Tags
14th century, 15th century, Adventure, Agincourt, Anglo-Saxon, armor, Bayeux Tapestry, feudalism, Fyrd, Gerry Embleton, Huscarl, Luttrell Psalter, Middle-earth, N.C. Wyeth, tapestry, The Lord of the Rings, Tolkien
Welcome, as always.
In this posting, we want to conclude what has turned out to be a kind of mini-series on Feudalism in Middle Earth. Two postings ago, we used the 14th-century Luttrell Psalter to illustrate what working the plowland behind the Rammas Echor might have looked like. In our last, we used the Bayeux Tapestry to offer another possible visual influence on Tolkien’s depiction of the Rohirrim: the conquering Normans. In this final posting, we will look at the forces of Rohan’s ally, Gondor and will use a number of sources, both medieval and modern.
In the Jackson movies, there is a kind of regularity, from Osgiliath to Minas Tirith in what we are shown.

This is not surprising if the cue for costuming has come primarily from one description:
“The Guards of the gate were robed in black, and their helms were of strange shape, high-crowned, with long cheek-guards close-fitting to the face, and above the cheek-guards were set the white wings of sea-birds; but the helms gleamed with a flame of silver, for they were indeed wrought of mithril, heirlooms from the glory of old days. Upon the black surcoats were embroidered in white a tree blossoming like snow beneath a silver crown and many-pointed stars. This was the livery of the heirs of Elendil, and none wore it now in all Gondor, save the Guards of the Citadel before the Court of the Fountain where the White Tree once had grown.” (The Return of the King, Chapter 1, “Minas Tirith”)
We have no wish to criticize—in this respect, at least—the creators of the films for taking what might appear to be an easy out: uniformity being cheaper than individuality, since it’s clear that, when it came to dramatic effects in the films in general, the old theatrical advertising line, “No Expense Was Spared To…” is really true. Instead, we want employ our former method of consulting medieval manuscripts, as well as another passage from the same chapter, to offer another possible view, one which might have influenced the author in his depiction of the defenders of Gondor.
We’ll begin with the passage:
“Leading the line there came walking a big thick-limbed horse, and on it sat a man of wide shoulders and huge girth, but old and grey-bearded, yet mail-clad and black-helmed and bearing a long heavy spear. Behind him marched proudly a dusty line of men, well-armed and bearing great battle-axes; grim-faced they were and shorter and somewhat swarthier than any men that Pippin had yet seen in Gondor…
And so the companies came…The men of Ringlo Vale…from the uplands of Morthond…five hundred bowmen…From the Anfalas…a long line of men of many sorts, hunters and herdsmen and men of little villages, scantily equipped save for the household of Golasgil their lord. From Lamedon, a few grim hillmen…Fisher-folk of the Ethir…Hirluin the Fair…with three hundreds of gallant green-clad men. Imrahil…with gilded banners bearing his token of the Ship and the Silver Swan, and a company of knights in full harness riding grey horses; and behind them seven hundreds of men at arms, tall as lords, grey-eyed, dark-haired, singing as they came.”
There is actually not a lot of detail here, but there are a few hints. First off, there are those “great battle-axes”. Here are two images from the Bayeux Tapestry of the Anglo-Saxon king, Harold’s, bodyguards, his huscarl, armed with their characteristic long-handled axes.

And here is a modern reconstruction.

Next, we have those five hundred bowmen from Morthond. The Tapestry can provide a useful image of those,

but perhaps what JRRT really was thinking of were the famous longbowmen of Crecy and Poitiers and Agincourt, whose skill and courage knocked down whole waves of equally brave French knights. Here are a pair of modern images by the brilliant historical illustrator, Gerry Embleton, himself a medieval reenactor.
Besides the huscarl, King Harold’s army was made up of the fyrd, a kind of militia drawn from the freemen of the countryside, who had to provide their own weapons and equipment and were only required to serve for limited periods—they would have been farmers, most of them, after all, and couldn’t be off the farm for too long without threatening their own livelihoods. Perhaps these could suggest that “long line of men of many sorts”. Here’s an image from the Tapestry of what appears to be the fyrd fending off a mounted Norman attack. You’ll notice the lack of defensive armor.

“gallant, green-clad men” is rather vague, but, suddenly, all we could see is Robin Hood and his Merry Men. And so we can’t resist including some of our favorite N.C. Wyeth illustrations.


And these could easily provide the model for the rangers in South Ithilien, couldn’t they?

Last, there is that “company of knights in full harness”. This presents a real problem. Knights from which period? The armor available at the time of the Bayeux Tapestry in the mid-11th century

and which, we suggested in our last, might be good for the Rohirrim, was very different from that of later times. Here’s the armor of the days of Sir Geoffrey Luttrell,
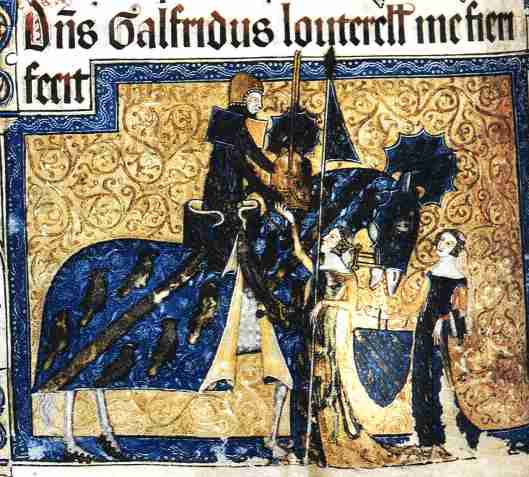

in the early 14th century—
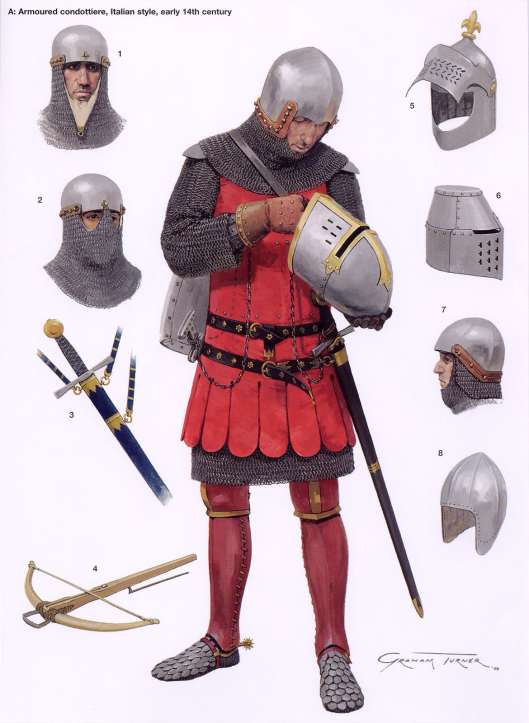

and here’s what the English archers would have faced as worn by their valiant French opponents at Agincourt, in 1415.
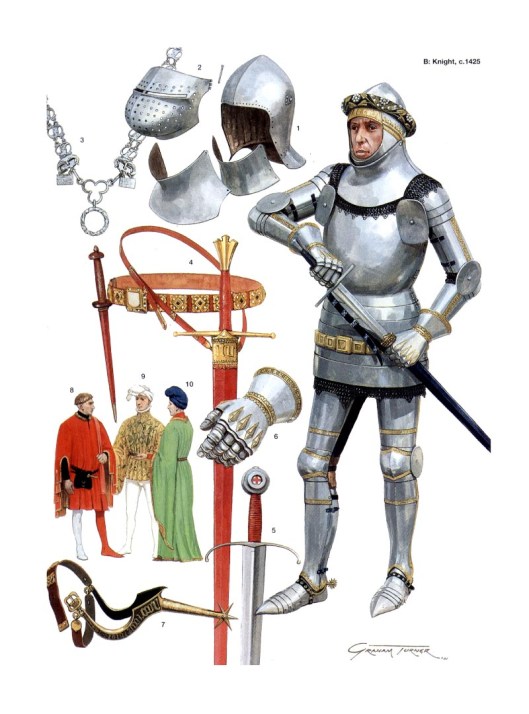

This handy chart can give you a diachronic (through-time) view of changes in medieval armor.

If we look at something produced through the workshop of William Morris, that strong influence upon JRRT, we find this group of knights from a set of tapestries produced in the 1890s.

The armor is pretty vague (the systematic study of the history of armor was still in its childhood then—if you’re interested in the early days, google Sir Samuel Rush Meyrick to learn about its first great scholar), but one of the helmets—the one to the far left in the background, looks like a visored sallet, which could date what we see in the tapestry to the later 15th century.

(Sharp-eyed readers who are Star Wars fans—we are—will recognize this general pattern from the technical people on the Death Star—

We might add that Morris and his friends were strongly influenced by pre-Renaissance and early Renaissance painters, so perhaps this picture, one of a set of 3 by Paolo Uccello from the middle of the 15th century, might also provide a possible model (and we’re glad to show you the whole set because we think that they’re just magical).


Taken all together, these produce a very different image from the films, don’t they? Much more individual, often much less well-equipped, more actual medieval, as we would imagine the author had had in mind. So—contrast this
with this:

Which do you prefer, dear readers?
Thanks, as always, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD