Tags
Chingiz Khan, Drogo, Frodo, Hobbit genealogy, Mongols, Normans, Prose Edda, Saint Drogo, Tolkien
Welcome, as ever, dear readers.
If you’re a Game of Thrones fan (and I include myself here), you’ll immediately think of Khal Drogo, the leader of a tribe of the nomadic Dothraki,
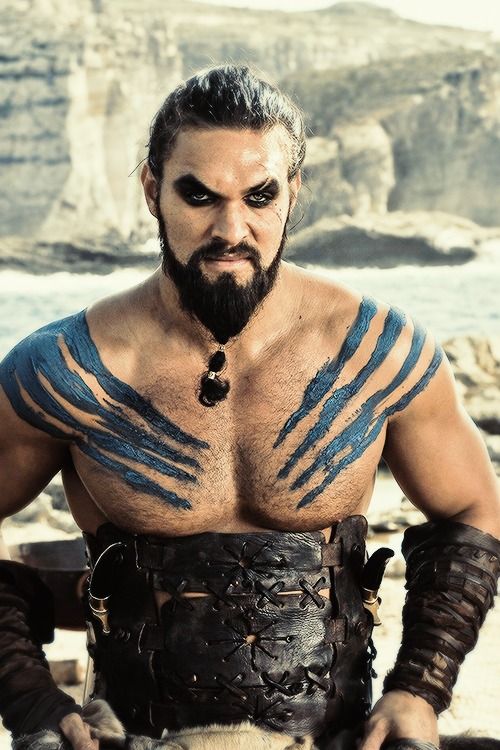

whether you’ve seen the films,

or read the books,

or both.
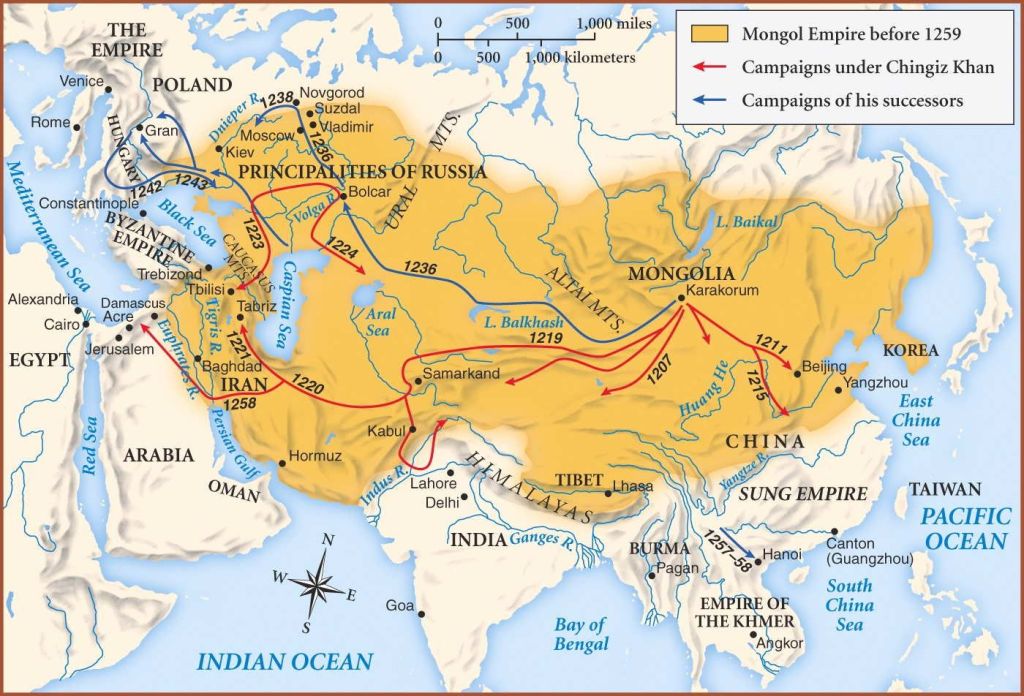
I’m presuming that “Khal” is modeled on “khan”, a word of disputed origin among scholars, but which signifies someone above “king”—imagine something more like “high king”—and is used as the title for the ruler of an “ulus”, a “horde” in English. (For more about the name, see: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Khan_(title) ) When you hear that word, you may think of Temujin, c.1162-1227AD, aka Chinggiz/Genghis Khan,

who founded the Mongol Empire and began the great wave of conquest from China to Russia. (More about him here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genghis_Khan I’ll add here that, so far, I’ve been unable to locate an artist for the illustration below.)

But he’s not the Drogo who is the subject of this posting.
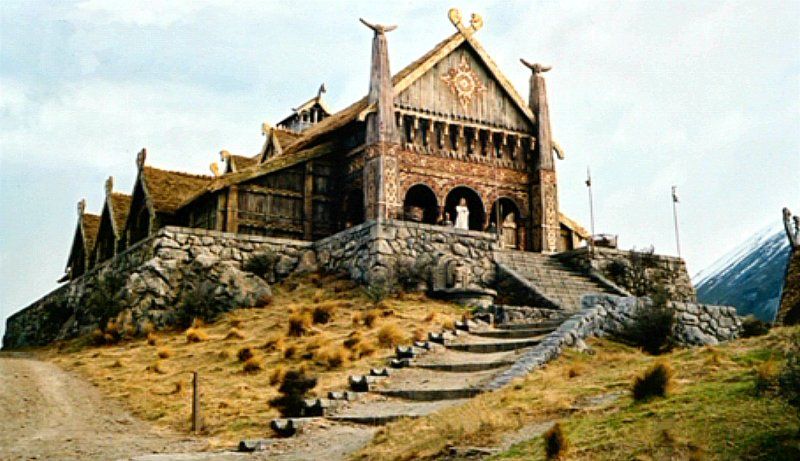
Instead, it’s a much more humble Drogo, but, without him, Sauron’s Ring

would, barring that near disaster,

(Ted Nasmith)
never have been destroyed and, with it, Sauron.

(another Nasmith—and you can see why he’s one of my favorite Tolkien illustrators: no scene too big and also no scene less known will stop him)
JRRT has reported to us the Hobbits’ passion for genealogy:
“All Hobbits were, in any case, clannish and reckoned up their relationships with great care. They drew long and elaborate family-trees with innumerable branches.” (The Lord of the Rings, Prologue I, “Concerning Hobbits”)
And here we see that name in the Appendices, C “Family Trees (Hobbits)”
I I I
Dora Drogo Dudo
1302-1406 1308-1380 1311-1409
= Primula I
Brandybuck I
I I
Frodo Daisy
1368 1350
= Griffo
Boffin
It is, of course, Frodo’s father, drowned in a boating accident thought suspicious by some. (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book One, Chapter 1, “A Long-expected Party)
I don’t have either the Hobbits’—or Tolkien’s—enthusiasm for genealogy, but I was curious, as I always am, about JRRT’s sources: just where did this name come from? It could be entirely from his fertile imagination, of course, but, as so much good scholarship has pointed to medieval sources for certain details in his works—think about those dwarvish names, right out of Icelandic saga material—the 13th-century Prose Edda of Snorri Sturluson (whose own name has a dwarvish ring and whose work you can read here: https://archive.org/details/proseedda01brodgoog/page/n54/mode/2up The dwarf name list is to be found on page 26)—I thought that a medieval influence might be possible.

At the moment, I have a short list of possible medieval candidates:
1. Drogo, the short-lived Duke of Brittany (reigned 952-958AD)—who may have been murdered by the connivance of his step-father, Fulk II, the Count of Anjou. (This is from the 11th-century Chronicle of Nantes, of which only fragments survive, but the murder plot does—Fulk threatens and persuades Drogo’s nurse to do away with him in his bath—see pages 109-110 in the 1896 edition of the fragments by Rene Merlet here: https://archive.org/details/lachroniquedenan00merl/page/108/mode/2up )
2. Drogo de la Beuvriere (? 11th century)—a companion of William the Conqueror, best known for poisoning his wife (these Normans and their allies seem to specialize in violence, don’t they?)—this information is in little bits of gossip, with the added fact that Drogo then borrowed travel money from William to enable his escape–https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drogo_de_la_Beuvri%C3%A8re
3. Drogo d’Hauteville, the Norman count of Apulia (died 1051AD)—the Normans had gradually conquered whole sections of Italy and Sicily in the 11th century

and this Drogo succeeded his brother, William, as count, only to be murdered!
4. and then there’s Saint Drogo (1105-1186AD)—a Flemish nobleman who, suffering from a disease that made it difficult for people to look at him (leprosy?), he became a hermit and, not surprisingly, is the patron saint of shepherds (feast day, April 16). As, unlike the other Drogos, he seems to have died of natural causes, after a long life, I think that we should end our catalogue here!

Thanks, as always, for reading.
Stay well,
Be very suspicious of ambitious Normans,
And remember that there’s always
MTCIDC
O
PS
Perhaps the violence done to so many of those Drogos influenced Tolkien in that nasty rumor about his Drogo?
PPS
If you are Hobbitish or Tolkienean in your interest in genealogy, there’s another Drogo—Drogo de Teigne—whom you can read about here—with the warning: if there were a genealogical rabbit hole, you’ll be standing at the mouth of it when you begin to read this: https://www.carolbaxter.com/Drew-families-of-Devonshire-and-Ireland?r_done=1