Tags
anglo-saxons, Dialogus, Domesday Book, Errantry, Gothic, History, janissaries, Janissary, literature, lotr, Mazarbul, Normans, Tolkien, William Duke of Normandy
As ever, dear readers, welcome.
If nothing else would tell us that Tolkien had a fine ear for rhythm and rhyme, just take this stanza from “Errantry”, first published in The Oxford Magazine, Vol.52, No.5–
“Of crystal was his habergeon,
His scabbard of chalcedony;
With silver tipped at plenilune
His spear was hewn of ebony.
His javelins were of malachite
And stalactite – he brandished them
And went and fought the dragon flies
Of Paradise, and vanquished them.”
In his rhyming, JRRT has used some rather specialized words:
habergeon an (often-half-sleeved) chain mail shirt—usually made of steel, not something as fragile as crystal might be
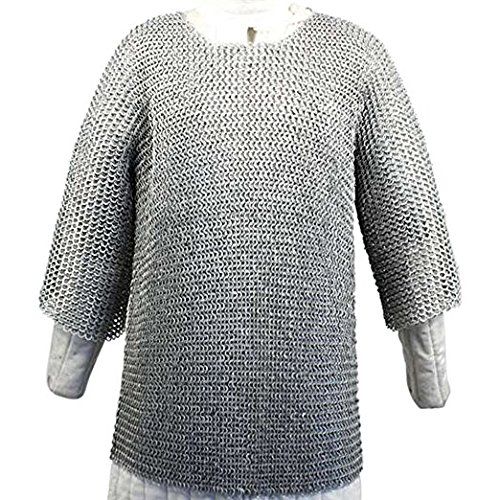

chalcedony a kind of silica which comes in a number of varieties and colors—here’s one—

plenilune full moon—the idea being that his spear was given its tip/blade at the full moon, suggesting perhaps a magical making?
ebony a dark hardwood which can be turned into a glossy black
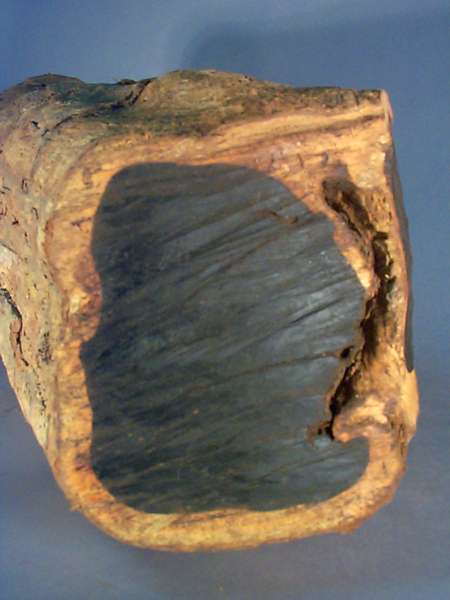

malachite another stone, which is copper-bearing

stalactite this isn’t a stone, but a stone deposit which hangs down in caves
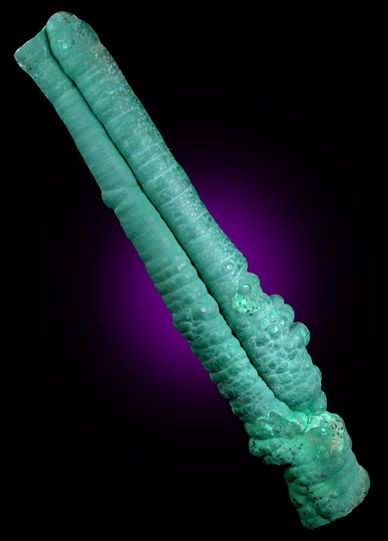
and is probably there for the internal rhyme with malachite, although malachite can be discovered in stalactites, so possibly JRRT is using two different possibilities at once
brandish to wave—something heroic warriors sometimes do with their weapons, in a boasting or threatening manner

(I haven’t been able to find an artist for this one, alas.)
For the “dragon flies of Paradise”, you’re on your own—although–

So, when it came to the soundscape of The Lord of the Rings (a subject which could use a lot of exploring—there are cues everywhere), I wasn’t surprised to see him play a little game with an unlikely toy, a drum.
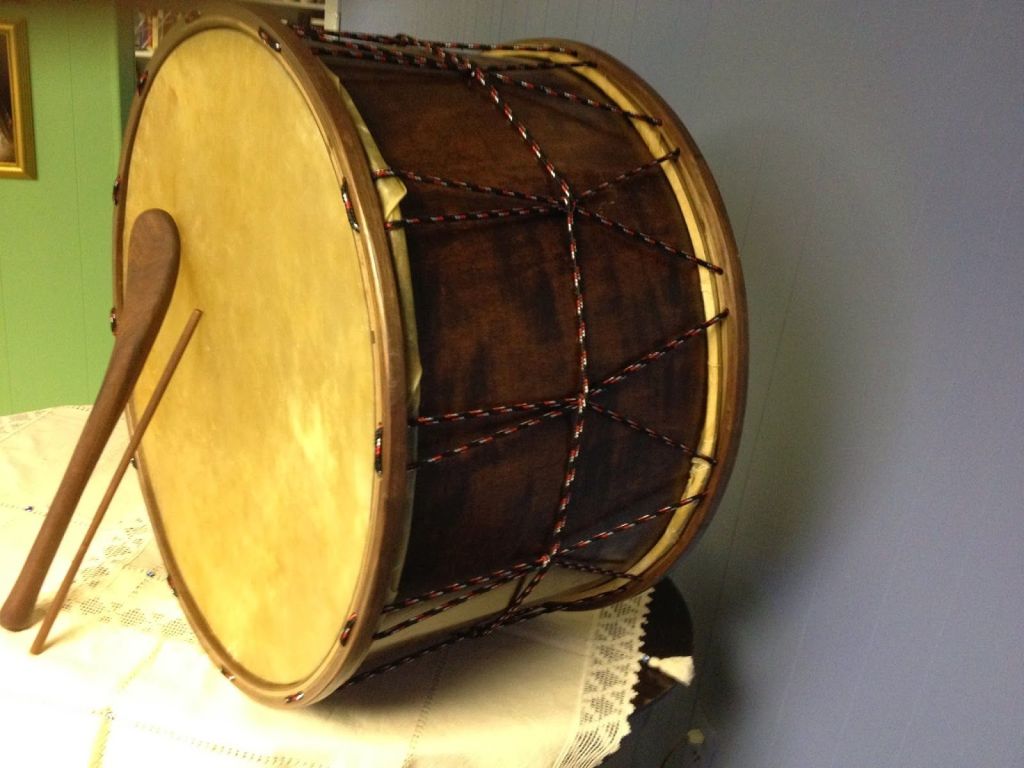

(a traditional Turkish drum—with two sticks, the larger for the top, the smaller for the underside, which gives it a distinctive double sound—you can hear—and see—some here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2eaxzv6obf8 These musicians are dressed as Janissaries, members of the Sultan’s elite troops
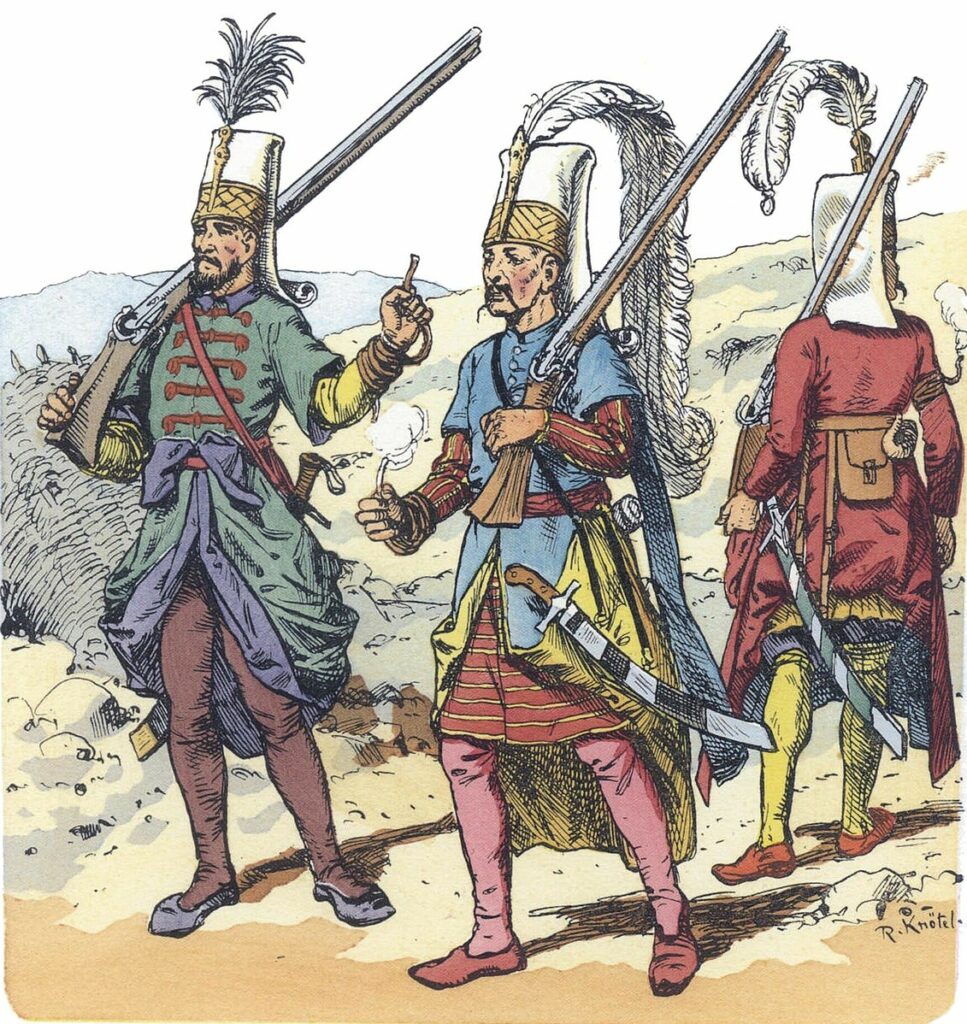

and you can see why such bands then influenced later 18th-century-early-19th-century composers like Mozart and Beethoven—and frightened defenders when they heard this music coming. Here’s Beethoven’s impression: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Nd0OjCO9x5Y )
Here’s a passage of that scape which recently caught my eye:
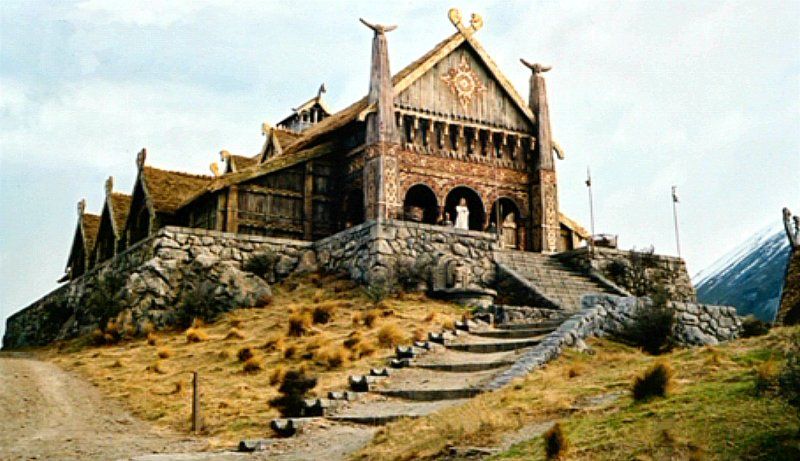
“Gandalf had hardly spoken these words, when there came a great noise: a rolling Boom that seemed to come from depths far below, and to tremble in the stone at their feet. They sprang towards the door in alarm. Doom, doom it rolled again, as if huge hands were turning the very caverns of Moria into a vast drum. Then there came an echoing blast: a great horn was blown in the hall, and answering horns and harsh cries were heard further off. There was a hurrying sound of many feet.” (The Fellowship of the Ring, Book Two, Chapter 5, “The Bridge of Khazad-dum”)
You see what I mean about soundscape: everything described, except the movement of the Fellowship, is a sound—and notice that even the place name in the chapter title, which has, in the original, a circumflex over the –u- in “dum” , lengthening the sound of the word, echoes that drum and its message: doom!
And “doom” is an interesting word.
A quick look at its past can take us as far back as Gothic, the ancestral cousin of the Germanic languages and our oldest surviving sample of such ancestors. Etymonline has “Gothic doms, ‘discernment, distinction’”– https://www.etymonline.com/word/doom but, using my on-line Gothic dictionary, we find domjan and afdomjan, where the basic sense seems to be “to establish”, from which comes the meaning “to judge” and possibly even “to condemn”. (Here’s the page: http://www.wulfila.be/gothic/browse/search/?find=domjan&mode=1 at the very helpful “Wulfila” site—Wulfila was the 4th-century AD translator of the Judeo-Christian Bible from Greek into Gothic. It’s interesting that, often the original Greek word is a form of krino, which probably original meant to “separate”, but came, in time to be used to mean “to judge, decide”, and even “to condemn”—see the Perseus page here: https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/morph?l=kri%2Fnw&la=greek&can=kri%2Fnw0#lexicon )
This brings us to what, I imagine, was a strong influence on Tolkien whenever he wrote that word: that oppressor of the conquered Anglo-Saxons, the so-called “Domesday Book”.

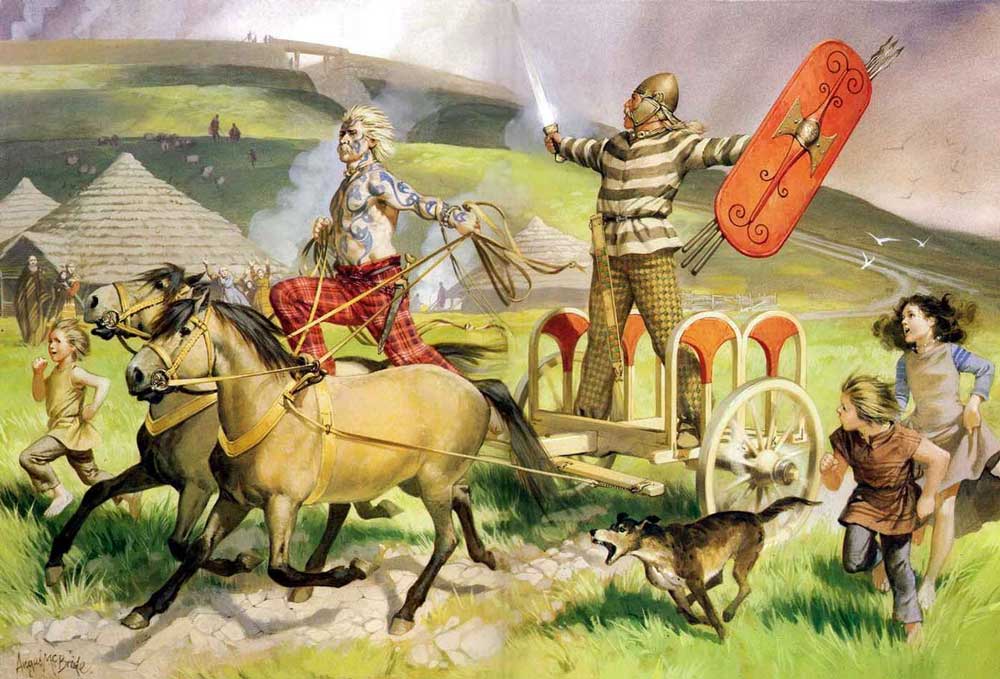
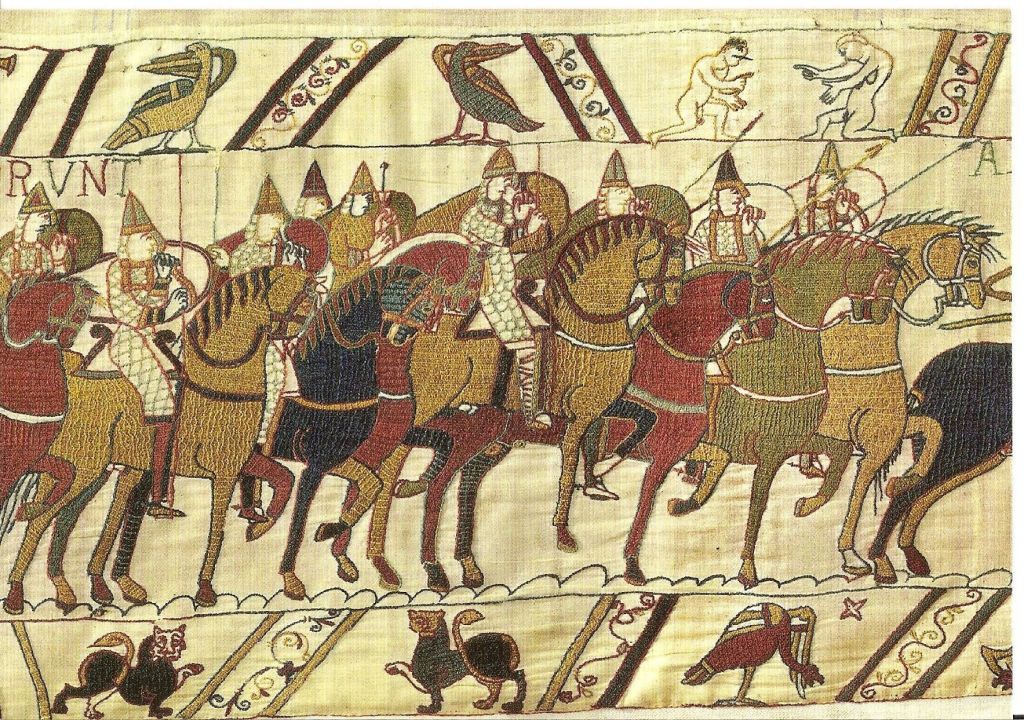
After the defeat of Harold Godwinson and his army at Hastings, in October, 1066,

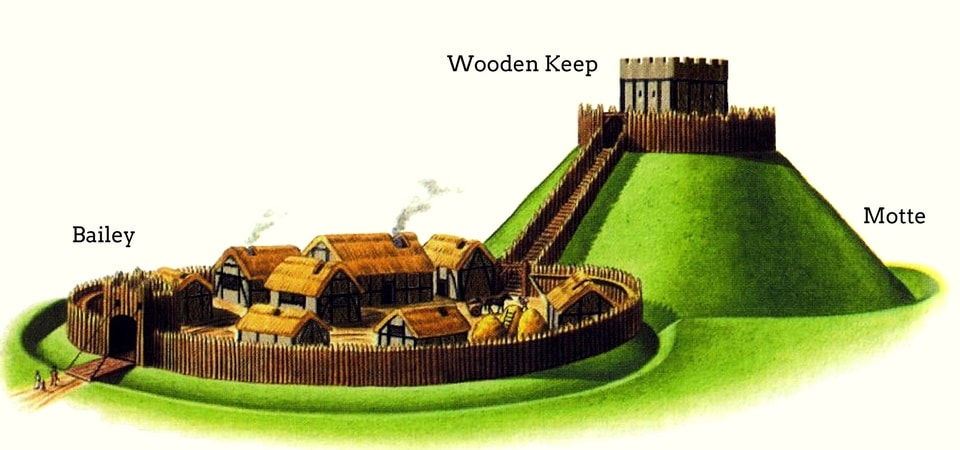
Duke William of Normandy drove a ruthless campaign of conquest throughout England, giving out land to his chief followers, who then built early castles, which we call “motte and bailey”, to protect themselves and to dominate the landscape.
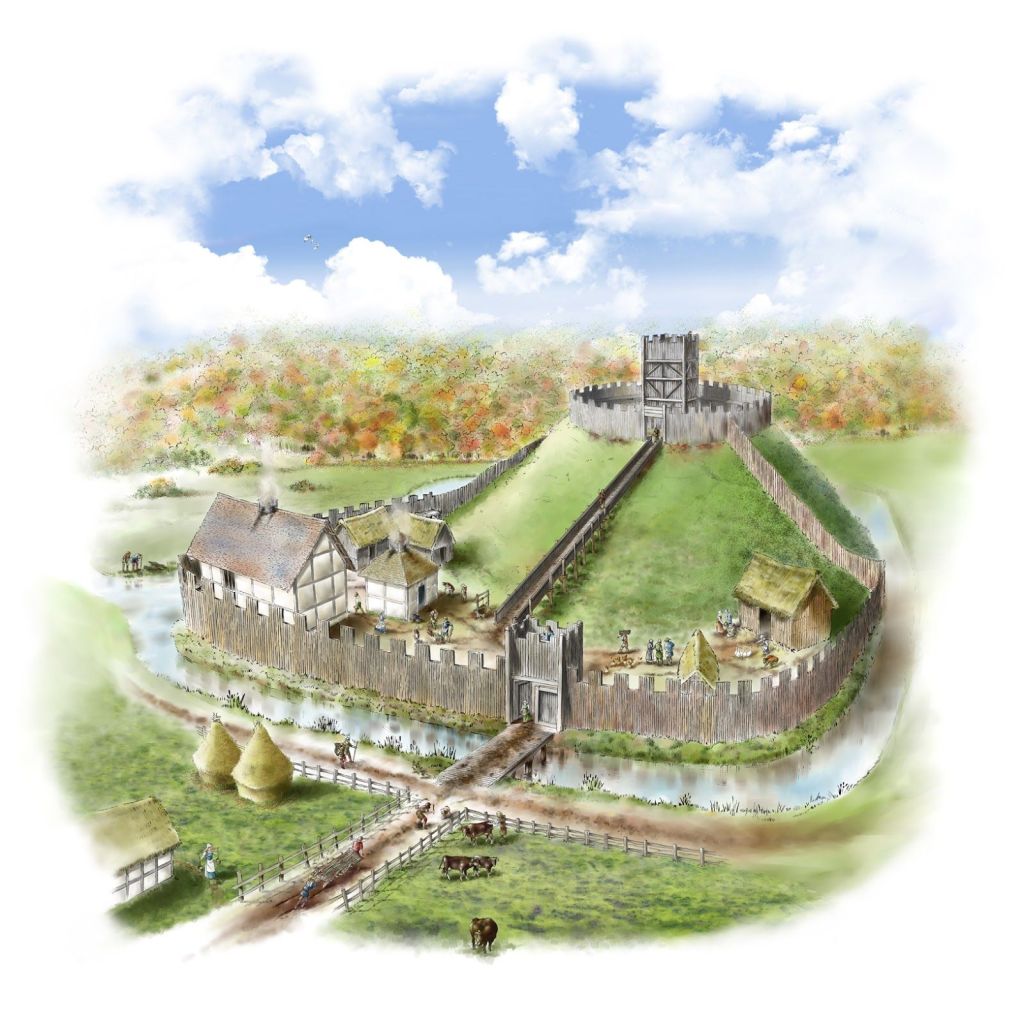

As well, perhaps helped by previous Anglo-Saxon tax records (easily accessible to the Norman officials because both they and their predecessors would have written in Latin), the Normans created a massive census, both of people and places, detailed practically down to the last chicken, asking, basically, “who is the owner? what does he own? what’s it worth? how much tax does he pay?” It had no name, originally, as such, being called Liber de Wintonia—“the Winchester Book”—because that’s where the manuscript was originally stored. (There were originally two volumes and you can read much more about them here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domesday_Book And you can see the work itself here: https://opendomesday.org/
The name by which we know it seems to have been a grim local joke, first known reference being in the 12th-century Dialogus de Scaccario, “Dialogue Concerning the Exchequer” (“scaccarium” being a chess board, because the table used for accounting was gridded like one—it’s explained, in fact, in the “Dialogue”, but you can read about it here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exchequer ).
In the text, the author (thought to have been Richard FitzNeal, the bishop of Ely, c.1130-1198), wrote:
“Hic liber ab indigenis ‘Domesdei’ nuncupatur id est dies iudicii per metaphoram.”
“This book is called by the locals ‘Doomsday’” : that is, as a metaphor, the Day of Judgment.”
(Dialogus de Scaccario, Book 1, Section 16B, which you can read here: https://archive.org/details/cu31924021674365/page/n119/mode/2up in Latin, or here, in English: https://avalon.law.yale.edu/medieval/excheq.asp#b1p16 This is a wonderfully practical text, explaining in enormous detail things like the vocabulary of the exchequer. As is so often the case with medieval Latin, it’s a very pleasant read, written in plain, straightforward language and being just what it says it is, a dialogue between a “magister” and a “discipulus” .)
Considering the choice of phrase, it isn’t surprising that that it was the choice of the “indigeni” . One part of William’s master plan of conquest was to take the land away from its original Anglo-Saxon (indigenous) land-holders

and hand it over to his own followers, thus dispossessing most of the former—and, because those owners had no recourse, it must have seemed very like the Last Judgment—the original Doomsday.

Thus, when the members of the Fellowship hear “boom” turn into “doom”, it can suggest not only a play with sound, but the same kind of catastrophic event, trapped, as they seem to be, in the record room of Mazarbul—

(Angus McBride)
And we can take this one step farther. As Tolkien’s income grew from the sale of his books, his frustration at the amount which disappeared into tax-paying grew, as he writes:
“A Socialist government will pretty well reduce me to penury on retirement! As it is socialist legislation is robbing me of probably ¾ of the fruits of my labors, and my ‘royalties’ are merely waiting in the bank until the Tax Collectors walk in and bag them. Do you wonder that anyone who can gets out of this island? Though soon there will be nowhere to go to escape the rising tide of ‘orquerie’.” (letter to Michael Tolkien, 6 November, 1956, Letters, 367)
So, when JRRT thought of “doom”, as a medievalist, might he also have been equating himself with those Anglo-Saxons, not only losing their homes, but forced to hand over their hard-earned cash

to those grim Normans, as well?
Thanks for reading, as always.
Stay well,
We’re only a month away, here in the US, from 15 April, our own “Domesday” for taxes owed,
And remember that, as ever, there’s
MTCIDC
O