Tags
battering ram, Fantasy, Helm's Deep, Helms Deep, Hera, Hornburg, mangonel, movies, siege, siege tower, sieges, The Lord of the Rings, The War Of the Rohirrim, Tolkien, trebuchet, undermining, Wulf
Welcome, as always, dear readers.
This is another in a short series of mini-reviews of The War of the Rohirrim, a film which I’ve now, as is my custom, seen several times before I review it. It’s complex enough, I would say, to make it worth taking it apart and reviewing different sections/details–for another in the series, see: Heffalumps? 31 December, 2025. The previous review was about the introduction of a mumak into the story, for which there was no textual authority in the 2+ pages of the original in Appendix A of The Lord of the Rings and, on the same theme, I want to talk a little more about that earlier war.
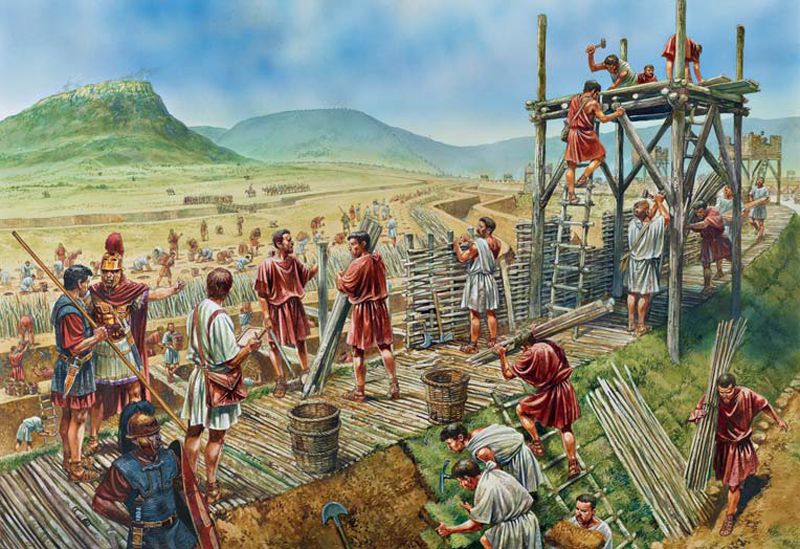
If you were an ancient Roman
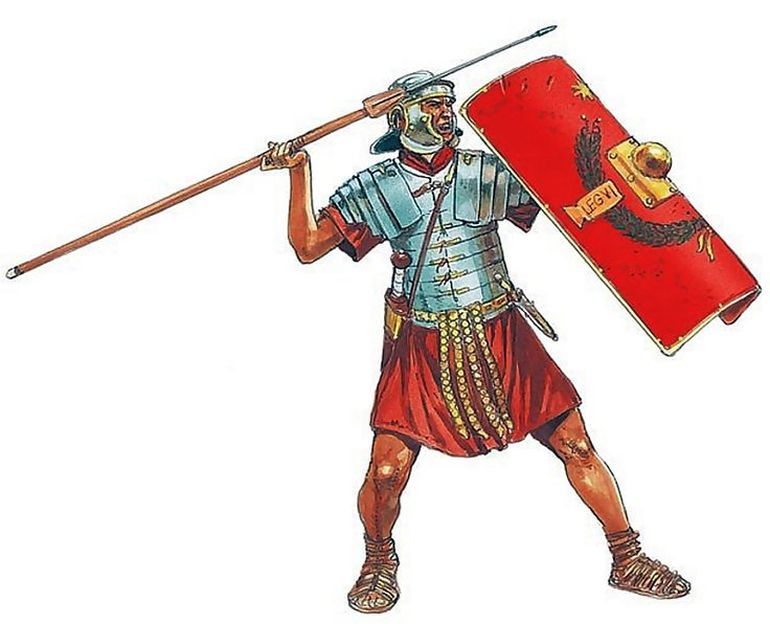
or medieval

soldier, and you were faced with an enemy’s wall,

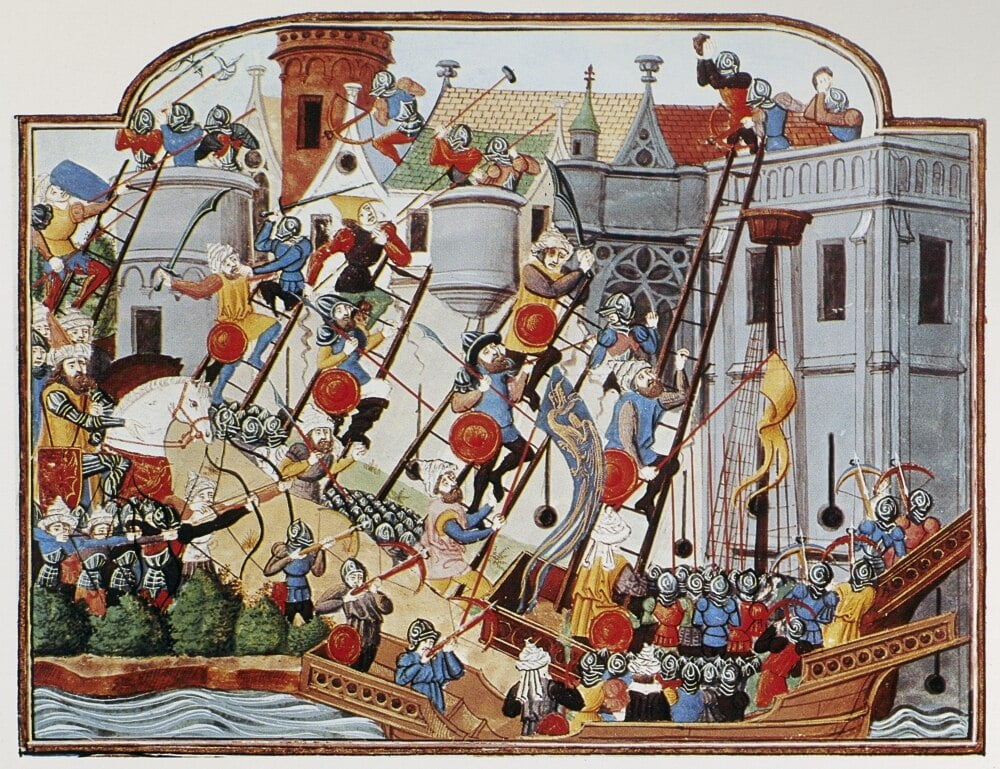
you would have a number of options. The most dangerous would be to pick up a ladder and attempt to climb—an escalade–

as, after all, high on a ladder, exposed to the enemy above you and, with men climbing below you making it difficult to climb down, you would be in a very awkward position—so perhaps other choices would be preferable?
One possibility would be to dig under.
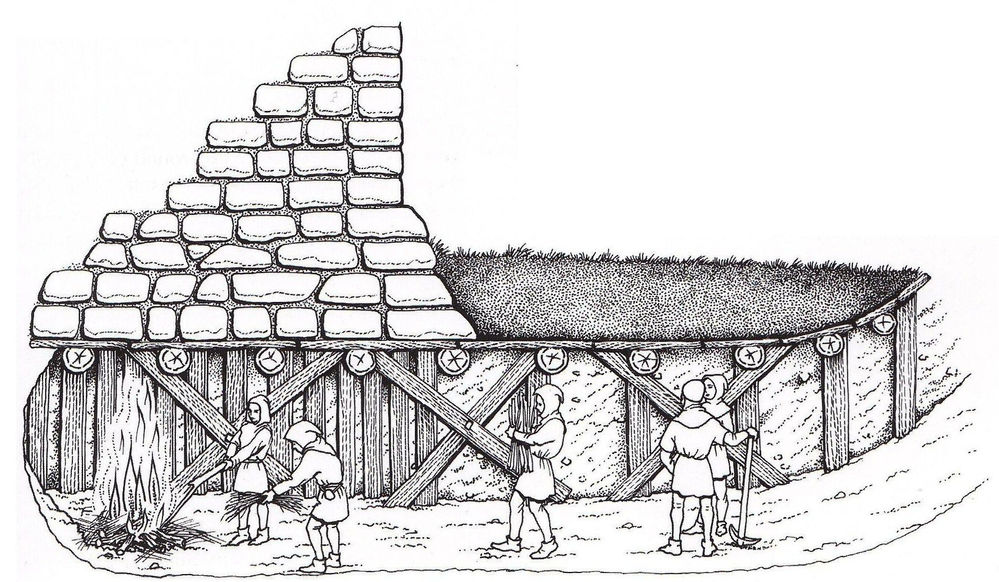
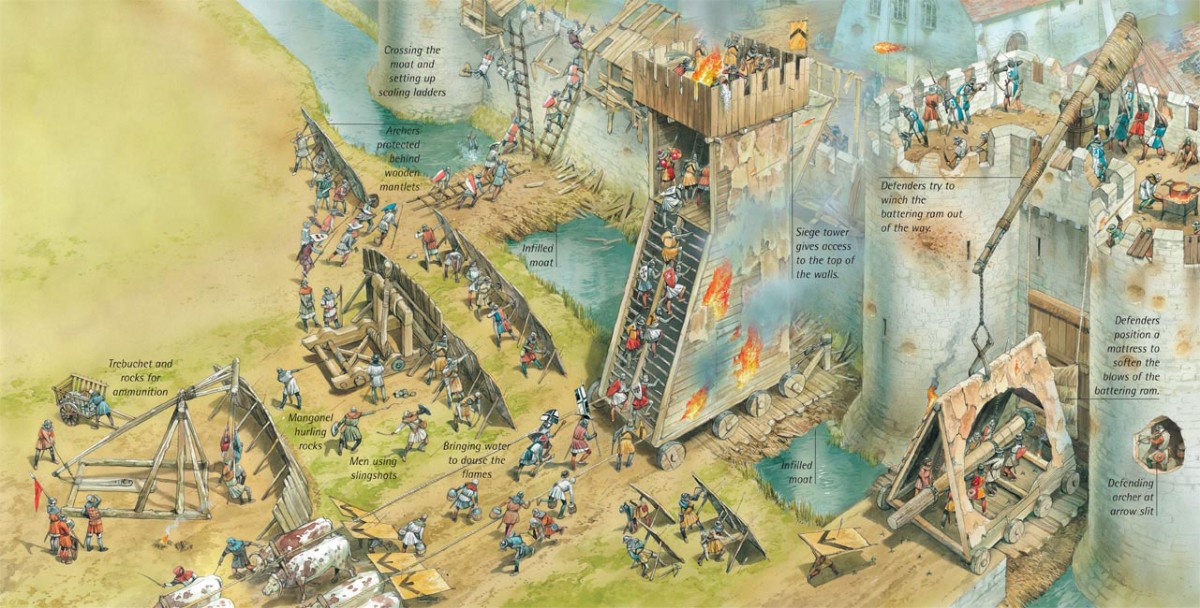
And here in this illustration we see two choices, really:
1. digging a tunnel all the way under the wall and popping out behind the defenders
2. undermining the wall: cutting away the ground below the wall, substituting wooden props for the missing ground, then setting fire to the props so that the wall above, lacking support, would come crashing down (or so you would hope) This worked at the siege of Rochester castle in AD1215, where it brought down a corner tower–
If, however, a wall had been built on a rocky base, as was sometimes the case, tunneling would not be a option.
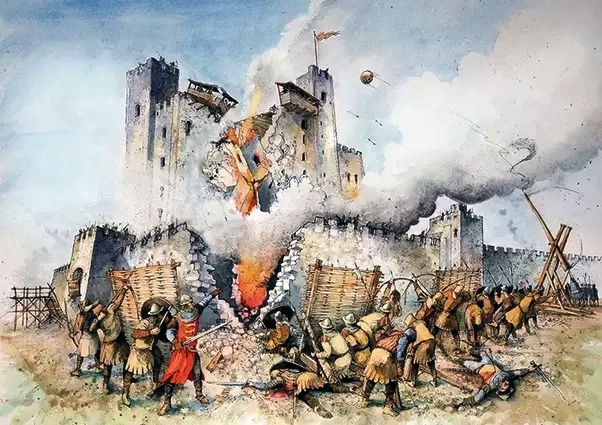
Another choice: try battering the wall with a ram (or the gates—often the weakest point)
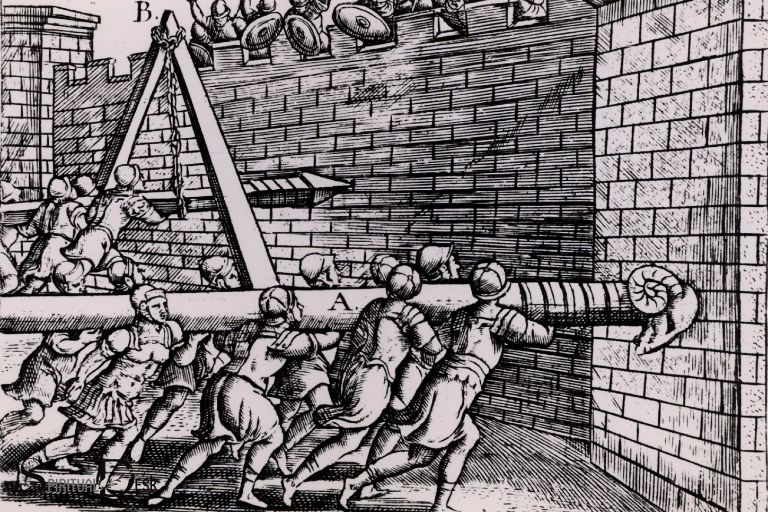

(Julius Caesar, in his commentaries on his campaigns in Gaul, used the image of battering to suggest that, although he was always inclined towards clemency, once one of his rams had touched an enemy’s town wall (in this case that of the Atuatuci) and those inside hadn’t surrendered–si prius quam murum aries attigisset se dedidissent—his clemency was at an end—and so was the town. See Caesar De Bello Gallico, Book II, Chapter XXXII (32) for the quotation, either in Latin here: https://www.thelatinlibrary.com/caesar/gall2.shtml or in English here: https://classics.mit.edu/Caesar/gallic.2.2.html Interesting to note that Caesar also describes the Roman use of a siege tower just before this—see Chapters XXX and XXXI.)

(Lincoln Renall—an artist who seems to be able to draw/paint anything—see more about his work here: https://lincoln.artstation.com/ )
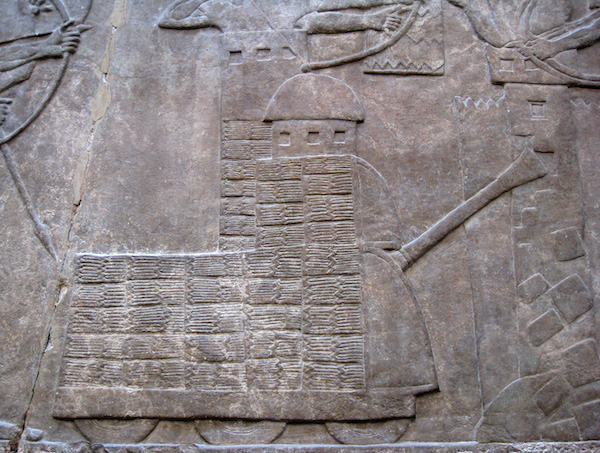
or, if the wall isn’t stone, but mud brick, try prying the wall apart—the ancient Assyrians even seem to have had a device dedicated to it (sometimes captioned as a “battering ram”, but it employed a kind of chisel, rather than a ram).

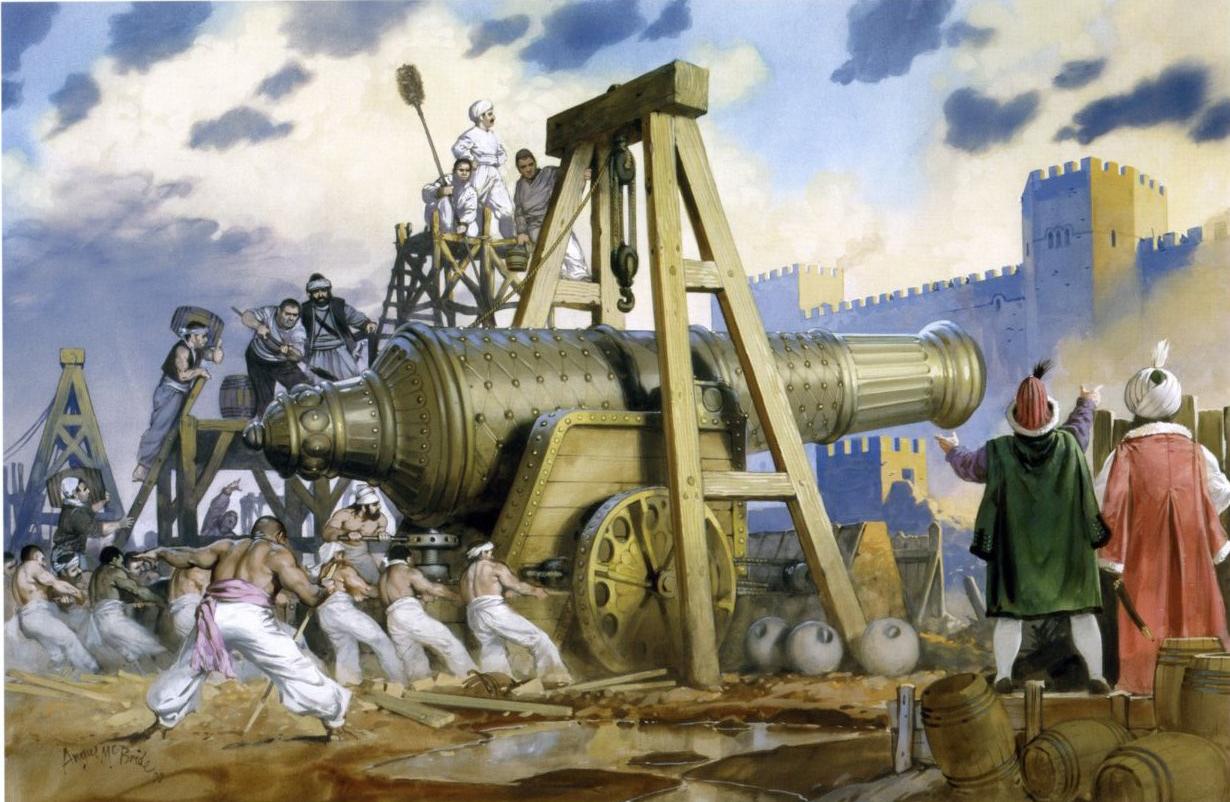
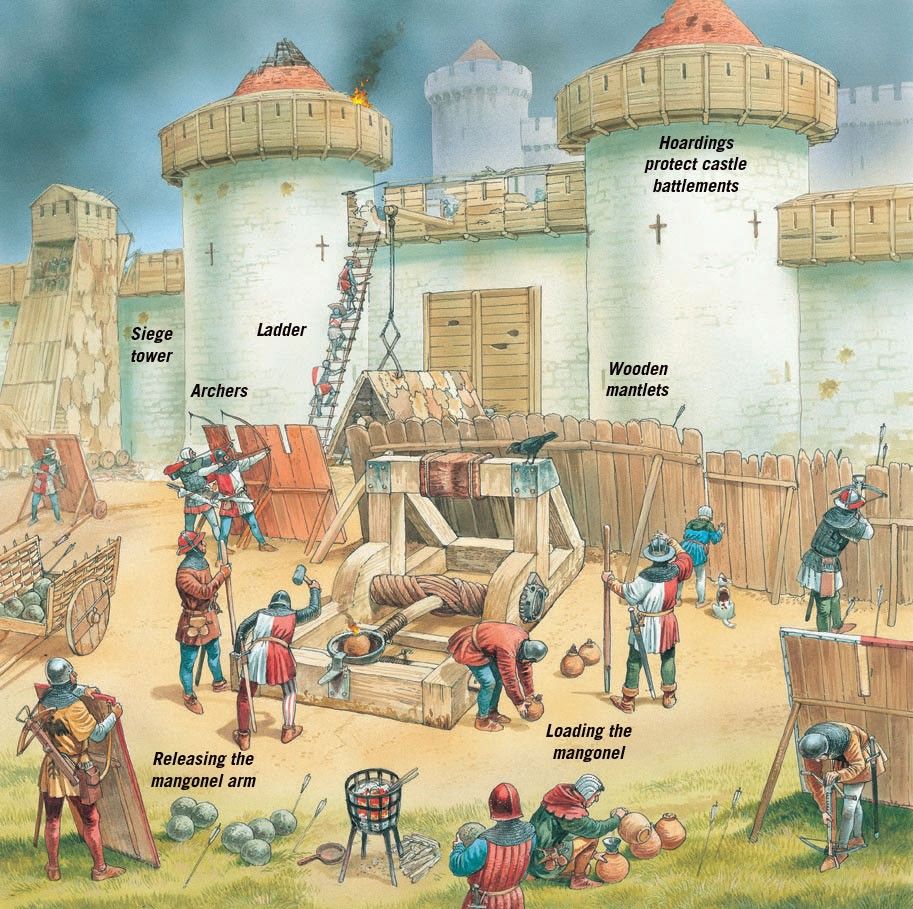
You might try a stone-thrower of some sort, gradually breaking down the wall from above, like this mangonel–

or its big brother, the trebuchet.
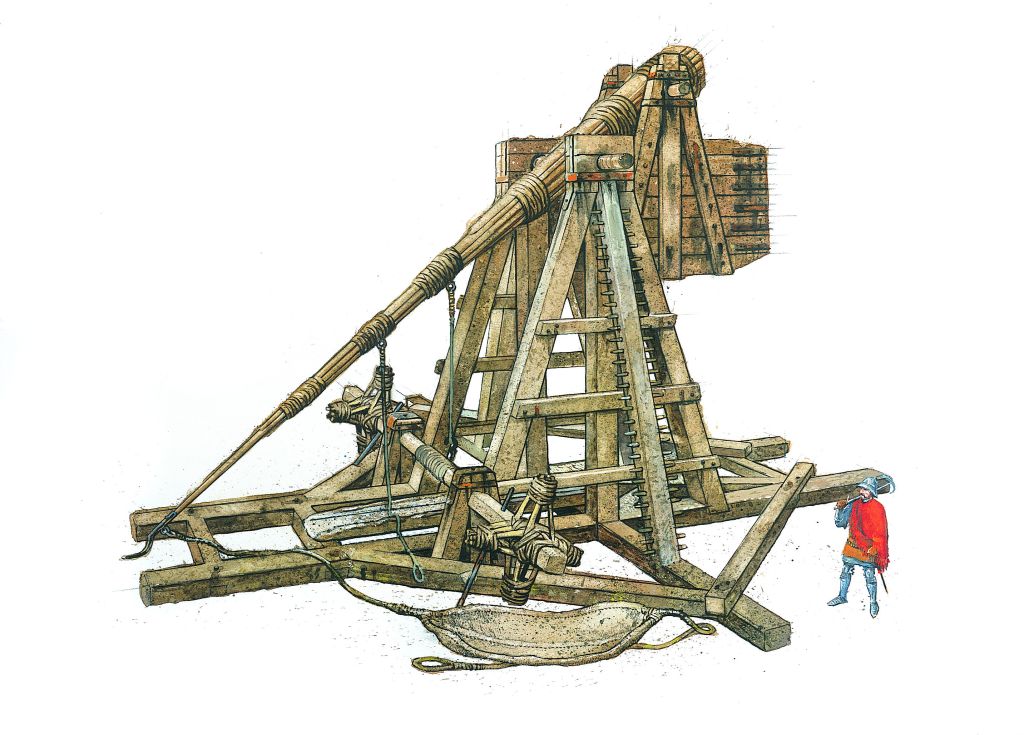

(for an interesting video on trebuchets and the damage they can do, see: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QVO8VznqMeQ )
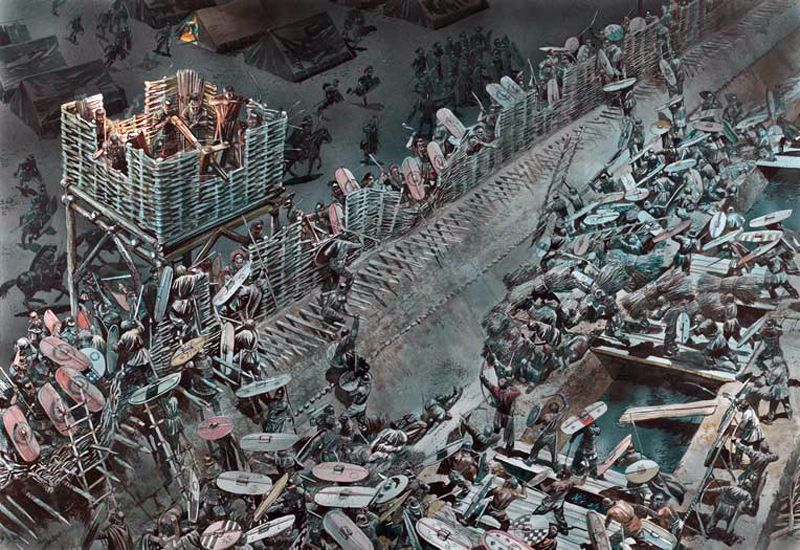
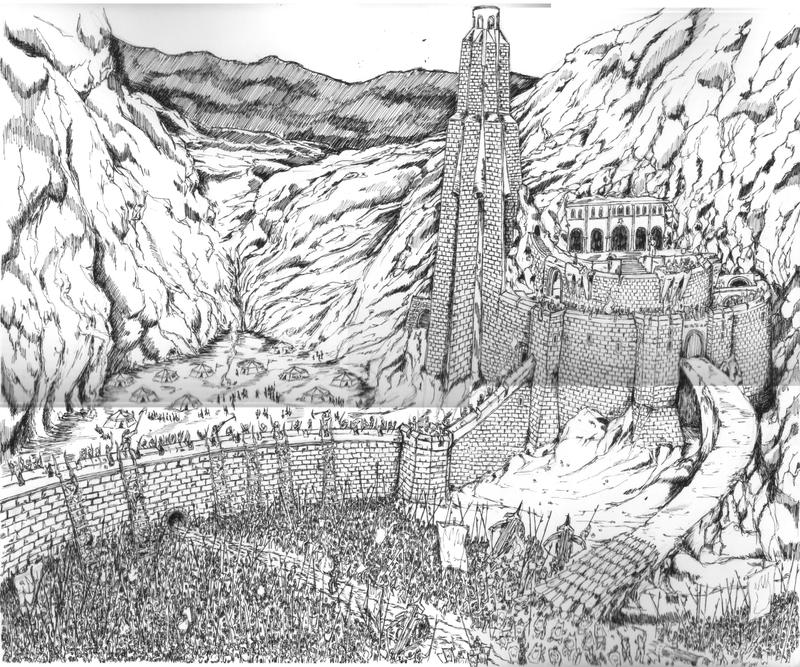
Then again, you could attempt to go over the wall with a siege tower, in what might be a safer manner than an escalade .
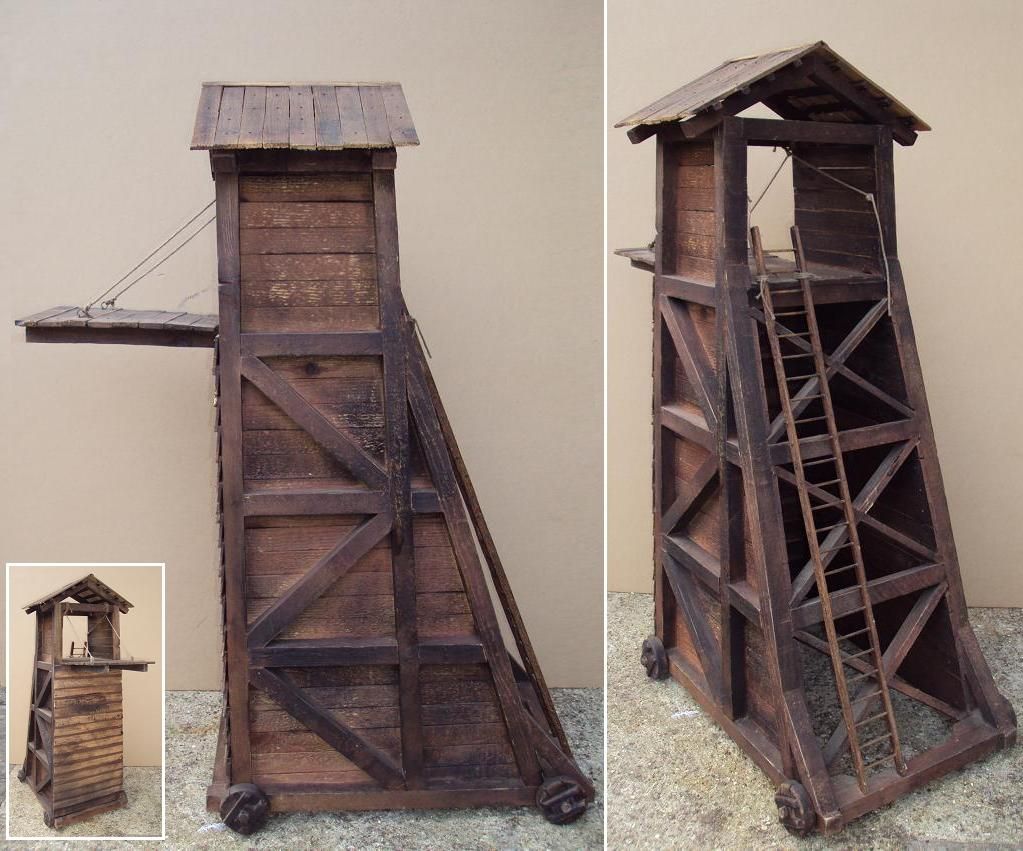

This is a machine made of wood, placed on rollers, built to approach a wall, but to be a little higher and, when it reaches the wall, a drawbridge is dropped and you and your companions rush across it, over the wall, and onto the walkway behind it, where, if your plan works, you then deal with the enemy soldiers there and move towards opening a gate below. Instead of climbing on a totally exposed ladder set against a hostile wall, then, you will climb on a ladder protected by the tower, safe until you reach that drawbridge. To further insure the attackers’ safety, the tower has to be rolled as close to the wall as possible and the drawbridge has to fall onto the wall so that the assault team (you) won’t be vulnerable for long in passing from the tower to the walkway, although, after that, you’re on your own. (The Atuatuci in Caesar’s narrative, first spot the tower from a distance and make fun of it, laughing at the idea that the Romans would build such a big thing so far away—until the Romans begin to move it closer and they stop laughing and talk surrender.)
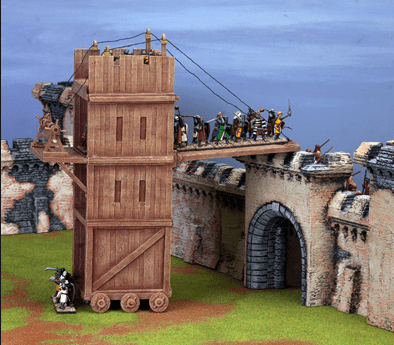
We hear of such towers at the siege of Minas Tirith:
“Then perceiving that the valour of the city was already beaten down, the hidden Captain put forth his strength. Slowly the great siege-towers built in Osgiliath rolled forward through the dark.” (The Return of the King, Book Five, Chapter 4, “The Siege of Gondor”)
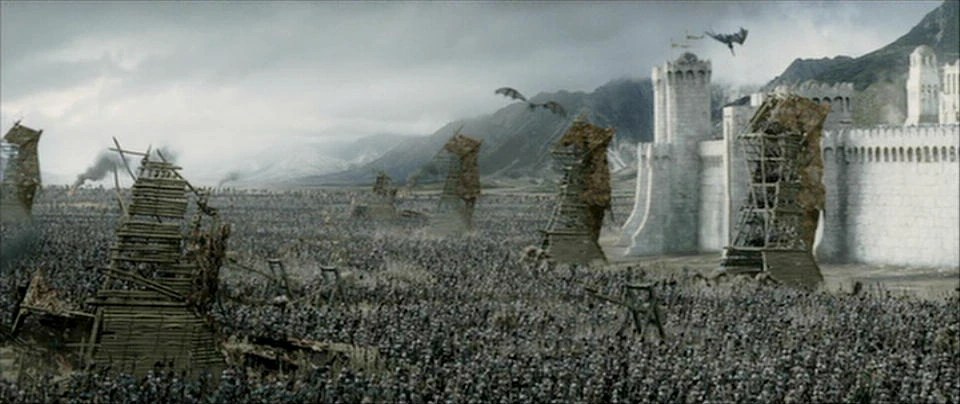

Saruman’s forces at the siege of Helm’s Deep don’t appear to use them, however, having only ladders,
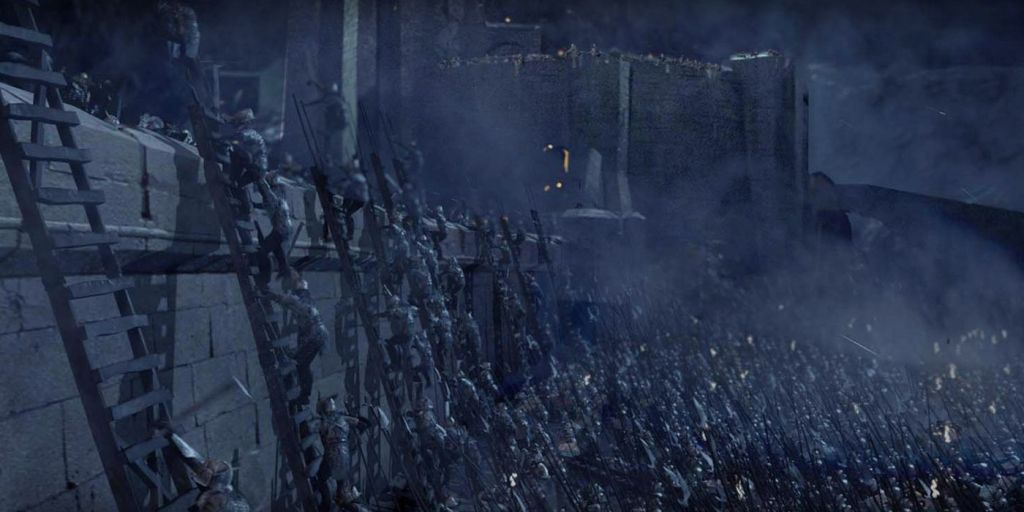

but of course they also have early gunpowder, or something like it.
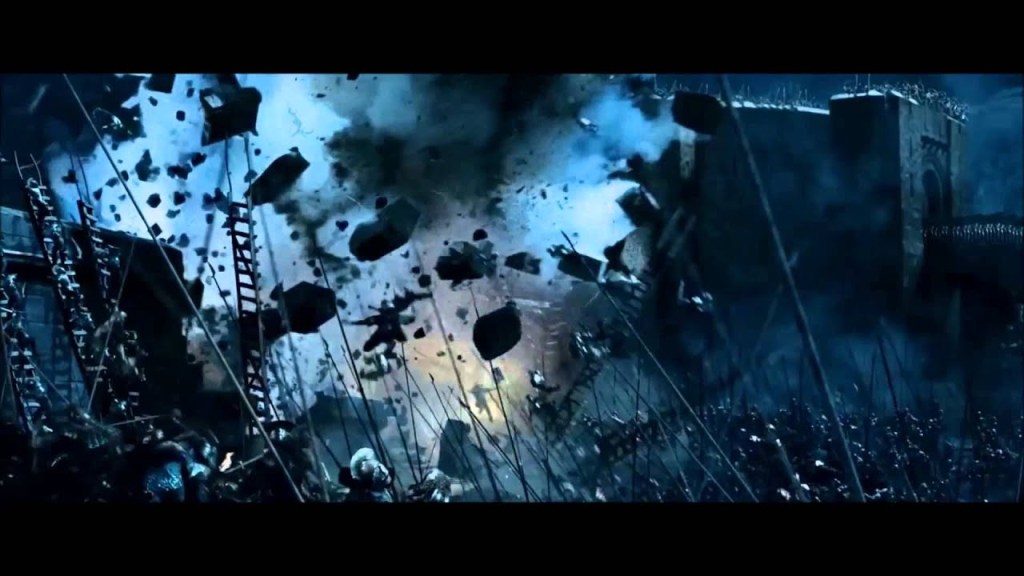

At the earlier attack on Helm’s Deep, almost 200 years before, as realized in 2024’s The War of the Rohirrim, we see an earlier use of a siege tower. And here, as in the case of the mumak, this was created by the screen writers—there’s no mention of such a device in the brief summary of that earlier war which appears in The Lord of the Rings. (See The Lord of the Rings, Appendix A, II “The House of Eorl”) The siege of Helm’s Deep went through a long winter (“November to March, 2758-9” says the text), but says nothing at all about anything but a kind of standoff, in which Rohan’s enemies lay outside the Hornburg and “Both the Rohirrim and their foes suffered grievously in the cold, and in the dearth which lasted longer.” And it lasted until:
“Soon after the winter broke. Then Frealaf, son of Hild, Helm’s sister, came down out of Dunharrow, to which many had fled, and with a small company of desperate men surprised Wulf in Meduseld and slew him, and regained Edoras. There were great floods after the snows, and the vale of Entwash became a vast fen. The Eastern invaders perished or withdrew and there came help at last from Gondor…Before the year (2759) was ended the Dunlendings were driven out, even from Isengard, and Frealaf became king.” (The Lord of the Rings, Appendix A, II “The House of Eorl”)
The film, however, has the siege continue while Wulf, the antagonist, commands the building of that siege tower—
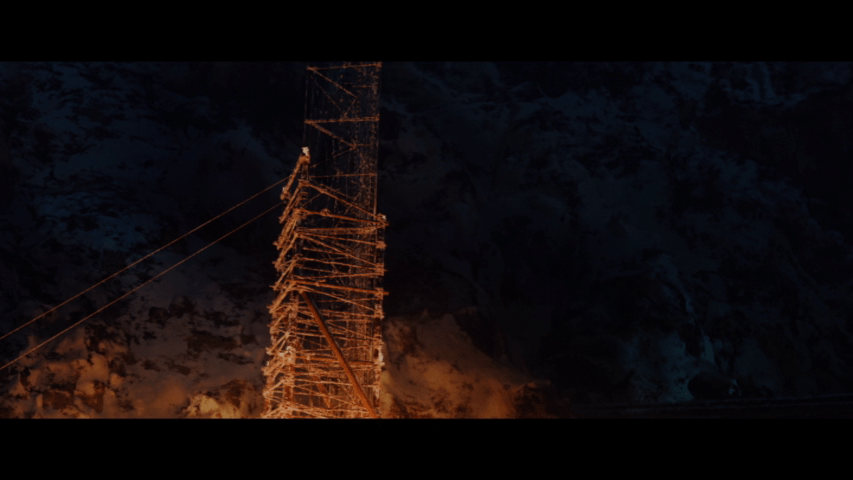

(I apologize for the somewhat dim image—it’s a screen capture from the film, the best I can provide as this whole scene is very dark in the film.)
And the tower, as depicted, is hardly something of the sort created by Roman or medieval siege engineers, being tall and spindly—rickety might also be a useful term—with no protection at all for those inside. In fact, it is built in place, rather than rolled up to the wall, so that, when finished, it needs an enormously long drawbridge which it seems like the entire besieging army then attempts to cross at once, including horses—something no ancient or medieval soldier would do, as, first, the bridge might not be able to take such weight and movement and, second, the watching enemy would fill such a mass of men and horses full of arrows before it could even cross to the wall.
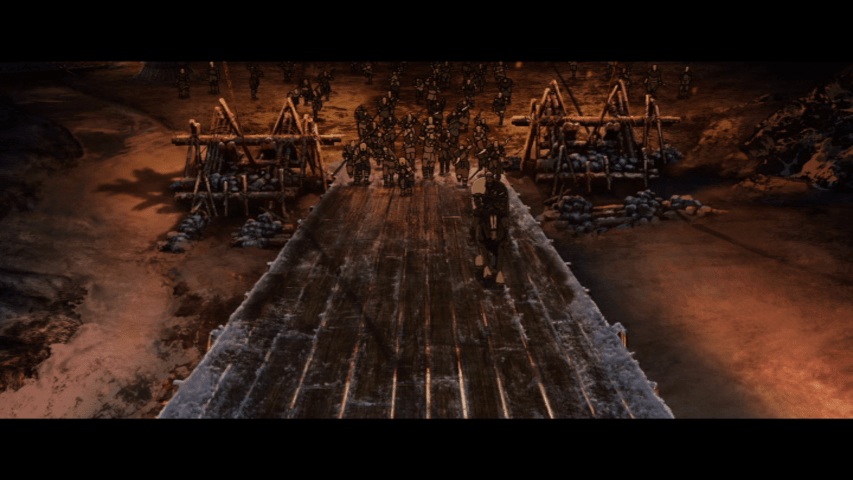

“Hera”, the protagonist, then confronts Wulf at first on that very drawbridge—and on horseback—
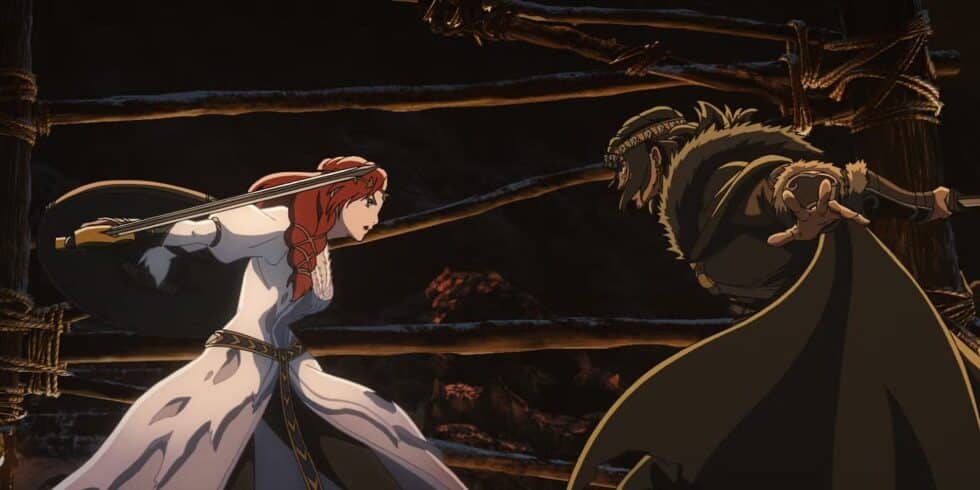
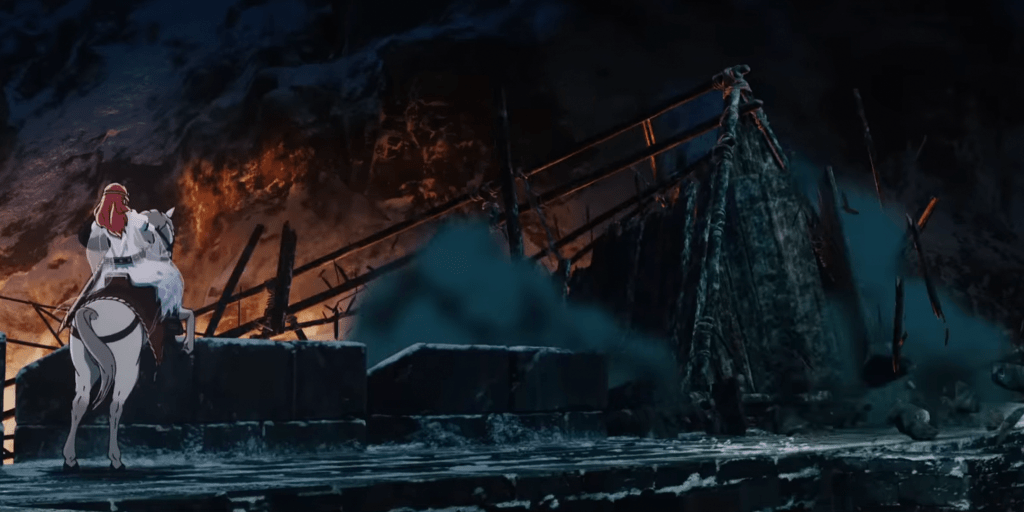

before finally killing him, rather improbably, with a shield, before standing back to see the besiegers fleeing from her cousin, Frealaf, coming like the cavalry in an old western.
(Frederick Remington)
As I’ve said before, I have nothing but praise for the hard work in making such a film, but look at what the script writers have done to Tolkien’s short text:
1. they employ a heroine plus several supporting characters, none of whom appears in JRRT’s text,
2. who then kills the main antagonist (who appears at the siege in the film when JRRT says that he’s back in Meduseld and is killed there)
3. after he attempts an assault via an impossible tower not mentioned in the narrative which Tolkien published.
As always, I approach films and books believing that those who create them are not out to cheat us, but to provide genuine entertainment and do so after long, hard labor, which clearly The War of the Rohirrim was. At the same time, I wonder about the honesty of making so many changes and additions to a text, then attaching it to the work of an author who, long dead, had no say in what was done and, in fact, had very strong feelings about others making changes to his work. With so many changes, it feels more like fan fiction, than the original, and, while I think fan fiction, if well-meaning, is a good tool for learning how to write, no one doing so should then attach the original author’s name to it. All one has to read are Tolkien’s comments on an earlier attempt at filming his work (see his letter to Forrest J. Ackerman, June, 1958, in Letters, 389-397 ) to imagine what Tolkien would say and the best I can say is that he would be both puzzled and probably very unhappy.
Thanks, as ever, for reading.
Stay well,
If not rickety towers, at least avoid rickety bridges,

And know that, as always, there’s
MTCDIC
O