Tags
Birmingham, Charles Dickens, Cottage industry, factories, Goblins, Hard Times, Hilary Tolkien, I Can't Find Brummagem, Industrial Revolution, Isengard, James Dobbs, John Ezard, Mabel Tolkien, Mills, Ornthanc, Sarehole, Sharkey, The Hobbit, The Scouring of the Shire, Tolkien, World War I
As always, dear readers, welcome.
We’ve always loved the lines
“By some curious chance one morning long ago in the quiet of the world, when there was less noise and more green…”
which open the paragraph in which Gandalf first appears in The Hobbit and the story actually begins.
For JRRT, green and quiet are the ideal, but things have clearly changed—as this sentence implies, now there is more noise and less quiet. In our time—and even before Tolkien’s childhood in the late 19th century—the green and quiet were and are going thanks to the Industrial Revolution. Or so we thought. Reading Tolkien, however, we begin to believe that it’s goblins:
“Now goblins are cruel, wicked, and bad-hearted. They make no beautiful things, but they make many clever ones. They can tunnel and mine as well as any but the most skilled dwarves, when they take the trouble, though they are usually untidy and dirty. Hammers, axes, swords, daggers, pickaxes, tongs, and also instruments of torture, they make very well, or get other people to do the work to make to their design, prisoners and slaves that have to work till they die for want of air and light. It is not unlikely that they have invented some of the machines that have since troubled the world, especially the ingenious devices for killing large numbers of people at once, for wheels and engines and explosions always delighted them, and also not working with their own hands more than they could help; but in those days and those wild parts they had not advanced (as it is called) so far.” (The Hobbit, Chapter Four, “Over Hill and Under Hill”)
In our last posting, we had linked this passage with the invention of poison gases by German scientists and their use first by German soldiers and then by the Allies in the Great War, but we would like to add to that idea that this may be in reality a larger indictment, of the Industrial Revolution and the effects it had had upon the English countryside.
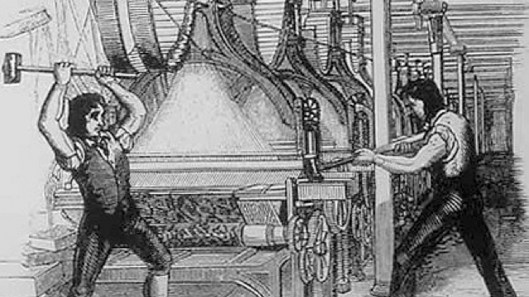
This revolution had begun in the 18th century, in Britain, when the country was first becoming a major mercantile and colonial power and the demand for British goods—especially British wool and cloth—was growing. A succession of inventions from the 1760s on had turned a (literal) “cottage industry” of clothing-making—

into something which produced thread and cloth on a massive scale in early factories.

These factories, often called “mills” because of their original use of waterpower,

as was done in the small factories which, all the way back to Roman times, had ground grain into flour,
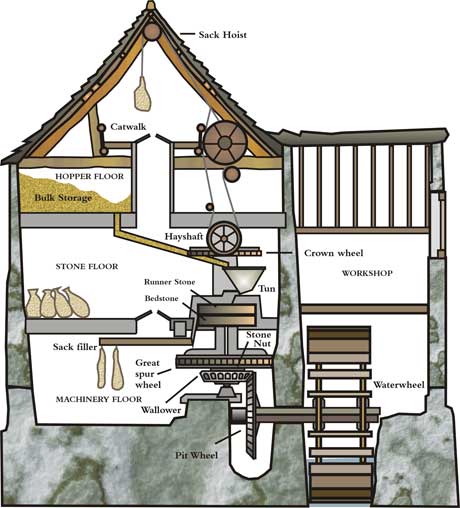
could also, in time, be run by steam power.

Mills of this sort soon became prototypes for factories built to mass-produce anything

and soon the air around cities was thick with smoke and industrial waste.

With no laws to stop them, mill/factory owners bought up land, employed people (many of them ex-cottage workers thrown out of work by the very factories they now sought work in) in near-slave conditions—including children–and polluted water and air with no fear of punishment. Here is Charles Dickens’ description of a town filled such places, from his 1854 novel, Hard Times:
“It was a town of red brick, or of brick that would have been red if the smoke and ashes had allowed it; but as matters stood, it was a town of unnatural red and black like the painted face of a savage. It was a town of machinery and tall chimneys, out of which interminable serpents of smoke trailed themselves for ever and ever, and never got uncoiled. It had a black canal in it, and a river that ran purple with ill-smelling dye, and vast piles of building full of windows where there was a rattling and a trembling all day long, and where the piston of the steam-engine worked monotonously up and down, like the head of an elephant in a state of melancholy madness. It contained several large streets all very like one another, and many small streets still more like one another, inhabited by people equally like one another, who all went in and out at the same hours, with the same sound upon the same pavements, to do the same work, and to whom every day was the same as yesterday and to-morrow, and every year the counterpart of the last and the next.”
Set this next to Gandalf’s description of what had happened to Isengard and you can see what we mean about goblins (here, Saruman and his orcs—but JRRT sometimes uses goblin and orc interchangeably) as what has destroyed the quiet and green:
“I looked on it and saw that, whereas it had once been green and fair, it was now filled with pits and forges…Over all his works a dark smoke hung and wrapped itself about the sides of Orthanc.” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book Two, Chapter 3, “The Council of Elrond”)

In 1895, Tolkien’s mother, Mabel,

who had been living in South Africa with her husband, brought her two sons, JRRT and Hilary, to the Birmingham area of England for a visit to relatives.
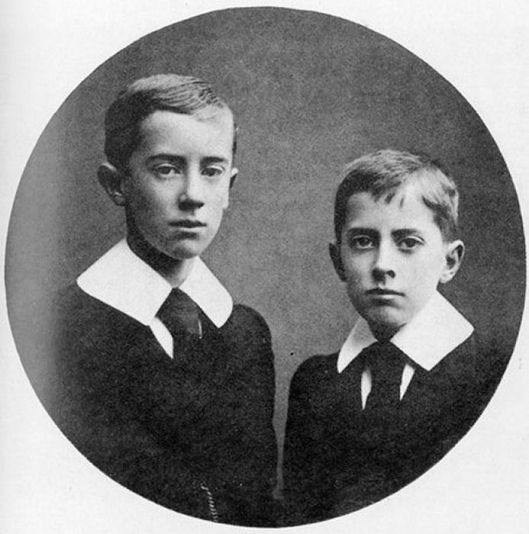

Unfortunately, while they were gone, Tolkien’s father died of rheumatic fever. Mabel decided to stay in England and found a place for her sons and herself at Sarehole, southeast of Birmingham itself.

Birmingham was a booming product of that Industrial Revolution, which we’re sure is why Mabel chose a tiny village several miles away.
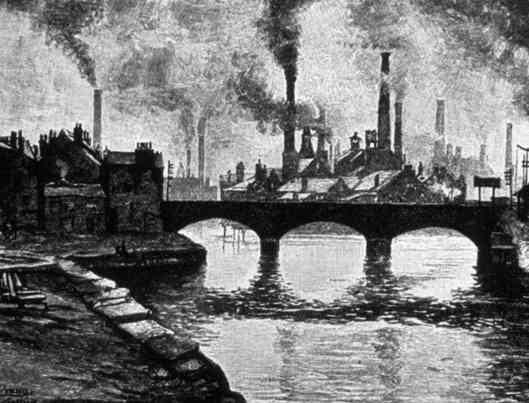

Birmingham was also an ancient settlement, (here’s a LINK to a minitour of the medieval town) but had mushroomed, both in factories and population even at the beginning of the 19th century, as this verse from a music hall song from 1828 by James Dobbs depicts:
‘I remember one John Growse,
Who buckles made in Brummagem,
He built himself a country house,
To be out of the smoke of Brummagem
But though John’s country house stands still,
The town itself has walked up hill,
Now he lives beside a smoky mill,
In the middle of the streets of Brummagem.”
(James Dobbs (1781-1837), “I Can’t Find Brummagem”. Brummagem is an old local nickname for Birmingham. Here’s a LINK so that you can see the whole song and its tune, which we know as “Duncan Grey”. If you go to the link, you’ll notice we’ve made a few editorial additions, which we knew from another version of the song and which help the words to better fit the tune.)
And yet, although Sarehole had an old mill, it was not like those in Birmingham or even in Dickens,

and, in later years, in fact, Tolkien saw the little village beyond it as a kind of paradise, as he said in an interview:
‘It was a kind of lost paradise,’ he said. ‘There was an old mill that really did grind corn with two millers, a great big pond with swans on it, a sandpit, a wonderful dell with flowers, a few old-fashioned village houses and, further away, a stream with another mill. I always knew it would go – and it did.’
(This is taken from an article by John Ezard in The Guardian for 28 December, 1991—here’s a LINK so that you can read all of it.)
This strong contrast between green and quiet and its opposites, as seen in Sarehole versus Birmingham, early in Tolkien’s life, and the two stages of Isengard, will appear again in the Shire as Saruman/Sharkey has planned. The green and quiet is literally uprooted and even Sandyman’s old mill is a victim of the goblinesque work as Farmer Cotton says:

“But since Sharkey came they don’t grind no more corn at all. They’re always a-hammering and a-letting out a smoke and stench, and there’s no peace even at night in Hobbiton. And they pour out filth a purpose; they’ve fouled all the lower Water, and it’s getting down into Brandywine.”
(The Return of the King, Book Six, Chapter 8, “The Scouring of the Shire”)

Those who work for Sharkey are men, but, as you can see, under his influence, they act very much like those destructive goblins with which we began. For all that he rode in automobiles and trains and used telephones and typewriters, JRRT was never quite happy in the modern world and, considering that the goblins seemed always poised to ruin more green and produce more noise at the command of a modern-day Saruman, it’s perhaps not surprising. It’s also not surprising, we would add, that his favorite creatures, trees, are the ones who destroy Saruman’s handiwork at Isengard and return it to a leafy park.

Thanks, as ever, for reading.
MTCIDC
CD
ps
In our next, we want to talk about another aspect of quiet which had changed from Tolkien’s childhood and may be a reason why there are Rohirrim and why JRRT himself enlisted in the volunteer cavalry…