Tags
Aragorn, Fantasy, Geoffrey Chaucer, Geoffrey of Monmouth, Historia Regum Britanniae, Howard Pyle, King Arthur, Le Morte d'Arthur, Merlin, NC Wyeth, Robert de Boron, Sigurd, Sir Thomas Malory, Strider, TH White, The Once and Future King, The Red Fairy Book, The Sword in the Stone, Tolkien, Trotter.
Welcome, dear readers, as ever.
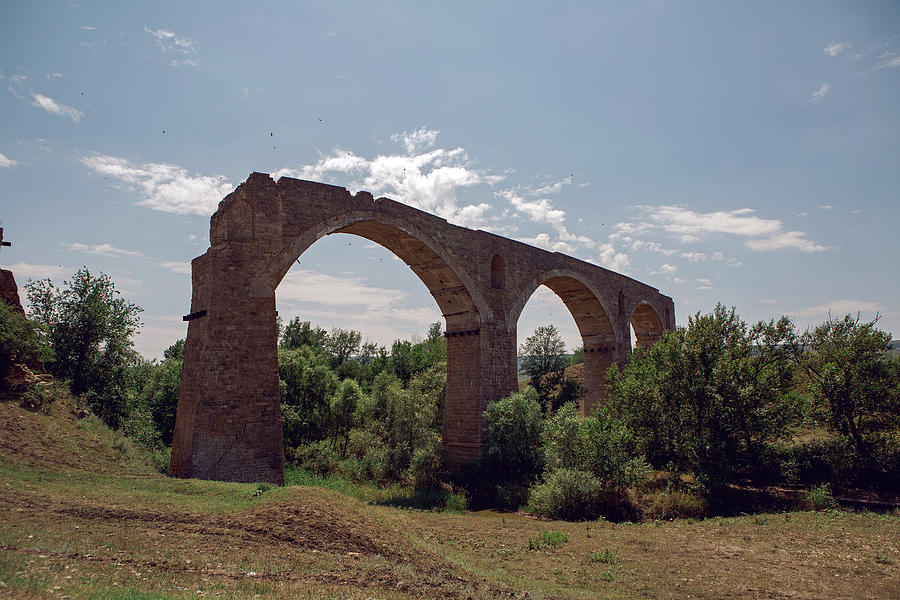
I had been outside on some land being cleared when I spotted this—

and, as someone who thinks and writes and teaches about adventure in literature, I immediately thought of this—

(This version of the scene is from Howard Pyle’s 1903 The Story of King Arthur and his Knights , which you can read here: https://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/60184/pg60184-images.html#CHAPTER_FIRST-A )
My own knowledge of King Arthur probably began with books like The Boy’s King Arthur, by Sidney Lanier, originally published in 1880, with perhaps the best known version being the 1917 edition, with its wonderful illustrations by N.C.Wyeth,

(Here’s your copy: https://archive.org/details/boyskingarthursimalo/mode/2up )
and Howard Pyle’s The Story of King Arthur and His Knights, mentioned above, before, as a teenager, I found the Imaginative and witty but ultimately melancholy T.H. White’s 1958 The Once and Future King,

(This is actually an omnibus volume of earlier White works, which you can read about here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Once_and_Future_King )
the first volume of which being made into a Disney movie, The Sword in the Stone in 1963,

all of which being direct descendants from Sir Thomas Malory’s Le Morte d’Arthur, written perhaps in the 1460s and one of the first books printed in England by William Caxton in 1485.

(Only 2 copies are known to exist: one in the Rylands Library in Manchester, the other in the Morgan Library in New York—this is the Morgan Library copy. You can read an 1893 edition here: https://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/46853/pg46853-images.html Malory’s book—and Malory himself—have been the subject of much scholarly work and debate and you can read a little about it and him here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Le_Morte_d%27Arthur )
I had known that, behind Malory, lies Geoffrey of Monmouth’s early 12th-Century Historia Regum Britanniae (aka De Gestis Britonum—that is, “History of the Kings of Britain” or “Concerning the Acts/Deeds of the Britons”), but there was something new to me in doing a little reading for this posting: the story of the sword and its stone. Because it’s in all the later versions, even forming the title of one part of White’s larger collection, I had assumed that it was a story which had always been part of the bigger history of Arthur, and yet it seems to have been an independent creation, by a French knight, Robert de Boron, in a poem entitled Merlin, dated to the end of the 12th, the beginning of the 13th-Century.

(This is from 13th-Century manuscript in the Bibliotheque nationale in Paris. The BnF has a short feature—in French—on it here: https://essentiels.bnf.fr/fr/litterature/moyen-age-1/ed6c3713-b2d5-4b94-8cac-a35fbd9471b1-mythe-arthurien/video/9ad866b9-c7ac-47b8-9356-9bcb793fb0ad-histoire-merlin )
The whole Arthur story is a tangle of English and French poems and prose works, showing what a fertile field it was for poets and story-tellers, just as Troy had been, many centuries before—and still could be for medieval creators, if we think of Geoffrey Chaucer’s Troilus and Criseyde as an example of a continued interest. (You can read Chaucer’s poem here: https://www.gutenberg.org/files/257/257-h/257-h.htm ) Who influenced whom, sometimes even who someone might have been, is a happy battlefield for scholars, so I’ll only point you to some discussion of de Boron and his poem here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robert_de_Boron#Further_reading and here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merlin_(Robert_de_Boron_poem) and include a 15th-century English prose translation of the Old French of the original here, which is quite readable, and not just if you’re used to Chaucer’s 14th-century English: https://metseditions.org/read/jy0W7X8HvLalIgvvC1z6jFMKyK4EakW )
For me, the important point of the story is really a question : who is to be king of England and how can he prove that he is the rightful king? And the answer is provided by that sword, as the 15th-century text reads:
“And the archebisshop lowted to the swerde and sawgh letteres of golde in
the stiel. And he redde the letteres that seiden, ‘Who taketh this swerde out of
this ston sholde be kynge by the eleccion of Jhesu Criste.’ “
(“And the archbishop bent over the sword and saw letters of gold in the steel. And he read the letters that said, ‘Who takes this sword out of the stone should be king by the choice of Jesus Christ.’ “)
This brings us to King Trotter.
It’s clear from his various letters and from Carpenter’s biography that Tolkien spent a lot of time in a kind of creative wandering before he settled upon various elements which make up the eventual The Lord of the Rings. As he writes to W.H. Auden:
“…the main idea…was arrived at in one of the earliest chapters still surviving…It is really given, and present in germ, from the beginning, though I had no conscious notion of what the Necromancer stood for (except ever-recurrent evil) in The Hobbit, nor of his connexion with the Ring. But if you wanted to go on from the end of The Hobbit I think the ring would be your inevitable choice as a link. If then you wanted a large tale, the Ring would at once acquire a capital letter; and the Dark Lord would immediately appear. As he did, unasked, on the hearth at Bag End as soon as I came to that point. So the essential Quest started at once. But I met a lot of things on the way that astonished me. Tom Bombadil I knew already; but I had never been to Bree. Strider sitting in the corner of the inn was a shock, and I had no idea who he was than had Frodo.” (letter to W.H. Auden, 7 June, 1955, Letters, 315-316)
In one of his wanderings, he had created a kind of Hobbit Ranger, “Trotter”. As Carpenter tells us:
[on a holiday at Sidmouth in 1938] “There he did a good deal of work on the story, bringing the hobbits to a village inn at ‘Bree’ where they meet a strange character, another unpremeditated element in the narrative. In the first drafts Tolkien described this person as ‘a queer-looking brown-faced hobbit’, and named him ‘Trotter’.” (Carpenter, 191)
And so, in fact, Tolkien had not initially met Strider in the Prancing Pony in Bree at all, but a completely different character, one who would, at a later date, disappear, to be replaced by Aragorn, son of Arathorn, who would, by the end of the story, be the king who has returned.

(the Hildebrandts)
But how will he ever prove that he is that king?
One clue is in the verses which are attached to a letter Gandalf had written to Frodo, but, neglected by the landlord of The Prancing Pony, was only delivered when Frodo and his friends had reached Bree:
“All that is gold does not glitter,
Not all those who wander are lost;
The old that is strong does no wither,
Deep roots are not reached by the frost.
From the ashes a fire shall be woken,
A light from the shadows shall spring;
Renewed shall be blade that was broken,
The crownless again shall be king.” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book One, Chapter 10, “Strider”)
When Pippin and Sam both express doubt about Strider’s identity, he makes a bold gesture, saying,
“ ‘If I had killed the real Strider, I could kill you. And I should have killed you already without so much talk. If I was after the Ring I could have it—NOW!’
He stood up, and seemed suddenly to grow much taller…Throwing back his cloak, he laid his hand on the hilt of a sword that had hung concealed by his side.”
But then:
“He drew out his sword, and they saw that the blade was indeed broken a foot below the hilt.”
As I have suggested in a previous posting (see “Swords Drawn”, 2 July, 2025), this sword appears to have been influenced by something which Tolkien had either read or had read to him as a child from Andrew Lang’s The Red Fairy Book, 1890.

(here’s a copy for you: https://archive.org/details/redfairybook00langiala/redfairybook00langiala/ )
In the last tale in the book, “The Story of Sigurd”, we find:
“ONCE upon a time there was a King in the North who had won
many wars, but now he was old. Yet he took a new wife, and
then another Prince, who wanted to have married her, came up
against him with a great army. The old King went out and fought
bravely, but at last his sword broke, and he was wounded and his men
fled. But in the night, when the battle was over, his young wife came
out and searched for him among the slain, and at last she found
him, and asked whether he might be healed. But he said
‘No’, his luck was gone, his sword was broken, and he must die. And he
told her that she would have a son, and that son would be a great
warrior, and would avenge him on the other King, his enemy. And
he bade her keep the broken pieces of the sword, to make a new sword
for his son, and that blade should be called Gram.” (Lang, “The Story of Sigurd” from The Red Fairy Book, 357)
Just as Sigurd, when other swords have failed his test, has his father’s sword reforged, so the smiths of Rivendell reforge Aragorn’s sword and he changes its name from Narsil to Anduril, and even shows it, via Saruman’s palantir, to Sauron, clearly as a threat, as this is the very sword Isildur used to cut the Ring from Sauron’s hand long ago. (see The Return of the King, Book Five, Chapter 2, “The Passing of the Grey Company”)
But returning to the opening of this posting, I would wonder just how surprised JRRT really was when he returned to the Prancing Pony and found, not Trotter, the hobbit, but Strider, aka Aragorn, son of Arathorn, descended from the ancient rulers of Gondor and himself the heir? Although he had mixed feelings about Arthurian legend (see from a letter to Milton Waldman, “late in 1951”, Letters, 202, among other places– even though, in the mid-1930s, he attempted and abandoned a long poem, “The Fall of Arthur”—see Carpenter, 171), Tolkien had been well aware of its stories from childhood (“The Arthurian legends also excited him.” Carpenter, 30) and it’s clear that no story he had ever read or heard ever completely disappeared from his mind and so we’re left perhaps with a question: did Aragorn arrive with the sword, either from Sigurd or Arthur, or did the sword, in Tolkien’s memory from his earliest years, come first, making Aragorn—who needed proof that he was the rightful king, just as Arthur did–come first?
In either event, I think that we should be thankful that both arrived as it’s hard to imagine the coronation not of Aragorn,

(the Hildebrandts)
but of “a queer-looking brown-faced hobbit”!
Thanks, as always, for reading.
Stay well,
Wander, if you will, but don’t be lost,
And remember that, as always, there’s
MTCIDC
O