Welcome, as always, dear readers,
I’m about to teach The Hobbit again, which is, as always, a pleasure—and also a repeated source of new things to think—and write—about.
Take this, for example:
“Chip the glasses and crack the plates!
Blunt the knives and bend the forks!
That’s what Bilbo Baggins hates—
Smash the bottles and burn the corks!”
(The Hobbit, Chapter One, “An Unexpected Party”)
Seven years ago, this formed a small part of an earlier essay, “Shire Portrait (2)” (8 February, 2017), in which the subject was the economy of the Shire.
JRRT was himself aware of just how much lay underneath that economy which he didn’t depict, writing:
“I am more conscious of my sketchiness in the archaeology and realien [“actualities/realities”] than in the economics: clothes, agricultural implements, metal-working, pottery, architecture and the like…I am not incapable of or unaware of economic thought; and I think as far as the ‘mortals’ go, Men, Hobbits, and Dwarfs, that the situations are so devised that economic likelihood is there and could be worked out…” (letter to Naomi Mitchinson, 25 September, 1954, Letters 291-292)
In that essay, I pointed out that, in Tolkien’s world, those threatened corks came primarily from Portugal, from the Quercus suber,

which, as the Wiki articles tells us, actually “is native to southwest Europe and northwest Africa”, suggesting, perhaps, that, in Middle-earth, it might be imported as far away as from Umbar, say, far to the south, had Tolkien bothered to go that far in expressing “economic likelihood”.

This cork bobbed up (they do, don’t they?) in my mind associated with something completely different, however, but certainly naturally: barrels.
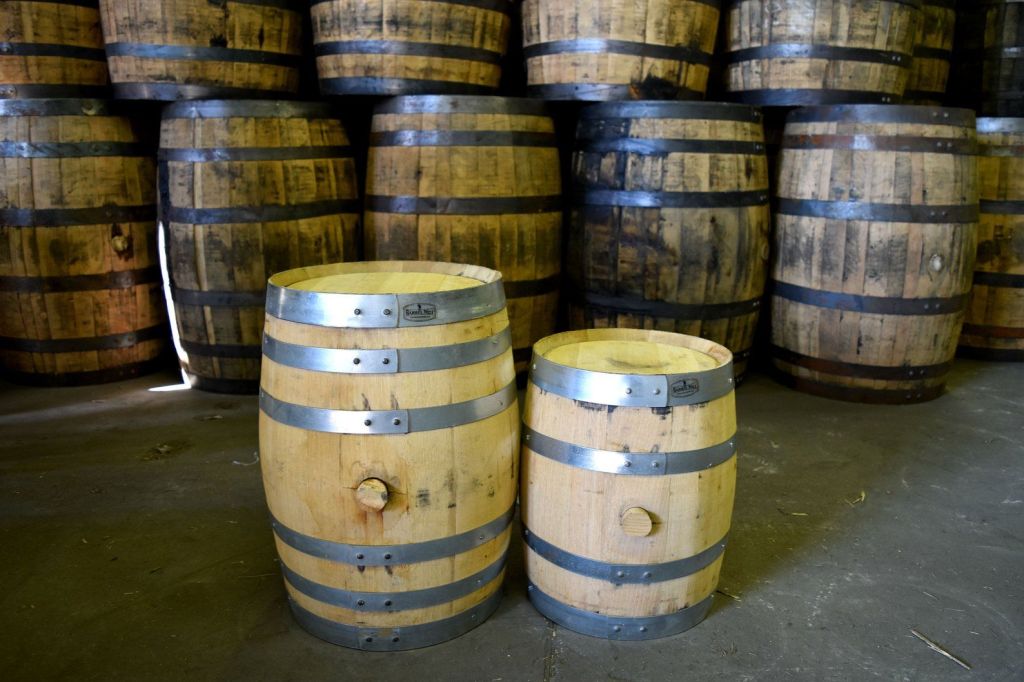

And this led me to what was, in fact, a mistaken idea.
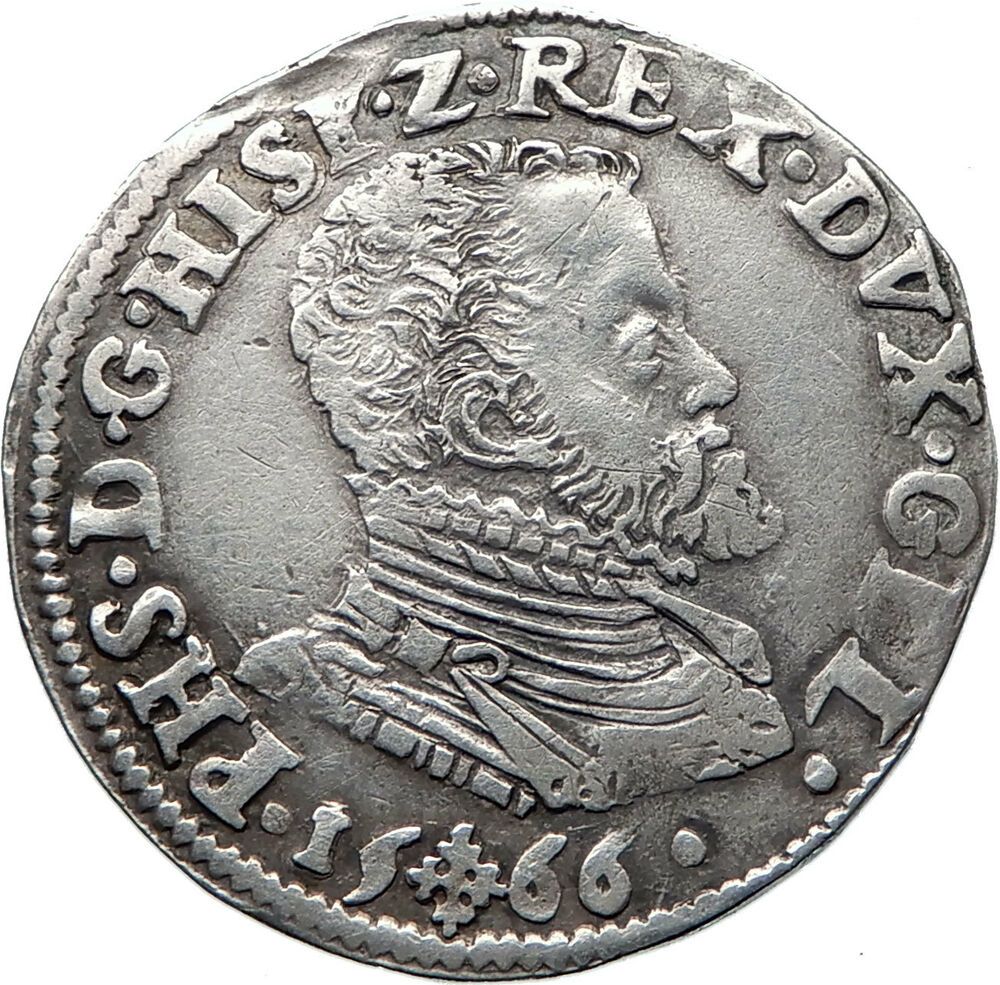
In the mid-1580s, Philip II of Spain,

a man for whom the term “religious obsessive” could have been coined, set his sights upon an attack on England. As “His Most Catholic Majesty”, he was already fighting what seemed like an endless war against his (to his mind) rebellious Protestant subjects in the Netherlands—the so-called “80 Years War” (1568-1648), or “Dutch Revolt”.
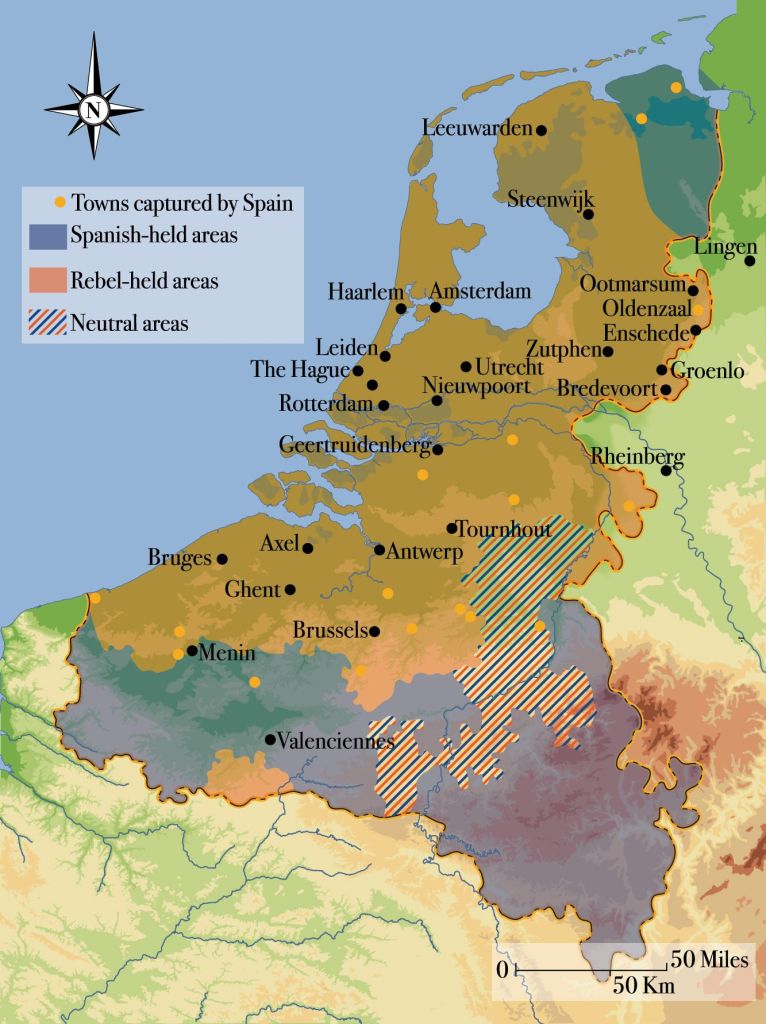
England, now a Protestant country under its queen, Elizabeth,

was helping that revolt. (Philip may also have been annoyed that, as he had once been married to Elizabeth’s half-sister, Mary, 1515-1558, queen of England, 1553-1558,

he probably thought that, after her death, he should have been king.)
As Spain, because of its looting of its New World possessions, was extremely rich,

it could afford a long war and, having lots of troops already across from England,

it seemed only a matter of:
1. building lots of landing craft for an invasion army
2. assembling a fleet—an armada, in Spanish, to protect those craft till they hit the beaches of England.

Such a fleet, sailing from Spain at least to the coast of France, where the invasion army was being assembled, as were the landing craft, would need large supplies of food and water to survive on the high seas.
Such supplies would be carried in a vast number of barrels.

Enter now one of Elizabethan England’s most dashing characters, Sir Francis Drake (1540-1596).

When it came to sailing, Drake seems to have done it all, including surviving a circumnavigation of the globe (1577-1580), but he was, from the Spanish view, a good reason to conquer England along, as Drake had, for years, but a challenge to their (in their minds) domination of the oceans, raiding their possessions in the New World, capturing and looting their treasure ships. (Under the Spanish form of his name, el Draque, he even supposedly had a significant price on his head: 20,000 ducats which, if I’ve got my figures right, would be almost $2,500,000.00 in today’s money—but the buying power would be substantially more—and I mean substantially.)
In 1587, Drake, with an English fleet, raided the Spanish coast, capturing and destroying ships and generally wreaking mayhem—and here’s where my mistaken idea comes in. I thought that he had, among other things, ruined the Spanish supply of corks and hence slowed down the Armada’s ability to supply itself with those barrels. (And I’m not the only one to have thought so—see this wonderfully silly Horrible Histories skit: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w6_UkLHcdJk )
In fact, during his raid on the Spanish coast, Drake’s men not only burned perhaps as many as 37 ships, but also not corks, but 1600-1700 tons of barrel staves,

enough to make 25-30,000 barrels,

barrels which would have held the Armada’s vital supplies.
This raid delayed the setting off for England by a year. New staves were made, and other ships replaced the ruined ones, however, and the Armada set off the next year, in 1588, but the staves were not the usual dried wood used for barrels, but green wood and often split, allowing the contents to be spoiled. As well, the English navy, though small, was superior to the Armada both in seamanship and its ability to deliver firepower,
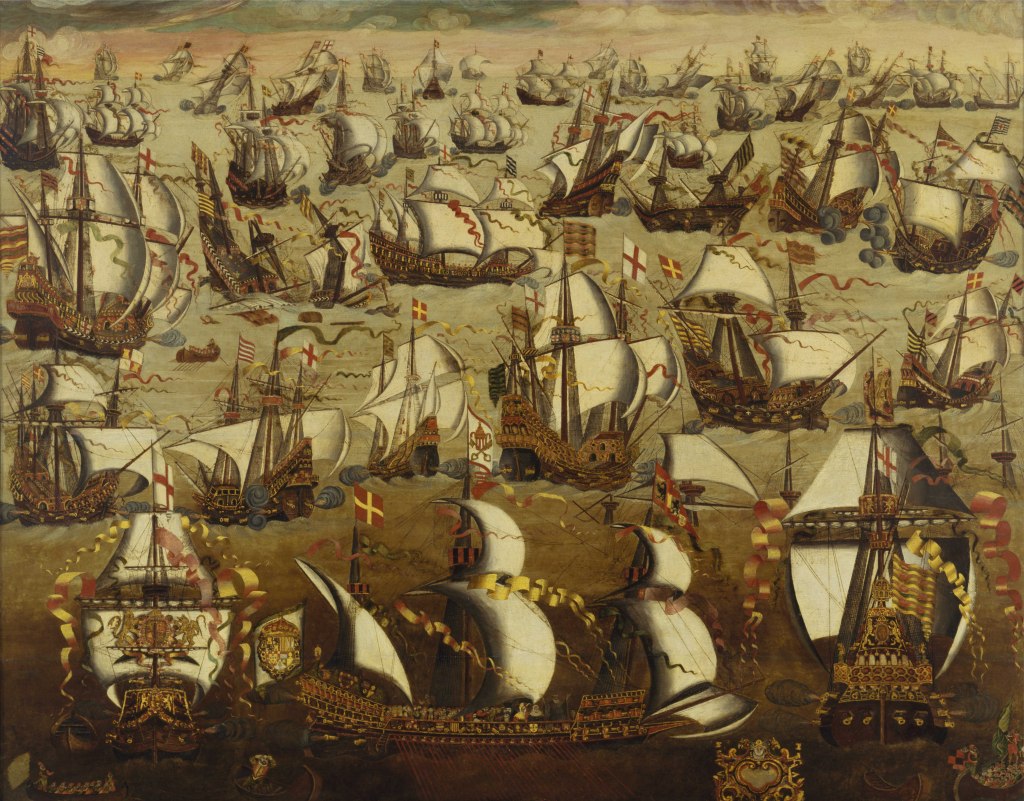

and the Spanish fleet was driven to flee north, eventually, many ships being lost on a circumnavigation of Britain,

and Philip’s planned invasion never took place.
And so, considering England’s escape and those barrels, perhaps I should have been thinking about another part of The Hobbit altogether…

(JRRT)
Thanks, as ever, for reading.
Stay well,
Avoid delusions of grandeur—remember what happened to the Armada,
Image20: armada
And remember that, as always, there’s
MTCIDC
O
ps
For a traditional view of Drake, see Julian Corbett’s 1899 2-volume work Drake and the Tudor Navy: https://archive.org/details/corbett-drake-and-the-tudor-navy-v-1/page/n5/mode/2up ; https://archive.org/details/corbett-drake-and-the-tudor-navy-v-2 For a still-cited work on the Armada, I would recommend Garrett Mattingly’s The Armada, 1959.

pps
For more on cork, see: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cork_(material)
ppps
“Corking”, meaning something like “first rate”, is first cited, as far as is presently known, as appearing in 1895 in Outing, An Illustrated Monthly Magazine of Recreation. Unfortunately, the OED (Oxford English Dictionary) doesn’t mention which issue, so, if you feel like a search, look here to begin with: https://archive.org/details/sim_outing-sport-adventure-travel-fiction_october-1894-march-1895_25_contents/page/n1/mode/2up