Tags
19th Century, An Introduction to Old Norse, Bag End, Beorn, Charles Dodgson, E.V. Gordon, Edwardian, Elvenking, Furniture, Goblins, Hildebrandts, House, Iron Age Farmhouse, Lewis Carroll, Listen with Mother, Master of Laketown, Monty Python, Norse house, Sackville-Bagginses, The Hobbit, Through the Looking-Glass, Tolkien, Victorians
Welcome, dear readers, as always.
Several times, Monty Python skits included the pattern, “Are you sitting comfortably? Then I’ll begin.”

It was clear, when we first heard it, that, like so much of Python material, it was one of those references which an audience in Britain in the early 1970s would have understood immediately and chuckled at, but it was only with the advent of the all-knowing Wikipedia that the reference came clear to us. (Here’s a LINK, so that, if you don’t know it already, you, too, can be suitably enlightened.)
But it made us think—not everything does, we promise!—of Tolkien and what must sound like a very odd subject—furniture.
Furniture?
Consider Bilbo’s Bag End:
“The Door opened on to a tube-shape hall like a tunnel: a very comfortable tunnel without smoke, with paneled walls, and floors tiled and carpeted, provided with polished chairs, and lots and lots of pegs for hats and coats…The tunnel wound on and on, going fairly but not quite straight into the side of the hill—The Hill, as all the people for many miles round called it—and many little round doors opened out of it, first on one side and then on another. No going upstairs for the hobbit: bedrooms, bathrooms, cellars, pantries (lots of these), wardrobes (he had whole rooms devoted to clothes), kitchens, dining-rooms, all on the same floor, and indeed on the same passage…” (The Annotated Hobbit, Chapter 1, “An Unexpected Party”)
Here is JRRT’s version of the entryway–with Bilbo—or is that JRRT himself? There appears to be a strong resemblance…
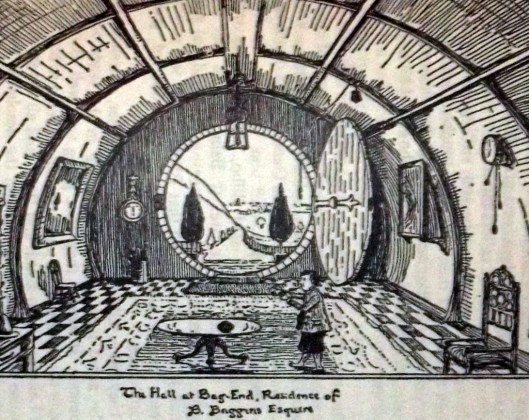

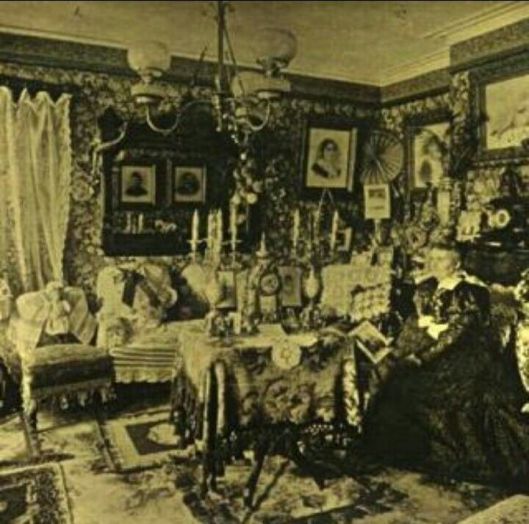
As the narrator tells us, “This hobbit was a very well-to-do hobbit…”, but, at the same time, we could easily see this description (ignoring the fact that it’s about a hole, albeit “not a nasty, dirty, wet hole…nor yet a dry, bare, sandy hole…it was a hobbit-hole, and that means comfort”) applied to the kinds of late-Victorian/Edwardian interiors with which Tolkien was familiar.

People of this world—middle-class England—seem to have loved to live among piles of possessions—heavy furniture, thick carpets, heavy drapes, and knickknacks galore.

(Oh–and swords, apparently.)
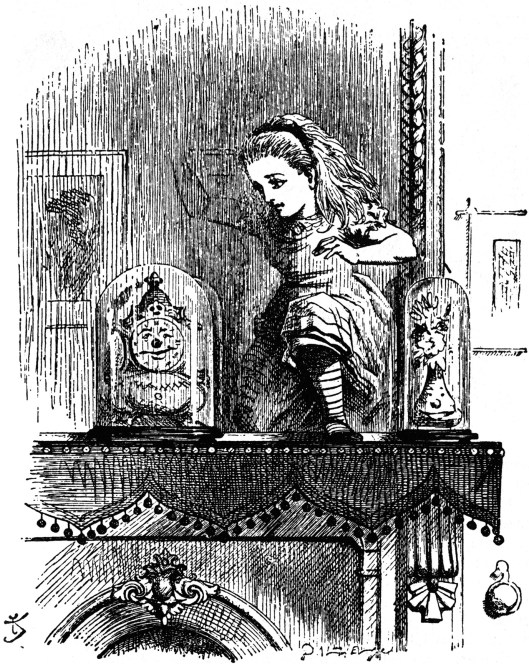
To us, this has a slightly claustrophobic effect—and we imagine that it may be why Alice in Through the Looking-Glass (1871) attempts to escape it–
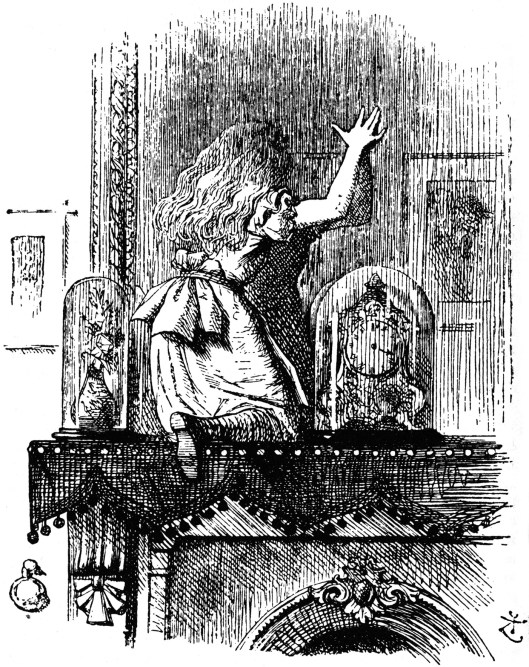

only to find herself in a distorted version of the same room on the other side of the mirror.
[Here’s the actual mirror, from the childhood home of the real Alice, which is said to have inspired Charles Dodgson/Lewis Carroll to write a sequel to the first Alice book.]

What about other Middle-earth interiors, beginning in The Hobbit?
Surprisingly, there is really nothing before the Dwarves and Co. reach Beorn’s house. There is no description of any inside in Rivendell and, beyond that, the only “indoors” we see before Beorn is the main cave of the goblins and the only “furniture” is this:
“There in the shadows on a large flat stone sat a tremendous goblin…” (The Hobbit, Chapter 4. “Over Hill and Under Hill”)

Beorn’s house, as we see in Anderson’s The Annotated Hobbit (170-171), appears to be based upon an illustration to be found in E.V. Gordon’s An Introduction to Old Norse (1927) (with an older history yet—see Anderson, 171).
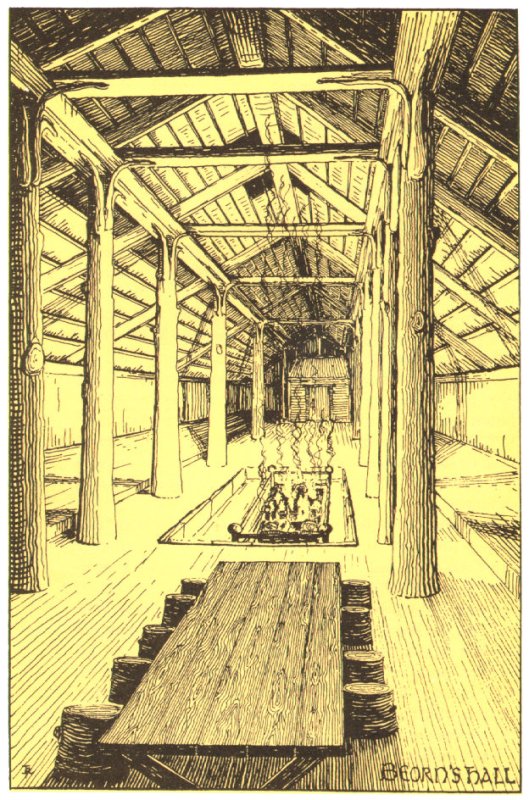

The Hildebrandts saw Beorn’s house as rather like a giant log cabin,

but we imagine the outside of Beorn’s house to look rather more like this view of an Iron Age farmhouse
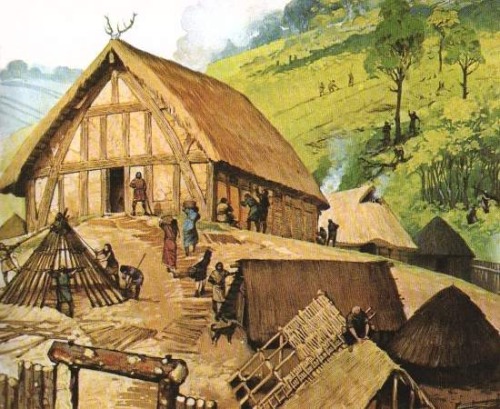

And here’s a reconstruction of a Norse house interior which is a little more “lived-in”, to give you the idea of what Beorn’s house might look like day-to-day (without the magic animals, unfortunately).

As Tolkien’s illustration shows, however, this is hardly based upon a Victorian parlor! As the narrator describes it (with magic animals as the kitchen staff):
“Quickly they got out boards and trestles from the side walls and set them up near the fire…Beside them a pony pushed two low-seated benches with wide rush-bottoms and little short thick legs for Gandalf and Thorin, while at the far end he put Beorn’s big black chair of the same sort…These were all the chairs he had in his hall…What did the rest sit on?…The other ponies came in rolling round drum-shaped sections of logs, smoothed and polished, and low enough even for Bilbo…” (The Hobbit, Chapter 7, “Queer Lodgings”)
Beyond Beorn’s house, there is mention that the Elvenking sat “on a chair of carven wood” (The Hobbit, Chapter 9, “Barrels Out of Bond”) and the Master of Laketown has a “great chair” (The Hobbit, Chapter 10, “A Warm Welcome”), but we have come deeper into the Middle-earth/medieval world, it seems, where furniture (at least in the narrator’s view) is sparse and we will only begin to see more abundance, at least in a general way, when we return to the Shire and the unwelcome event of the auction of Bilbo’s possessions on June 22nd:
“The legal bother, indeed, lasted for years…and in the end to save time Bilbo had to buy back quite a lot of his own furniture.” (The Hobbit, Chapter 19, “The Last Stage”)
“Furniture” is, unfortunately, a vague word, mentioned just previously in relation to the Sackville-Bagginses who were “busy measuring his [Bilbo’s] rooms to see if their own furniture would fit.” We’ll have to make do here with our original idea of Bilbo the Middle-earth Victorian’s house,

but, in our next, we’ll have a look at households (and palaces) in The Lord of the Rings, to see what we may find (and we have a hunch the inventory will include a quantity of thrones…)
Thanks, as ever, for reading!
MTCIDC
CD


















