Tags
ABC Alphabetical Railway Giude, Agatha Christie, anachronism, Bag End, Bradshaw's Railway Companion, clocks, Egyptian, feudalism, Gros Horloge, hour glases, Liverpool and Manchester Railway, Macbeth, Medieval, Normandy, Pope Sylvester II, railways, Rouen, Salisbury Cathedral clock, Shakespeare, sundial, The Lord of the Rings, Tolkien, Wapping tunnel, water clocks, Wells Cathedral
Welcome, as always, dear readers.
In our last, we puzzled over something in the entryway to Bag End.

It’s that thing to the left of the door. It looks rather like a clock (which is what we thought before examining it more closely), but it is, in fact, a barometer—and a very puzzling thing for Bilbo to have, as we suggested.
On the right hand wall, however, there is another puzzling object: an actual clock.
In our world, of course, this is no puzzle at all, clocks being so common. In fact, our major way of indicating time in English is to say, “It’s 11 o’clock”, where “o’clock” is a contracted form of “of the clock”. Even if, like many in our world, you get your time from your phone, you’ll still say this, won’t you?

This has been the case since the 16th century, as we can see in Shakespeare’s plays—including moments when characters who live in times before clocks still talk about them, as in Macbeth, Act II, Scene 4, where Macbeth’s cousin, Ross, says to an Old Man, “By th’clock ‘tis day”, when the historical Macbeth lived in the 11th century AD, perhaps 200 and more years before clocks began to appear in western Europe.
Although we’ve seen it regularly cited that Pope Sylvester II

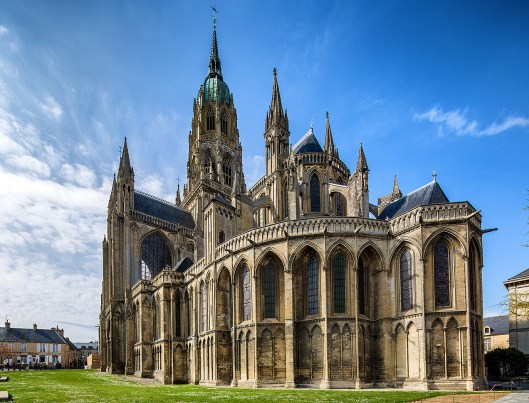
invented the first mechanical clock in the 990s AD, we have yet to see anything in the way of concrete evidence that this is so. Rather, we see the first clocks to have appeared in the later 14th century, including the Salisbury Cathedral clock, which perhaps dates from 1386.
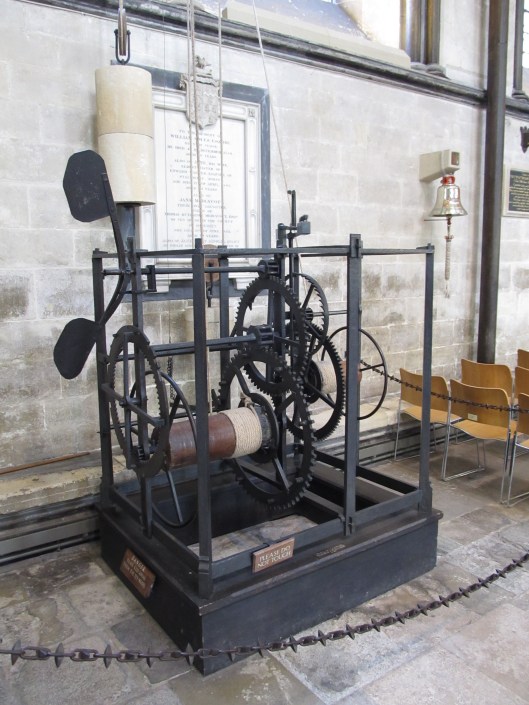
Likewise there is the clock of Wells Cathedral, tentatively dated to about the same time
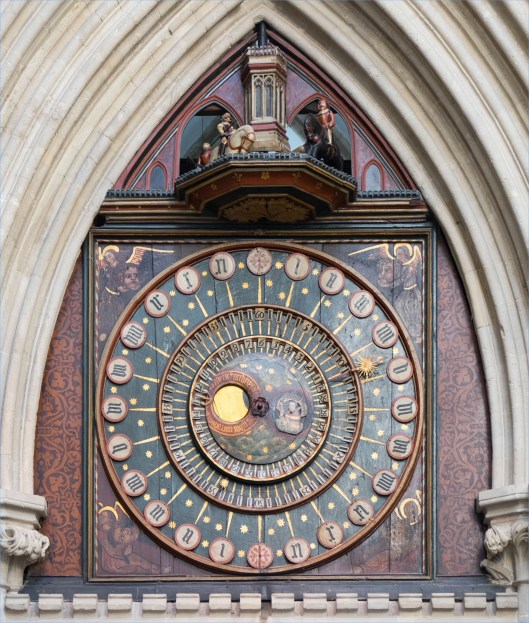

or the Gros Horloge in Rouen, in Normandy, whose internal workings date from 1389.
And the pendulum clock—which is what is visible on the right hand wall of Bag End—is an even later invention, credited to the Dutch scientist of the mid-17th century, Christian Huygens.
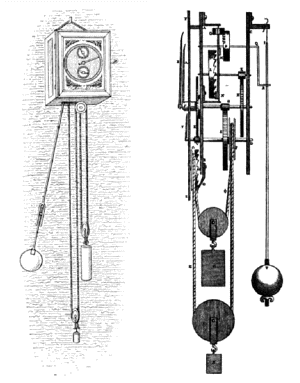

Long before such devices, people marked time by such things as hour glasses (possibly medieval? Lots of discussion about this, but there is documentation that medieval ships’ captains began to use them)

and water clocks (used in Athenian court rooms to control speeches—when citations of established law were read in court, the order was to “stop the clock”, as reading law as evidence clearly wasn’t considered to be part of a speech)
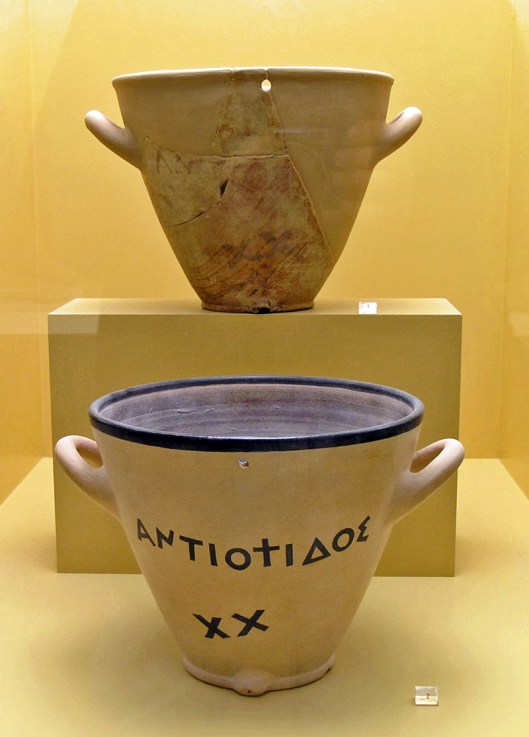

and even put the sun to work, using its moving shadow to tell the time. (This is the earliest sundial we’ve seen—it’s Egyptian, from the 13th century BC)

(And just a linguistic footnote on “telling time” as a sort of pun. On the one hand, we read time off a device—and, if asked, aloud—so that we are “telling—that is reciting—the time”. At the same time, an older usage of the verb “to tell” was “to count”. This is preserved in the “teller” in a bank, by someone “telling” a rosary, and by “tolling” a bell. It can also be seen in other Germanic languages, like Danish, which has the verb “taelle”, “to count”, and German, “zaehlen”. So, when you “tell” time, you’re both deciphering the information from a device—possibly aloud—and doing so by counting.)
All of which leads us back to Bilbo’s clock, on a wall in the Shire.
As far as we can tell, at the end of the Third Age, the Shire was primarily a non-feudal medieval agricultural world.

Such worlds are, considering how much the sun is involved in growing things like grain,

governed by daylight, which is, on the whole, easy to mark and measure. (A difficulty for sundials, of course, is that the sun changes position throughout the year and the hours of daylight can vary greatly. Perhaps this is why there is a famous sundial motto: “Horas non numero nisi serenas”—“I count only the fair—that is, sunny—hours”.)

So why is there a pendulum clock on that wall?
A partial answer might be the same as that for the barometer: JRRT is recreating something from his own past, or even from his present—the big dial looks later to us than the 1890s. Just as in the case of that reference to Bilbo shrieking “like the whistle of an engine coming out of a tunnel” (The Hobbit, Chapter One, “An Unexpected Party”), it mirrors Tolkien’s own world—a world in which railways in Britain were a major influence on changes in marking time.
Railways had begun to appear in 1830, with the Liverpool and Manchester Railway.

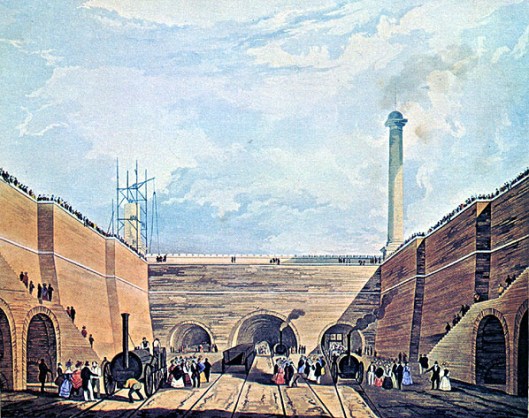
(And here, by the way, is an engineering marvel of the time—the 1.25-mile long Wapping tunnel, dug to allow the railway’s passage into Liverpool and the first such tunnel to be constructed under a city. Seeing this 1831 illustration, it’s easy to imagine what kind of shriek Bilbo must have made!)

By 1840, building and traffic had increased dramatically and, as the rail lines stretched across England, an awkwardness appeared: there was no uniform time standard. Towns close to each other might share the same time, but those between London and Liverpool, say, had their own methods of marking time and so attempting to produce a dependable schedule for a train’s journey was nearly an impossibility along the 178 miles (287km) between the two cities.
Those in charge of the early railways quickly saw the difficulty and began, as early as 1840, to standardize the measurement of time along their routes. By the late 1850s, standardization had been mainly achieved—although it was only in the 1880s that the government stepped in to complete the progress.
This regularizing of time produced, on the one hand, standard railway timetable books, like Bradshaw’s Railway Companion
(first published in 1839 and often consulted by Watson and Holmes on their extra-London adventures) and The ABC Alphabetical Railway Guide

(first published in 1853 and the basis of Agatha Christie’s 1936 novel, The ABC Murders). On the other hand, it also produced standardized time in general, eventually going global, something which the industrial revolution increasingly demanded as part of its production cycle and now so deeply ingrained that virtually everything we do is influenced by it and we even incorporate it into our bodies, either tying it to our wrists

or wear it as part of our clothing.

Work, school, even fun (movies begin on time schedules, television is one long schedule, as well as certain elements of the internet—although the internet does offer the subversive possibility of doing things “on your own time”), all of it moves to the measured tick of time. In 1937, the year after Agatha Christie’s novel based upon railway timetables was published, JRRT would have felt it, from his lecture schedule to the evening radio broadcasts of the BBC.
Almost as if it were a gathering force of the MODERN WORLD, then, the measurement and standardization of time has crept up, from the later medieval world on. We can see that Shakespeare was influenced by it—in Julius Caesar (1599?), Act II, the jumpy Brutus and Cassius listen to the sound of a clock striking three—in a world where there would be no clocks to strike for almost 1400 years (but providing us with the title of this post). Is it any wonder, then, that clocks could have slipped into Middle-earth? And, besides, they do have a use for Bilbo—how else could he shout to the dwarves as he left them, “If ever you are passing my way…don’t wait to knock! Tea is at four…” (The Hobbit, Chapter Eighteen, “The Return Journey”)?
Thanks, as ever, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD