Tags
1930s England, A Long-Expected Party, Bellerophon, Governor of the King's Posts, Henry VIII, London, mail coach, Orality, Penny Black, pillar box, Pony Express, Postal Service, Postmen, Rowland Hill, Royal Mail, semata lugra, Shire, Shirriffs, Sir Brian Tuke, stamps, The Illiad, The Lord of the Rings, Tolkien
(For Aunt Cathy—she knows why.)
“Mr. Bilbo has learned him his letters—meaning no harm, mark you, and I hope no harm will come of it.” Gaffer Gamgee, The Fellowship of the Ring, Ch.1, A Long-Expected Party
Welcome, as always, dear readers.
We’ve written a little before about aspects of literacy in Middle-earth and we will probably do so again, since the idea of reading and writing in what is, basically, an heroic world interests us very much.
Ordinarily—with a few exceptions (South Slavic pjesme, “songs” sometimes have examples)—we don’t think of writing as being an important feature of heroic stories, but our interest in such things began some years ago with an odd little reference in The Iliad. In all of the story (or in Homer in general for that matter), this is the only mention of what appears to be writing. We say “appears” because the actual writing is called semata lugra, not, in fact, a clear reference to writing, but often translated as something like “baneful signs”. We won’t get into the long, complex controversy over orality and literacy in Homer (although we have strong opinions on the subject) here, but rather point to what these semata were supposed to do. They were inscribed on tablets.


The tablets were sealed and given to a carrier—in this case, the hero Bellerophon—

to take with him to the person who would open the tablets, read them, and then—have him killed! That certainly makes those semata lugra. The fact that the tablets were closed suggests that, whatever those “signs” were, the sender thought that the carrier would be able to read them, too, giving us a wider picture of the use of such signs, whatever they might actually be.
But now we come to the Shire, and to a world which is domestic, long before some of its inhabitants become heroic.
At the beginning of The Hobbit, Bilbo is enjoying a pipe in the morning air when a very disturbing figure appears.

His mocking words are soon too much for the Hobbit, who “Then…took out his morning letters, and began to read, pretending to take no more notice of the old man.” (The Hobbit, Ch.1, An Unexpected Party)
As we were once intrigued by the semata lugra, we are now interested in these letters. Douglas Anderson, in his note (15) to this sentence in The Annotated Hobbit supplies the information that “In England in the 1930s there were at least two mail deliveries per day—hence the distinction of morning letters.” (39) If the Shire is like 1930s England, which it sometimes appears to be, even as Tolkien denies that “There is no special reference to England in the ‘Shire’—except of course that of an Englishman brought up in an ‘almost rural’ village of Warwickshire on the edge of the prosperous bourgeoisie of Birmingham…” (draft of a letter to Michael Straight, “probably January or February 1956”, Letters, 235), then Bilbo is in the enviable position of one who is in the care of The Royal Mail—or, in this case, its Shire equivalent. Or is he?
The Royal Mail as a branch of government took off in the time of Henry VIII, with the appointment of Sir Brian Tuke (respell that and where in the Shire might you find him?) as Master of the Posts (1512), then Governor of the King’s Posts (1517).

Much, if not most of the correspondence of that period was literally royal—the government’s business, not private correspondence, but, over time, this gradually changed until, by the late 18th century, postmen had an official uniform

and there were places were letters were received and sorted.
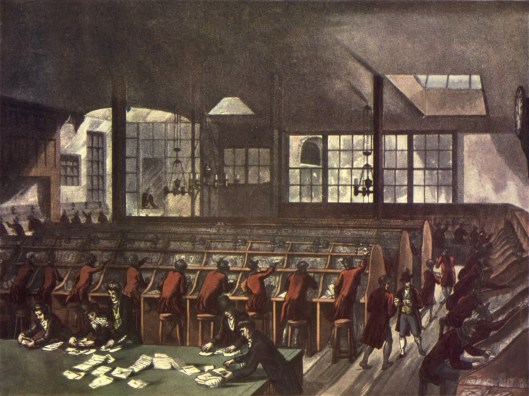
There were problems of corruption in the system, as well as a basic difficulty: the sender didn’t pay for the letter—the receiver did. Thus, there was no assurance that the service would be paid for, beyond whatever government subsidies were allowed to it. All of this began to change in 1837, however, with this privately-printed and circulated pamphlet

by the education (and, in time more general) reformer, Rowland Hill.

He proposed to reverse the process: the sender would pay and there would be strict regulation of the charge (and, for ordinary letters a very low charge at that). Initially, the idea was to use an already franked (that is, with a mark showing that it had been paid for) form on which one might write a message, fold it, and send it.

This was not a new idea and had been used since the 17th century, at least.
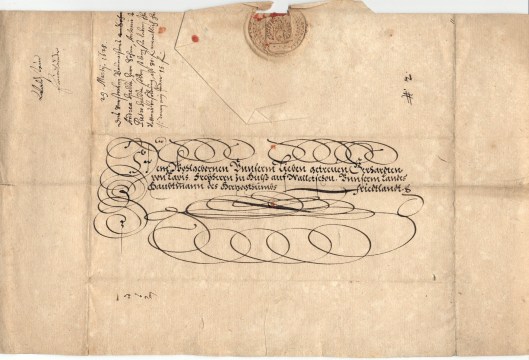
Hill quickly followed this with the idea of a stamp which could be readily attached to a letter—commonly a sheet which, once written upon, could then be folded into its own container.
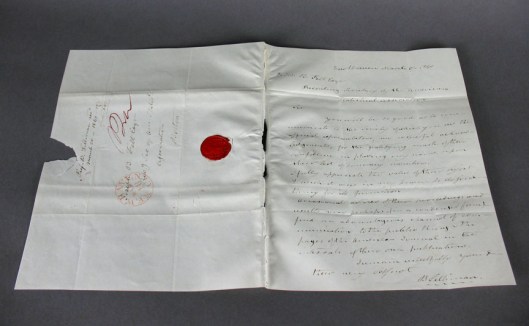
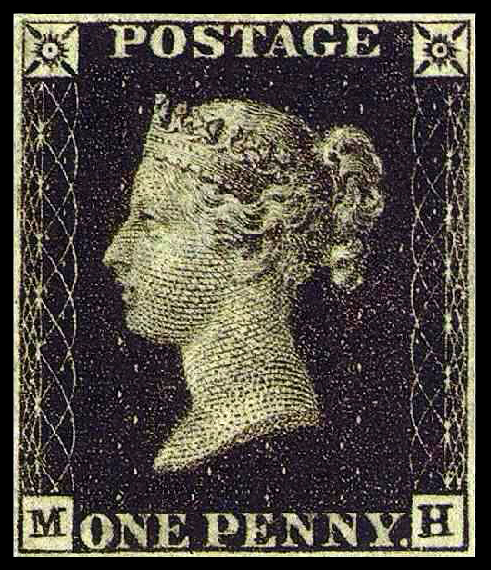
This could also be attached as we do, to a pre-made envelope, into which the folded letter might be placed. This was the first modern stamp, the so-called “Penny Black”.

After 1853, there were even special public mail boxes into which you might place your letters for collection.

Delivery in big cities like London would, by the late 19th-century, begin at 7:30 in the morning and go to 7:30 in the evening, so that you could write a note to a friend across the city, drop it into a pillar box (mailbox to people in the US) at 7:30 am

and expect a reply sometime during the same day.
Behind all of this was an increasingly-complex government backed by a well-established bicameral legislature, with an increasingly-large tax base. But what of the Shire?
The government of the Shire seems to be sketchy, at best. Tolkien gives us the total picture on in the Prologue to The Lord of the Rings.
“The only real official in the Shire at this date was the Mayor of Michel Delving (or of the Shire), who was elected every seven years…As mayor almost his only duty was to preside at banquets…But the offices of Postmaster and First Shirriff were attached to the mayoralty, so that he managed both the Messenger Service and the Watch. These were the only Shire-services, and the Messengers were the most numerous, and much the busier of the two. By no means were all Hobbits lettered, but those who were wrote constantly to all their friends (and a selection of their relations) who lived further off than an afternoon’s walk.
The Shirriffs was the name that the Hobbits gave to their police…There were in the Shire only twelve of them, three in each Farthing, for Inside Work.”
So, in contrast to the elaborate workings of the Royal Mail, we are left with a series of questions: if there is a Postmaster—and clearly there is a post—how does it work? Is it all on foot? Is there the equivalent of the Pony Express? Nob, at the Prancing Pony, is called a “slow-coach”—were there once mail coaches, as in England?

(Is this the only mention of such carriages in all The Lord of the Rings and The Hobbit? There are certainly wagons—there was even an invasion of “the Wainriders” once upon a time—see Appendix A of The Lord of the Rings.)
How were letters collected? Distributed? Is there a central post office, perhaps in Michel Delving, the closest thing to a capital in the Shire? And, of course, how was it all paid for? In an earlier posting, we talked a little about coinage in Middle-earth and we tried to imagine what Gondorian currency might have looked like—can we imagine Shire postage stamps?
When you read the following, think of your own postal service and join us in wondering about all of the above:
“Before long the invitations began pouring out, and the Hobbiton post-office was blocked, and the Bywater post-office was snowed under, and voluntary assistant postmen were called for…” The Fellowship of the Ring, Ch.1, A Long-Expected Party

Thanks, as ever, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD































