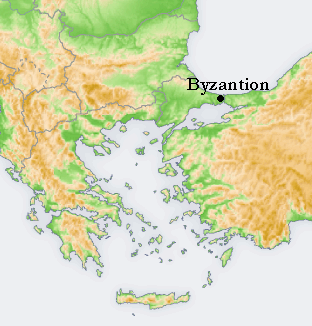
The position was also well-chosen for defense, being at the end of a peninsula—the main strategy then being its walling-off from the mainland.

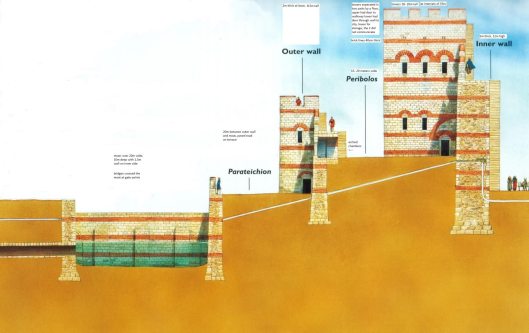
There is, of course, a big difference here between the 7 levels and 7 gates of Minas Tirith and the two walls—the older inner 4th-century one of Constantine and the slightly-later (early 5th century) walls of Theodosius II. Nevertheless, those later walls were well-constructed, in two successive lines, with a moat on the outside.

The Theodosian walls were about a mile-and-half from the older, Constantine wall, encompassing a population which, at its height, may have been over 400,000 in number. By the time of its fall to the Ottoman army in 1453, that number had dropped to perhaps only 50,000, which reflected the gradual shrinking of the empire from its greatest size, in the 6th century

under the emperor Justinian

when it encompassed the majority of the Mediterranean basin, to its last, worn-out phase in the early 15th century, when it controlled a few scattered outposts, but mainly the area directly around the capital.

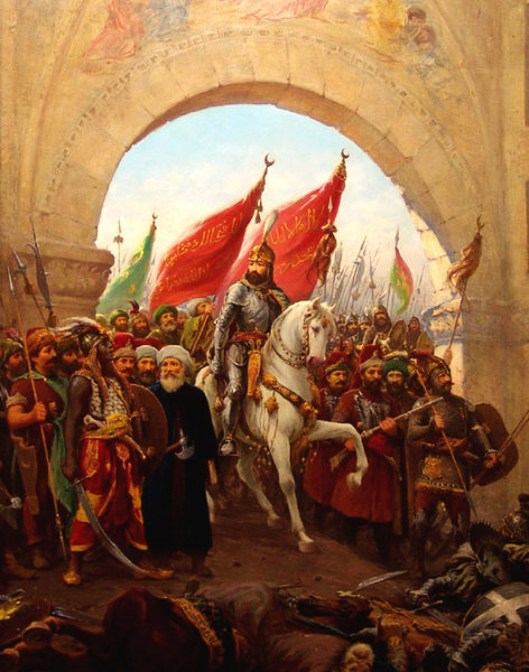
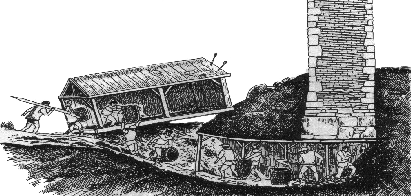
This shrinking of the empire and of its population proved disastrous for the capital. When the Ottoman army, under Mehmet II, arrived outside the walls in the spring of 1453, the imperial government could only provide 7000 defenders, 2000 of whom were foreigners, to defend about 3 and ½ miles of wall (that’s 5 ½ km). Against them were anywhere from 50 to 80,000 attackers, who brought with them (or cast on the spot), massive artillery pieces and, after a 53-day siege, broke into the city and put an end to an empire which had lasted for over 1100 years.
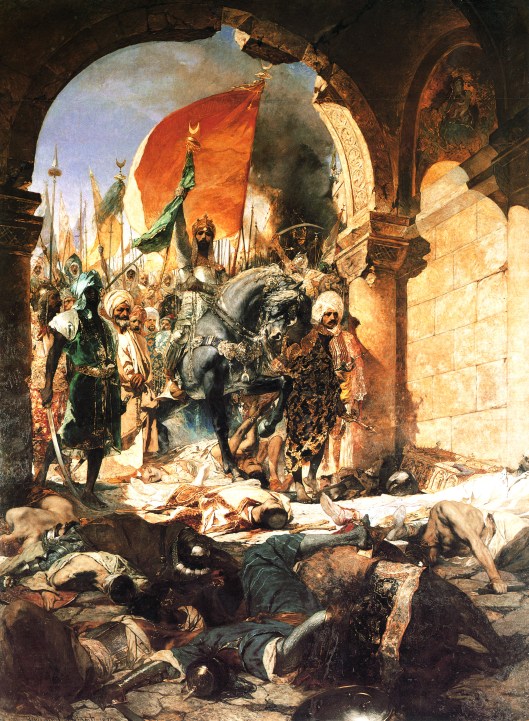


And this is the last sad similarity with Gondor and its capital, as we see through Pippin’s eyes:
“Pippin gazed in growing wonder at the great stone city, vaster and more splendid than anything that he had dreamed of, greater and stronger than Isengard, and far more beautiful. Yet is was in truth falling year by year into decay, and already it lacked half the men that could have dwelt at ease there. In every street they passed some great house or court over whose doors and arched gates were carved many fair letters of strange and ancient shapes: names Pippin guessed of great men and kindreds that had once dwelt there; and yet now they were silent, and no footsteps rang on their wide pavements, nor voice was heard in their halls, nor any face looked out from door or empty window.”
The Lord of the Rings, Book 5, Chapter 1, “Minas Tirith”
And, just as in the case of Constantinople, the capital of Gondor was hard-pressed to defend itself. Luckily for it, however, there was an uncrowned king with a ghostly army, a brave reinforcement of southern yeomen, a mass of wild horsemen from the north, a wizard, and the fulfillment of an ancient prophecy about a witch king to aid it in its hour of need…
Thanks, as always, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD