As ever, dear readers, welcome.
If you flip to the back of The Letters of J.R.R. Tolkien,

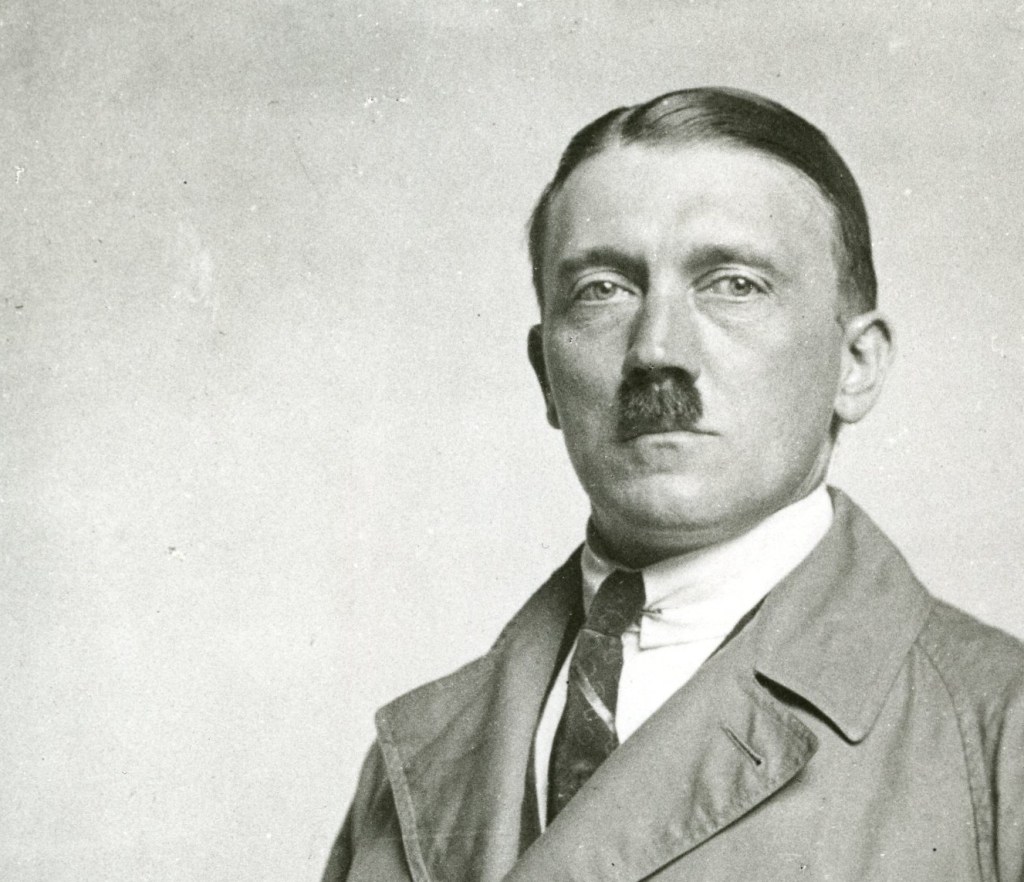
and page through the index to the aitches, you’ll find five references to Adolf Hitler. The first, to his son, Michael, simply mentions the idea that Hitler must soon attack Britain (letter to Michael Tolkien, 12 January, 1941, Letters, 64). The third is to another son, Christopher, and makes a brief reference to Stalin and Hitler (letter to Christopher Tolkien, 22 August, 1944, Letters, 131). Both of these are neutral in tone. The second, however, has more the tone of a rant:
“Anyway, I have in this War a burning private grudge—which would probably make me a better soldier at 49 than I was at 22: against that ruddy little ignoramus Adolf Hitler (for the odd thing about demonic inspiration and impetus is that it in no way enhances the purely intellectual stature: it chiefly affects the mere will).” (letter to Michael Tolkien, 9 June, 1941, Letters, 77)
And the fourth and fifth (in the same letter) have a similar tone:
“We knew that Hitler was a vulgar and ignorant little cad, in addition to any other defects (or the source of them)…” (letter to Christopher Tolkien, 23-25 September, 1944, Letters, 133)
Both of which are entirely understandable, of course. In terms of his family, two of his sons were involved in the Second World War, Michael as an anti-aircraft gunner, Christopher as a pilot, and Tolkien worried very much about both, as various letters to them make very plain.
That “burning private grudge”, however, was about something entirely different—and characteristic of JRRT—was his anger at the Nazi perversion of what he thought of as “that noble northern spirit”, as he says in that letter to Michael:
“Ruining, perverting, misapplying, and making for ever accursed, that noble northern spirit, a supreme contribution to Europe, which I have ever loved and tried to present in its true light.”
This being under the direction of:
“…a man inspired by a mad, whirlwind, devil: a typhoon, a passion: that makes the poor old Kaiser look like an old woman knitting.”
For all that Tolkien descends to name-calling (not his usual method of dealing with whom or what he doesn’t like), there is a certain—I won’t call it respect—but wary awe of someone he calls a “mad, whirlwind, devil” and, as always when I think about JRRT, his time, and his influences, I wonder about how he his impression of that “vulgar and ignorant little cad”—and “whirlwind devil”—might have influenced his work.
Germany after the Great War was economically and socially in ruins. The 1919 Treaty of Versailles, blaming Germany for the war and designed to exact severe punishment for that, had done much to put her in that condition.

When Germany was unable to pay the amount demanded on time, parts of western Germany were then occupied by several of the Allies.
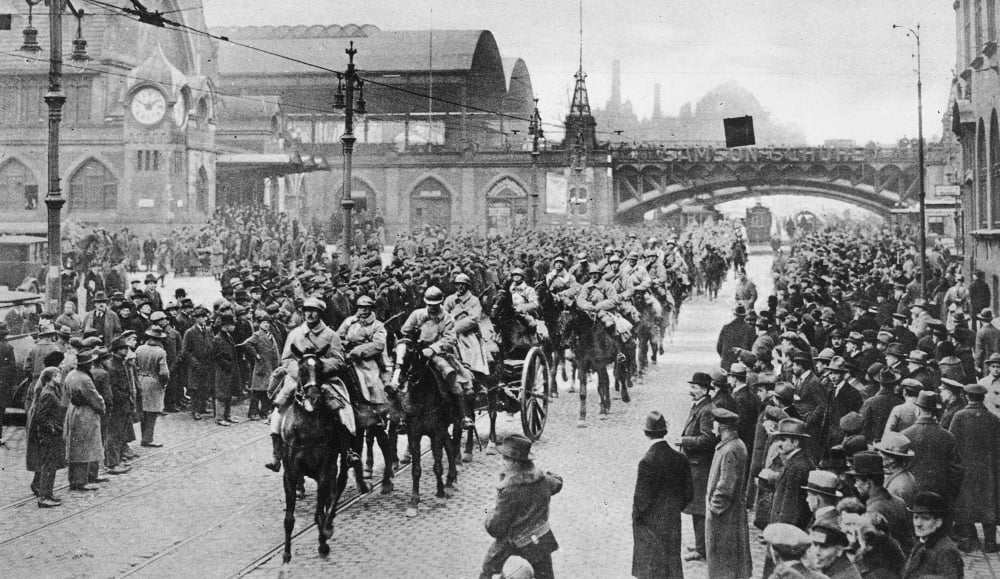

Bankruptcy, monetary depreciation,

and ideas of revolution swirled—including a brief attempt at revolution in Munich, in 1923.

The leader of this attempt was an ex-serviceman named Hitler.
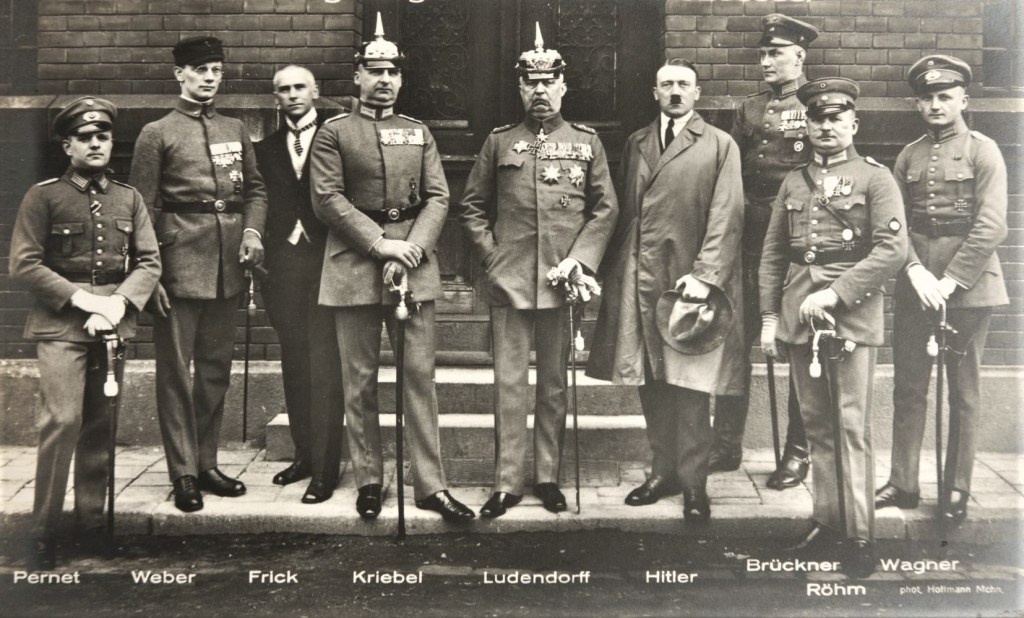

With a sympathetic court, instead of being executed for treason, he was given a light sentence and soon was out on the streets again, presenting himself not as a violent revolutionary, but as a reformer, someone who was working to bring his country back from the wreckage it has suffered from war, a brutal treaty, a ruined economy, and social unrest (some of which he himself had inspired—and would continue to inspire).
In time, he was so successful at this that he became his country’s director, under the very neutral title of Fuehrer, “Leader” and the economy did improve, living conditions did improve—

but under all of this improvement was something else and here I’m immediately reminded of Sauron:
“Sauron was of course not ‘evil’ in origin…until he became the main representative of Evil of later ages. But at the beginning of the Second Age he was still beautiful to look at, or could still assume a beautiful visible shape—and was not indeed wholly evil, not unless all ‘reformers’ who want to hurry up with ‘reconstruction’ and ‘reorganization’ are wholly evil, even before pride and the lust to exert their will eat them up.” (draft of a letter to Peter Hastings, September, 1954, Letters, 284)
“But many of the Elves listened to Sauron. He was still fair in that early time, and his motives and those of the Elves seemed to go partly together: the healing of the desolate lands. Sauron found their weak point, suggesting that, helping one another, they could make Western Middle-earth as beautiful as Valinor.” (to Milton Waldman, typescript, “late 1951”, Letters, 212)
And here are the consequences:
“[Sauron] lingers in Middle-earth. Very slowly, beginning with fair motives: the reorganizing and rehabilitation of the ruin of Middle-earth, ‘neglected by the gods’, he becomes a reincarnation of Evil, and a thing lusting for Complete Power—and so consumed ever more fiercely with hate (especially of gods and Elves). All through the twilight of the Second Age the Shadow is growing in the East of Middle-earth, spreading its sway more and more over Men…” (to Milton Waldman, typescript, “late 1951”, Letters, 211)
The title of this posting, as I’ll bet you all know, is part of a remark which Frodo makes just after Strider has appeared and approached him at The Prancing Pony in Bree:
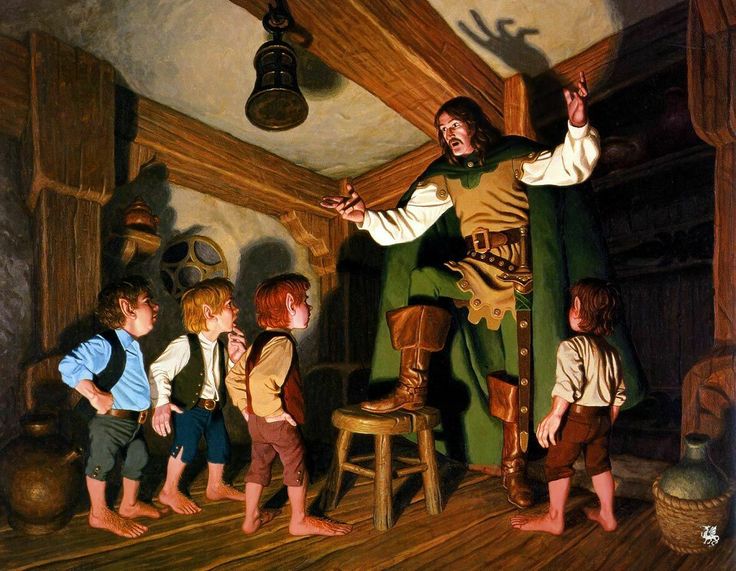

(the Hildebrandts)
“You have frightened me several times tonight, but never in the way that the servants of the Enemy would, or so I imagine. I think that one of his spies would—well, seem fairer and feel fouler, if you understand.”
To which Strider makes a reply one would never expect Hitler—or Sauron– to have made—
“ ‘I see,’ laughed Strider. ‘I look foul and feel fair. Is that it?’ “

As always, thanks for reading.
Stay well,
When it comes to reformers, it might always be wise to question their ultimate motives,
And remember that, as always, there’s
MTCIDC
O